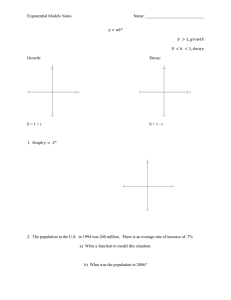
Radioactive decay used as a clock
advertisement
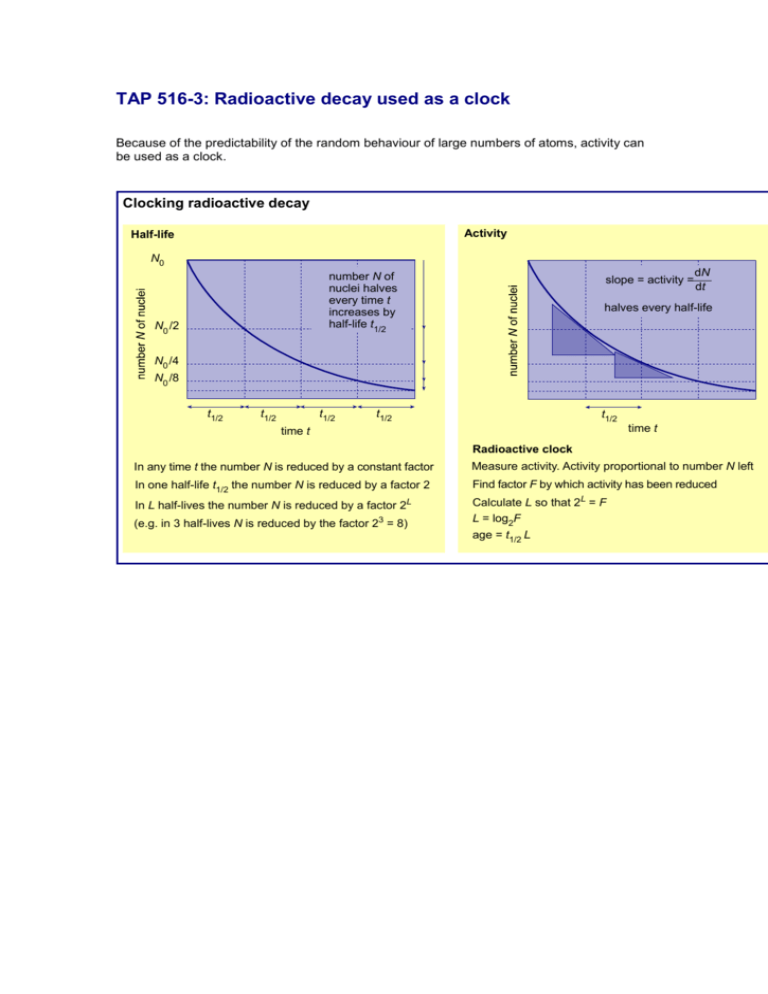
TAP 516-3: Radioactive decay used as a clock Because of the predictability of the random behaviour of large numbers of atoms, activity can be used as a clock. Clocking radioactive decay Activity Half-life N0 number N of nuclei halves every time t increases by half-life t1/2 N0 /2 slope = activity = dN dt halves every half-life N0 /4 N0 /8 t1/2 t1/2 t1/2 t1/2 t1/2 time t time t Radioactive clock In any time t the number N is reduced by a constant factor Measure activity. Activity proportional to number N left In one half-life t1/2 the number N is reduced by a factor 2 Find factor F by which activity has been reduced In L half-lives the number N is reduced by a factor 2 L (e.g. in 3 half-lives N is reduced by the factor 23 = 8) Calculate L so that 2L = F L = log2F age = t1/2 L Practical advice This diagram is reproduced here so that you can talk through it, or adapt it to your own purposes. External reference This activity is taken from Advancing Physics chapter 10, Display material 20O