Test1-1
advertisement

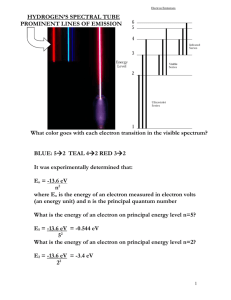
EE403/503 Introduction to Plasma Processing Examples solutions Test 1: Basic Atomic Theory Example 1. How fast is an Electron and a Hydrogen atom at room temperature? Electrons: me = 9.1 x 10-31 Kg k = 1.38 x 10-23 J/K (Boltzmann’s Constant) T = 293K 3 1 kT mv 2 2 2 3kT v m v 1.2 10 5 m / s Hydrogen: mH = 1.66 x 10-27 Kg k = 1.38 x 10-23 J/K (Boltzmann’s Constant) T = 293K 3kT m 2703m / s v rms vrms Example 2. In the vacuum tube shown in the figure below, determine the location, velocity and energy of e, H and H+ at the time when the electron arrives at one of the electrodes. All three particles are initially at rest. me = 9.1 x 10-31 Kg k = 1.38 x 10-23 J/K (Boltzmann’s Constant) T = 293K Time for electron arrives at the anode t 1 x at 2 (x = distance travel) 2 = Electric Field) a F me F qE (E dV 2 1 dx 2 qE 1.6 10 19 1 a 1.76 1011 m / s 2 31 me 9.1 10 1 1 x at 2 (1) (1.76 1011 )t 2 2 2 6 t 3.37 10 s E Electron: Location : at the anode Velocity: v at 1.76 1011 3.37 10 6 v 5.93 10 5 m / s 1 1 Energy: E mv 2 (9.11 10 31 )(5.93 10 5 ) 2 2 2 19 E 1.6 10 J 1.0eV Ion: qE 1.6 10 19 1 9.58 10 7 m / s 2 me 1.67 10 27 1 1 x at 2 (9.58 10 7 )(3.37 10 6 ) 2 2 3 x 0.5 10 m = 0.5 mm from the center toward cathode v at 9.58 10 7 3.37 10 6 v 323m / s 1 1 E mv 2 (1.67 10 27 )(323) 2 2 2 23 E 8.7 10 J 5 10 4 eV a Location: Velocity: Energy: Atom: qE 0 E 0 me me x 0 at the center v 0 at rest E0 a Location: Velocity: Energy: Example 3. Using the Bohr’s model, write a program to: (1) Calculate the five lowest energy states including the ground state of hydrogen atoms in eV. (2) Calculate the ionization potential of hydrogen atoms in eV. (3) Find the energy states of hydrogen atoms that can absorb photons with wavelengths in the visible range (400-700 nm). (1): 1 En 13.59921 2 n n=1 E1 = 0 eV n=2 n=3 n=4 n=5 (2): (3): E2 = 10.19 (eV) E1 = 12.08 (eV) E1 = 12.74 (eV) E1 = 13.05 (eV) 1 1 2] 2 n1 n2 RH = 13.6 eV n1 = 1 Eionization RH 13.6eV E RH [ E photon E hv hc (6.63 10 34 )(3 10 8 ) 400nm E photon 4.97 10 19 3.1eV 700nm E photon 2.84 10 19 1.6eV Series Lyman Balmer Paschen n2 = n E (eV) (nm) 12 13 14 15 10.20 12.09 12.75 13.06 121.32 102.37 97.06 94.78 23 24 25 1.89 2.55 2.86 655.15 485.29 433.30 34 35 0.66 0.97 1871.85 1279.58 Visi