What is Hospital Readmission - Health Systems Institute
advertisement

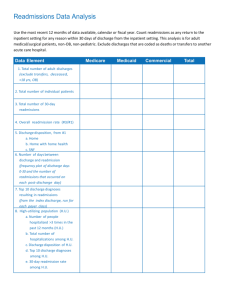
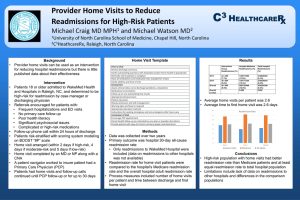
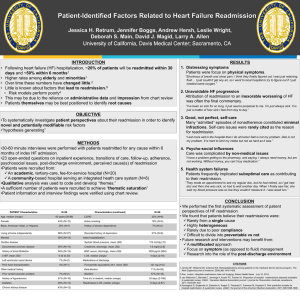
Hospital Readmissions Pramit Sengupta Health System Institute Georgia Institute of Technology What is Hospital Readmission A readmission is defined as a hospitalization that occurs shortly after a discharge; which is most often measured as within 30 days but it could be shorter or longer. Such readmissions are often but not always related to a problem inadequately resolved in the prior hospitalization. Hospital Readmission They also can be caused by deterioration in a patient’s health after discharge due to inadequate management of their condition, misunderstanding of how to manage it, or lack of access to appropriate services or medications. Prevalence of Readmission For most patients who leave the hospital, the last thing they want is to return anytime soon. Yet, many Medicare patients discharged from an inpatient stay find themselves back in the hospital within 30 days. Major Factor for Readmission Multiple factors contribute to avoidable hospital readmissions: they may result from poor quality care or from poor transitions between different providers and care settings. Cost of Readmission Hospital readmissions are massively expensive. A recent study of Medicare patients found that one in five admissions results in a bounce back within 30 days of discharge, costing the federal government an estimated $17.4 billion per year. Top Diseases for Initial Hospitalization • • • • • • Diabetes Mellitus Hypertension Drug Abuse Heart Failure Urinary Tract Disorder Asthma Measures to Reduce Hospital Readmission A review of studies published from 1998 to 2008 revealed that a variety of quality improvement and process redesign approaches have lowered readmission rates. These includes: close coordination of care in the post-acute period, early post-discharge follow-up care, enhanced patient education and selfmanagement training, and extending the resources and clinical expertise available to patients over time. Identify High Risk Patients The hospitals identify and target patients at the highest risk for readmissions, particularly heart failure patients, the very elderly, patients with complex medical and social needs, and those without the financial resources to obtain post-hospital care. Care Management Begin care management and discharge planning early, target high-risk patients, and ensure frequent communication across the care team. Telephone calls, Tele monitoring Maintain a lifeline with high-risk patients after discharge through telephone calls, tele monitoring, or other practices. Educate the patient Educate the patient about his or her diagnosis throughout the hospital stay Post-discharge services Organize post-discharge services Healthcare Information Technology Use of health information technology (e.g., electronic health records, patient registries, and risk stratification software) to improve quality and integrate care across settings. Hospital Acquired Infections Use of Technology Twice daily, Raymond Racette from Phillipston, Mass. downloads information about the fluid levels in his heart, and off it goes to the hospital. Community Health Providers Align hospitals’ efforts with those of community providers to provide a range of care. While this may be best achieved in integrated systems, such cooperation can be facilitated through collaborative relationships among hospital and community providers. Discharge Instructions Easy to understand discharge instruction Medical Reconciliation Medication reconciliation is the process of comparing a patient's medication orders to all of the medications that the patient has been taking. Questions