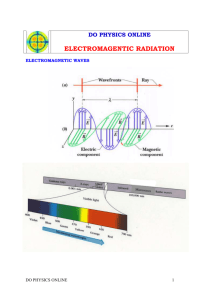
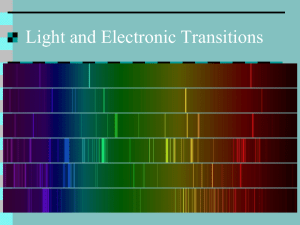
visible light
advertisement

Electron As a Particle and Wave Electrons get excited when energy is absorbed by using heat or electrical energy Excited electrons move back to their ground state when they release the same amount of energy that was absorbed (conservation). Light energy (electromagnetic radiation) is released when an electron returns to a lower energy level Light Energy Light travels as a wave and is made of photons. Light contains quanta energy called photons (Einstein) Speed of light in a vacuum 3.0 x 108 m/s How fast is that?? It would take 2.5 seconds for radar waves traveling at the speed of light to travel 478,000 miles -- leave the earth, bounce off the moon and return!! Speed of Light c = the speed of light c = λv λ = wavelength v = frequency Wavelength: one wave, the distance of one crest and one trough (Unit: meters) Frequency: # of waves per second (Unit: s-1 or Hertz, Hz) The Electromagnetic Spectrum Radio Waves Microwaves Infrared Radiation VISIBLE LIGHT ROY G BV Ultraviolet X-Rays Gamma Rays Low Frequency, Long Wavelengths v = 1010 Hz λ = 10-1 m VISIBLE LIGHT 400 – 800 nanometers Nanometer = 10-9 m High Frequency, Short Wavelengths v = 1020 Hz λ = 10-12m http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electromagne tic_spectrum http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Visible_light Max Planck Energy is absorbed and emitted in discrete units of light energy called quanta (also known as photons) The energy of a light quantum corresponds to the energy difference between two energy levels. E = hυ Energy is equal to Planck’s constant multiplied by frequency h = 6.63 x 10-34 J•s Photoelectric Effect Absorption of light striking a metal with a certain frequency, has enough energy to release an electron (photon) of light Sample Problems Yellow light with a frequency of approximately 6.0 x 1014 Hz is the predominant frequency in sunlight. What is the energy of this light? 4.0 x 10-19 J A quantum of a certain color of visible light is found to have an energy of 5.0 x 10-19 J. What is the color of this light? Violet because the frequency is 7.5 x 1014 Hz which is equivalent to 400 nm (the shortest wavelength for light) Changing Energy Levels Excited State: When an e- has gained energy to jump to a higher energy level Ground State: Most stable (original location of the electron) Excited electrons lose energy to return to stability This releases energy as electromagnetic radiation (a photon of light) Conservation of Energy The energy absorbed always equals energy emitted. Recall that electrons can not be in between energy levels; however electrons can skip and move up 2,3,4… levels at a time. The energy is released similarly. Either in large amounts (drop back several energy levels) or the electrons can jump back one energy level at a time. Photoelectric Effect Electron as a particle is ejected from the surface of a metal exposed to a specific frequency of light Photon “a packet of light” E = h http://www.bing.com/videos/search?q=ph otoelectric+effect+video&FORM=VIRE1#vi ew=detail&mid=63FE23E8E374EEB1237C6 3FE23E8E374EEB1237C