Table A1a: Patient encounter clinical subcategories, by hospital
advertisement
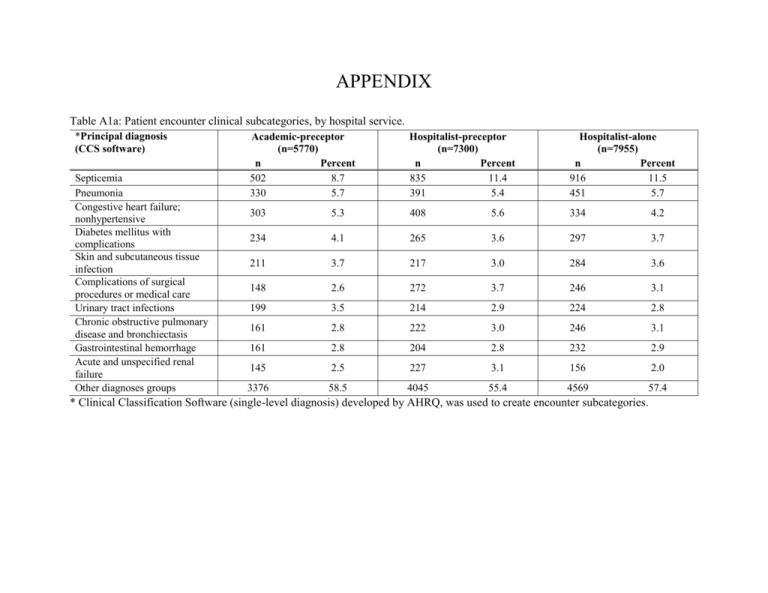
APPENDIX Table A1a: Patient encounter clinical subcategories, by hospital service. *Principal diagnosis (CCS software) Septicemia Pneumonia Congestive heart failure; nonhypertensive Diabetes mellitus with complications Skin and subcutaneous tissue infection Complications of surgical procedures or medical care Urinary tract infections Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and bronchiectasis Gastrointestinal hemorrhage Acute and unspecified renal failure Other diagnoses groups Academic-preceptor (n=5770) n Percent 502 8.7 330 5.7 Hospitalist-preceptor (n=7300) n Percent 835 11.4 391 5.4 Hospitalist-alone (n=7955) n Percent 916 11.5 451 5.7 303 5.3 408 5.6 334 4.2 234 4.1 265 3.6 297 3.7 211 3.7 217 3.0 284 3.6 148 2.6 272 3.7 246 3.1 199 3.5 214 2.9 224 2.8 161 2.8 222 3.0 246 3.1 161 2.8 204 2.8 232 2.9 145 2.5 227 3.1 156 2.0 3376 58.5 4045 55.4 4569 57.4 * Clinical Classification Software (single-level diagnosis) developed by AHRQ, was used to create encounter subcategories. Table A1b: Comorbid conditions for all patient encounter, by hospital service. *Comorbidities Hypertension Fluid and electrolyte disorder Deficiency Anemias Diabetes w/o Chronic Complications Chronic Pulmonary Disease Congestive Heart Failure Renal Failure Depression Alcohol Abuse Liver Disease Drug Abuse Coagulation Deficiency Other Neurological Disorders Diabetes with Chronic Complications Hypothyroidism Psychoses Obesity Weight loss Rheumatoid Arthritis/Collagen Vascular Diseases Valvular Disease Pulmonary Circulation Disorders Paralysis Peripheral Vascular Disease Academic-preceptor (n=5770) Percent n 3354 58.1 2349 40.7 2164 37.5 1543 26.7 1473 25.5 1466 25.4 1244 21.6 1056 18.3 978 17.0 894 15.5 836 14.5 680 11.8 650 11.3 637 11.0 611 10.6 595 10.3 455 7.9 394 6.8 Hospitalist-preceptor (n=7300) n Percent 4621 63.3 2959 40.5 2863 39.2 2067 28.3 1996 27.3 2133 29.2 1905 26.1 1461 20.0 842 11.5 1045 14.3 785 10.8 735 10.1 925 12.7 973 13.3 974 13.3 721 9.9 573 7.9 556 7.6 Hospitalist (n=7955) n Percent 4540 57.1 3060 38.5 2794 35.1 2079 26.1 2273 28.6 1974 24.8 1720 21.6 1429 18.0 977 12.3 940 11.8 884 11.1 685 8.6 920 11.6 894 11.2 869 10.9 833 10.5 677 8.5 723 9.1 387 6.7 603 8.3 474 6.0 364 358 302 294 6.3 6.2 5.2 5.1 516 482 467 413 7.1 6.6 6.4 5.7 441 448 434 414 5.5 5.6 5.5 5.2 Academic-preceptor (n=5770) Percent n Metastatic Cancer 242 4.2 Solid Tumor without Metastasis 205 3.6 Blood loss anemia 129 2.2 HIV and AIDS 100 1.7 Lymphoma 61 1.1 Chronic Peptic Ulcer Disease 5 0.1 *Comorbid conditions were determined using the Elixhauser Method. *Comorbidities Hospitalist-preceptor (n=7300) n