Quantum questions
advertisement
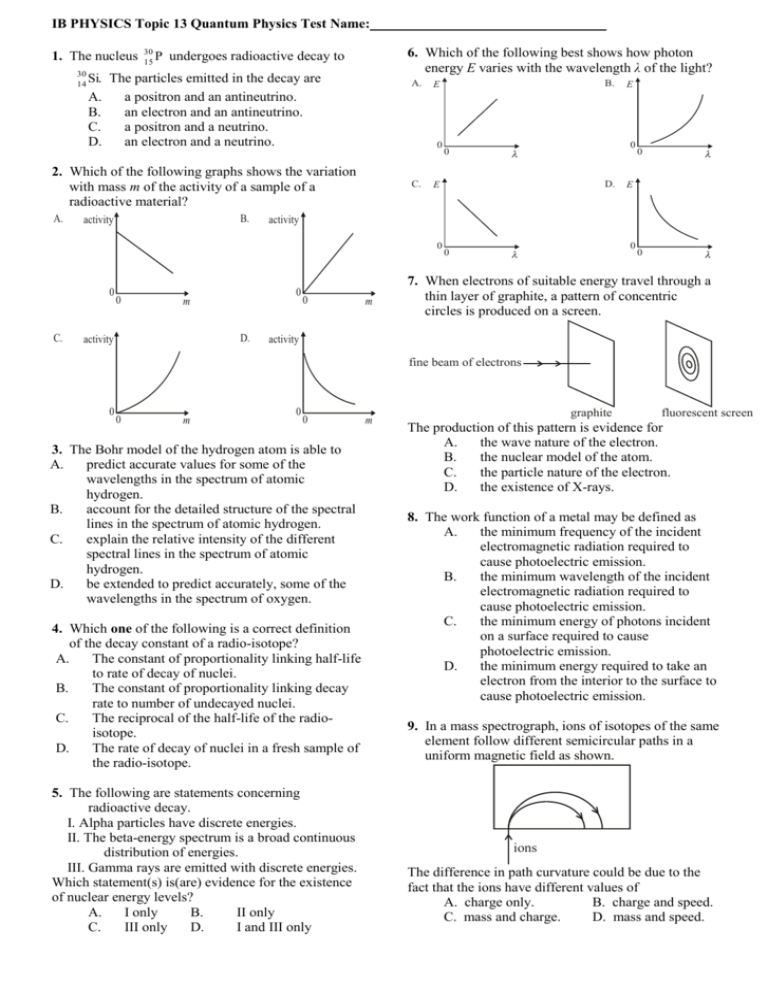
IB PHYSICS Topic 13 Quantum Physics Test Name: 1. The nucleus 30 Si. 14 A. B. C. D. 30 P 15 6. Which of the following best shows how photon energy E varies with the wavelength λ of the light? undergoes radioactive decay to The particles emitted in the decay are a positron and an antineutrino. an electron and an antineutrino. a positron and a neutrino. an electron and a neutrino. A. 0 2. Which of the following graphs shows the variation with mass m of the activity of a sample of a radioactive material? A. B. activity C. C. 0 D. activity D. 0 E activity 0 m E 0 0 E 0 0 B. E 0 m 0 0 0 7. When electrons of suitable energy travel through a thin layer of graphite, a pattern of concentric circles is produced on a screen. activity fine beam of electrons 0 0 m 0 0 3. The Bohr model of the hydrogen atom is able to A. predict accurate values for some of the wavelengths in the spectrum of atomic hydrogen. B. account for the detailed structure of the spectral lines in the spectrum of atomic hydrogen. C. explain the relative intensity of the different spectral lines in the spectrum of atomic hydrogen. D. be extended to predict accurately, some of the wavelengths in the spectrum of oxygen. 4. Which one of the following is a correct definition of the decay constant of a radio-isotope? A. The constant of proportionality linking half-life to rate of decay of nuclei. B. The constant of proportionality linking decay rate to number of undecayed nuclei. C. The reciprocal of the half-life of the radioisotope. D. The rate of decay of nuclei in a fresh sample of the radio-isotope. 5. The following are statements concerning radioactive decay. I. Alpha particles have discrete energies. II. The beta-energy spectrum is a broad continuous distribution of energies. III. Gamma rays are emitted with discrete energies. Which statement(s) is(are) evidence for the existence of nuclear energy levels? A. I only B. II only C. III only D. I and III only m graphite fluorescent screen The production of this pattern is evidence for A. the wave nature of the electron. B. the nuclear model of the atom. C. the particle nature of the electron. D. the existence of X-rays. 8. The work function of a metal may be defined as A. the minimum frequency of the incident electromagnetic radiation required to cause photoelectric emission. B. the minimum wavelength of the incident electromagnetic radiation required to cause photoelectric emission. C. the minimum energy of photons incident on a surface required to cause photoelectric emission. D. the minimum energy required to take an electron from the interior to the surface to cause photoelectric emission. 9. In a mass spectrograph, ions of isotopes of the same element follow different semicircular paths in a uniform magnetic field as shown. ions The difference in path curvature could be due to the fact that the ions have different values of A. charge only. B. charge and speed. C. mass and charge. D. mass and speed. 10. Some of the energy levels of the hydrogen atom Electrons are excited to the 0.85 eV level. How are shown below. (not to scale) many different photon frequencies will be –––––––––––––– – 0.54 eV observed in the emission spectrum of hydrogen? –––––––––––––– – 0.85 eV A. 3 B. 4 –––––––––––––– – 1.51 eV C. 5 D. 6 –––––––––––––– – 3.39 eV –––––––––––––– – 13.6 eV Short Answer questions Write your response in the space provided 11. Light is incident on a clean metal surface in a vacuum. The maximum kinetic energy KEmax of the electrons ejected from the surface is measured for different values of the frequency f of the incident light. The measurements are shown plotted below. 2.0 1.5 KEmax / × 10–19 J 1.0 0.5 0.0 4.0 4.5 5.0 5.5 6.0 6.5 7.0 7.5 8.0 14 (a) f / × 10 Hz Draw a line of best fit for the plotted data points. (1) (b) Use the graph to determine (i) The Planck constant. .............................................................................................................................................................. (2) .............................................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................................. (ii) The minimum energy required to eject an electron from the surface of the metal (the work function). (3) .............................................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................................. (c) Explain briefly how Einstein’s photoelectric theory accounts for the fact that no electrons are emitted from the surface of this metal if the frequency of the incident light is less than a certain value. (3) .............................................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................................. 12. This question is about the wave nature of electrons. (a) Describe the de Broglie hypothesis. .............................................