QUIZ 4 Solution
advertisement

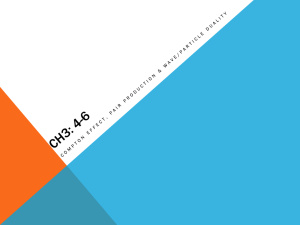
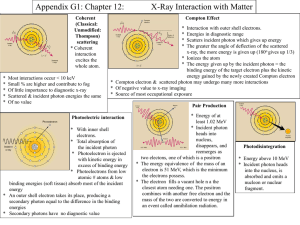
QUIZ 4 Solution The X-ray beam attenuates due to photons either being absorbed by the atoms of the material, or being scattered away from their original directions of travel. For the range of photon energies most commonly encountered for diagnostic imaging (from 20 to 150 keV), the mechanisms responsible for these two contributions to attenuation are the photoelectric and the Compton effects. Photoelectric absorption consists of an x-ray photon imparting all its energy to a tightly bound inner electron in an atom. The electron uses some of this acquired energy to overcome the binding energy within its shell, the rest appearing as the kinetic energy of the thus freed electron. The Compton scattering, on the other hand, consists of the interaction of the x-ray photon with either a free electron, or one that is only loosely bound in one of the outer shells of an atom. As a result of this interaction, the x-ray photon is deflected from its original direction of travel with some loss of energy, which is gained by the electron. As a consequence, the X-ray photons lose all or some of their energy due to photoelectric absorption and Compton scattering respectively, which results in attenuation.