Percent 294 4.0 311 4.3 166 2.3 150 2.1 72 1.0 7 0.1 n 239 318 148 76 50 6 Hospitalist (n=7955) Percent 3.0 4.0 1.9 1.0 0.6 0.1 Table A1c: Readmission events within 14, 30 and 60 days, by hospital service. Readmission 14-day 30-day 60-day Academic-preceptor (n=5770) n Percent 504 8.7 867 15.0 1313 22.8 Hospitalist-preceptor (n=7300) n Percent 670 9.2 1094 15.0 1746 23.9 Hospitalist (n=7955) n Percent 604 7.6 1013 12.7 1640 20.6 Table A2: Unadjusted patient outcomes reported on the absolute scale- 30-day readmission rate, LOS, index hospitalization cost, cumulative cost (index encounter plus readmissions within 30 days of discharge). Outcome Academic-preceptor Hospitalist-preceptor Hospitalist-alone 30-day Readmission Rate 15.6 15.7 11.7 95% CI (14.3, 17.0) (14.5, 17.0) (10.8, 12.7) Length of Stay * Days 5.52 5.52 6.15 95% CI (5.42, 5.61) (5.43, 5.61) (6.05, 6.25) Cost of Index Encounter* US $ 15211 15245 16728 95% CI (14961, 15466) (14909, 15588) (16338, 17128) Cumulative Hospital Cost within 30 days* US $ 18883 17932 20777 95% CI (18445, 19333) (16633, 19331) (19277, 22394) Estimates from generalized estimating equation are reported on the original scale and adjusted for clustering, unadjusted for covariates. * The variable was log-transformed; ratios reported are the antilog of the parameter estimate, which can be interpreted in the original scale. We included a smearing estimator in log-linear models to account for retransformation bias. Table A3: Unadjusted patient outcomes 30-day readmission, length of stay, difference in cost of index hospitalization, and difference in cumulative cost (index encounter plus readmissions within 30 days of discharge). Outcome Academic-preceptor vs. Hospitalist-alone Hospitalist-preceptor vs. Hospitalist-alone Academic-preceptor vs. Hospitalist-preceptor 30-day Readmission Odds Ratio 1.20 1.18 1.01 95% CI (1.08, 1.32) (1.08, 1.30) (0.92, 1.11) p value <0.001 <0.001 0.83 Length of Stay* Difference in Days -0.40 -0.38 -0.02 95% CI (-0.50, -0.30) (-0.48, -0.28) (-0.13, 0.09) p value <0.001 <0.001 0.7280 Index Hospitalization Cost* Cost Difference (US $) -966 -903 -66 95% CI (-1298, -625) (-1309, -486) (-382, 991) p value <0.001 <0.001 0.6838 Cumulative Hospital Cost within 30 days* Cost Difference (US $) -976 -1490 559 95% CI (-1741, -176) (-2765, -115) (-320, 1477) p value 0.0172 0.0342 0.2169 Estimates from generalized estimating equation are reported on the original scale and adjusted for clustering, unadjusted for covariates. * The variable was log-transformed; ratios reported are the antilog of the parameter estimate, which can be interpreted in the original scale. We included a smearing estimator in log-linear models to account for retransformation bias.