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................................. (2) 2 An experiment is carried out in which a beam of electrons is scattered from a single nickel crystal. A schematic diagram of the apparatus is shown below. Vacuum Nickel crystal Incident electron beam Electron “gun” Scattered electron beam The electrons are accelerated in the electron “gun” by a potential difference of 75 V. (b) Determine the wavelength associated with the electrons as predicted by the de Broglie hypothesis. .............................................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................................. (4) The number n of electrons scattered per second through an angle θ is measured. The graph below shows the variation with angle θ of n. n 0 0 (c) Suggest how the shape of this graph supports the de Broglie hypothesis. .............................................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................................. ……….....…….................................................................................................................................................. (3) 13. Diagram 1 shows part of the emission line spectrum of atomic hydrogen. The wavelengths of the principal lines in the visible region of the spectrum are shown. Diagram 2 shows some of the principal energy levels of atomic hydrogen. (a) Show, by calculation, that the energy of a photon Diagram 1 Diagram 2 of red light is 1.9 eV. Red (R) Blue (B) Violet (V) ........................................................................................ 0 –0.54 –0.85 –1.5 656 nm 486 nm 434 nm –3.4 wavelength ....................................................................................... ....................................................................................... ....................................................................................... ..................................................................................(3) (b) (i) On Diagram 2, draw arrows to represent: The electron transition that gives rise to the red line (label this arrow R). (ii) A possible electron transition that gives rise to the blue line (label this arrow B). Energy / eV (1) –13.6 (1) 3 14. (a) The half-life of a radioactive isotope is 10 days. Calculate the fraction of the sample that remains after 25 days. .............................................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................................. ……….....…….................................................................................................................................................. (2) (b) A radioactive material has a half-life of 6.02 hours. If the original activity is 640 Bq, calculate the activity after 8 hours. .............................................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................................. ……….....…….................................................................................................................................................. (2) (c) A 1.49 µg sample of 13N7 has a half-life of 10 minutes. (i) How many nuclei are present initially? Avogadro’s number = 6.02 x 1023. .............................................................................................................................................................. ……….....…….................................................................................................................................................. (1) (ii) What is the initial activity? .............................................................................................................................................................. ……….....…….................................................................................................................................................. (2) (iii) What is the activity after 1 hour? .............................................................................................................................................................. ……….....…….................................................................................................................................................. (2) (iv) After how long will the activity be less than 1 per second? .............................................................................................................................................................. .............................................................................................................................................................. ……….....…….................................................................................................................................................. (2) 4