Atomic Structure Test
advertisement
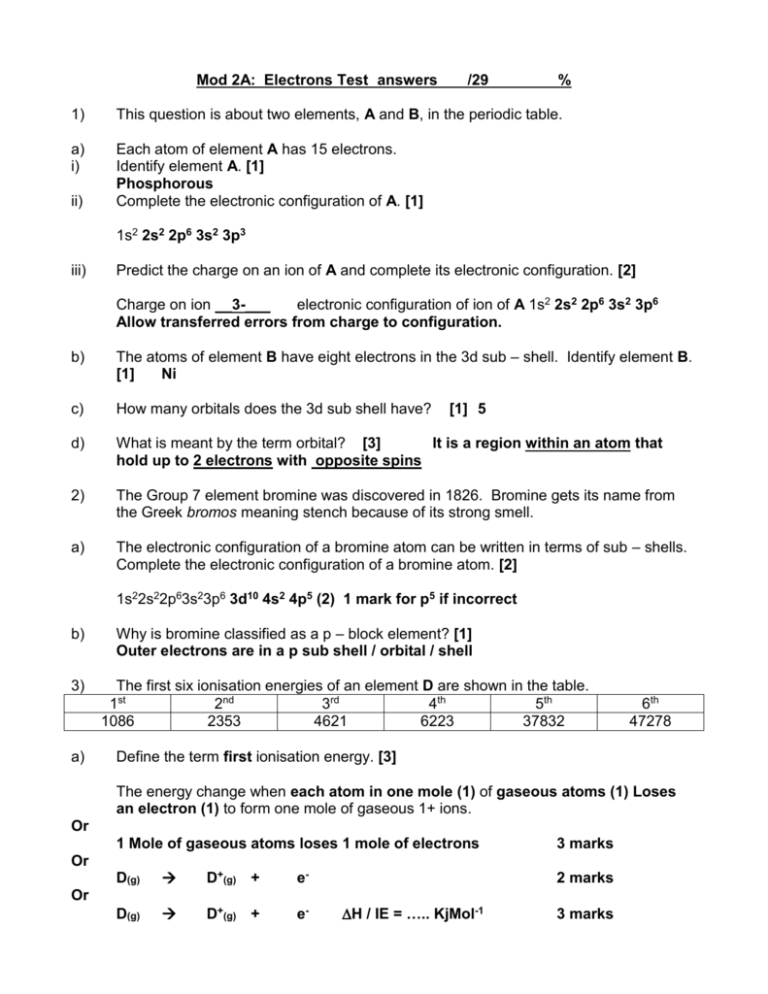
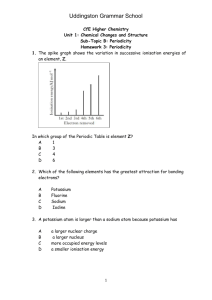
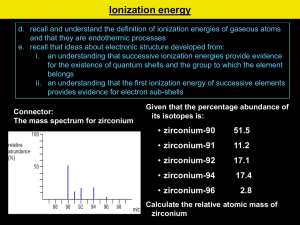
Mod 2A: Electrons Test answers /29 % 1) This question is about two elements, A and B, in the periodic table. a) i) Each atom of element A has 15 electrons. Identify element A. [1] Phosphorous Complete the electronic configuration of A. [1] ii) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p3 iii) Predict the charge on an ion of A and complete its electronic configuration. [2] Charge on ion __3-___ electronic configuration of ion of A 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 Allow transferred errors from charge to configuration. b) The atoms of element B have eight electrons in the 3d sub – shell. Identify element B. [1] Ni c) How many orbitals does the 3d sub shell have? d) What is meant by the term orbital? [3] It is a region within an atom that hold up to 2 electrons with opposite spins 2) The Group 7 element bromine was discovered in 1826. Bromine gets its name from the Greek bromos meaning stench because of its strong smell. a) The electronic configuration of a bromine atom can be written in terms of sub – shells. Complete the electronic configuration of a bromine atom. [2] [1] 5 1s22s22p63s23p6 3d10 4s2 4p5 (2) 1 mark for p5 if incorrect b) 3) a) Why is bromine classified as a p – block element? [1] Outer electrons are in a p sub shell / orbital / shell The first six ionisation energies of an element D are shown in the table. 1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 1086 2353 4621 6223 37832 6th 47278 Define the term first ionisation energy. [3] The energy change when each atom in one mole (1) of gaseous atoms (1) Loses an electron (1) to form one mole of gaseous 1+ ions. Or 1 Mole of gaseous atoms loses 1 mole of electrons 3 marks Or D(g) D+(g) + e- D(g) D+(g) + e- 2 marks Or H / IE = ….. KjMol-1 3 marks b) Write an equation, including state symbols, to represent the third ionisation energy of element D. [2] D2+(g) D3+(g) + e- (1) – equation (1) – state symbols Can use any example or letter instead of D, ‘-‘ not required on electron c) Use the table to deduce which group of the Periodic Table contains element D. [3] Group ___4____ Explanation Sharp rise in successive ionisation energy between 4th and 5th IE (1) Which marks a change to a new shell / energy level / 4e in outer shell (1) ***Mention of – orbital / sub shell cancels mark 2. This question is about aluminium oxide, Al2O3. Successive ionisation energies provide evidence for the arrangement of electrons in atoms. The graph below shows the 8 successive ionisation energies for oxygen. Log ionisation energy 4) a) i) 2 3 4 5 6 7 Electrons removed 8 Write an equation, including state symbols, to represent the second ionisation energy of oxygen. [2] O+(g) ii) 1 O2+(g) + e- (1) – equation (1) – state symbols How does the graph provide evidence for the existence of two electron shells in oxygen? [2] Large difference between 6th and 7th IE (1) Which marks a different shell (closer to the nucleus) (1) iii) the O+ ion, is smaller than the O atom OR the electron repulsion/shielding is smaller OR the proton : electron ratio in the 2+ ion is greater than in the 1+ ion ALLOW the outer electrons in an O+ ion are closer to the nucleus than an O atom DO NOT ALLOW ‘removed from next shell down’ 1 b)i) Complete the electronic configuration for an aluminium atom. [1] 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1 ii) Sketch a graph to show the thirteen successive ionisation energies of aluminium. [2] Ionisation energy 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Ionisation number Sharp rise between 3rd and 4th (1) Sharp rise between 11th and 12th (1) For 2,8,3 (pattern the wrong way round) = 1 iii) Sketch and label the shapes of the orbitals present in an aluminium atom. [2] s spherically drawn (1) p figure of 8 shape drawn (1)