Periodic Trends
advertisement

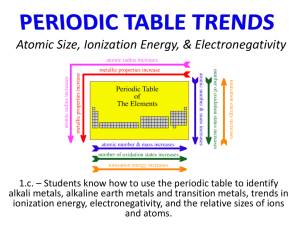
DRAFT DOCUMENT LAB 12 PERIODIC TRENDS In the 1800’s Mendeleev used the chemical and physical properties of the elements to develop an arrangement of the elements that today we call the periodic table. In this lab activity you will investigate how three properties of the elements – atomic radius, ionization energy, and electronegativity – vary according to the atomic number of the elements. You will be making a 3-dimensional model of these properties for some of the representative elements and use it to describe and explain the trends in these properties. OBJECTIVES When you have completed this activity, you should be able to 1. Use a model to describe the trends in several physical properties of the elements. 2. Relate these trends to the electron configuration of the elements. MATERIALS 96-Well microplate Ruler Calculator Forceps Scissors Straws, 3 colors Ruler Periodic table PROCEDURE 1. Each pair of students will prepare a 3-dimensional model for at least one of the properties of the elements. You will then share your results will students in other groups. Your group has been assigned to make a model for the property ______________________________. Use masking tape to label the well plate with this property. 2. In order to make the 3-D model you need to cut the straws to scale so their heights represent the relative values for each element. On the Data Table provided, convert the values for your assigned property to a scale in centimeters by using the conversion factors given below. Round your answers to the nearest tenth of a centimeter. An example is given for each property. Property Atomic radius Ionization Energy Electronegativity Conversion Factor Example (For Hydrogen) 32 pm x 1cm = 1.07 cm ( 1.1 cm) 1 cm =30 pm 30 pm 1312 kJ x 1cm = 3.28 cm ( 3.3 cm) 1 cm = 400 kJ 400 kJ 2.2 units x 1cm = 2.75 cm ( 2.8 cm ) 1 cm= 0.8 unit 0.8 unit 75 DRAFT DOCUMENT LAB 12 3. Use the diagram of the well plate provided below to plan the placement of the elements. Your well plate should be oriented to correlate with the elements of the periodic table. Row 1 represents the first period, with well H1 as Hydrogen and well A1 as Helium. Row 2 represents the second period with well H2 as Lithium and well A2 as Neon. Rows 3 and 4 contain the elements in periods 3 and 4, omitting the transition elements. Write the symbols for the elements in the circles. 4. Select colored straws to represent your property. 5. Carefully measure and cut a piece of straw for each element. Following the diagram you completed in Procedure 3, insert each piece into the appropriate well of the microplate. 76 DRAFT DOCUMENT LAB 12 ANALYSIS 1. Examine your tray and those of other student groups. How do the properties change as you look from top to bottom within a group or family? Atomic radius Ionization energy Electronegativity 2. As you look from left to right across the periodic table, how do the properties change? Atomic radius Ionization energy Electronegativity 3. Write the electron configuration for the following alkali metals (Group 1). Li Na K In what way are the electron configurations for group 1 similar? How do the electron configurations differ as you move down group 1? 77 DRAFT DOCUMENT LAB 12 4. Write the electron configuration for the elements in period 2, from Li to Ne. Li Be B C N O F Ne What do all the electron configurations above have in common? How do these electron configurations differ? How do the number of protons differ? 5. In terms of electron configuration, explain the trend in atomic radius. Down a group Across the period from left to right 6. In terms of electron configuration, explain the trend in ionization energy. Down a group Across the period from left to right 78 DRAFT DOCUMENT LAB 12 7. In terms of electron configuration, explain the trend in electronegativity. Down a group Across the period from left to right 8. Look at your model again. Why do you think we say that the properties of the elements are “periodic”? 9. On the diagram of the periodic table below draw and label arrows that show the direction in which the three properties ( atomic radius, ionization energy, electronegativity) increase. 79 DRAFT DOCUMENT LAB 12 10. Write a paragraph explaining why atomic radius, electronegativity, and ionization energy show periodic trends. The following rubric will be used to assess your understanding. Scoring tool: Score Students use patterns illustrated in model and electron configuration of the elements to explain clearly why the three properties are periodic. Specific examples are given for each trend. Students use patterns illustrated in model and explain in general terms how the electron configuration of the elements cause the properties to be periodic. 3 Students can describe the patterns illustrated by the models and relate the patterns to electron configuration with some errors. 2 Students can describe the patterns illustrated by the models but do not explain in terms of electron configuration. Students cannot describe the patterns illustrated by the models 11. 4 1 0 Some of the elements show exceptions to the trends. Look at your model and select an element that seems to have an unusual value for one of these properties. Try to explain why this happens by writing the electron configuration for this element and looking for a definite change from the element before it. 80 DRAFT DOCUMENT LAB 12 PROPERTIES OF REPRESENTATIVE ELEMENTS Element Atomic Atomic Straw Ionization Straw Electronegativity Straw number radius length(cm) Energy (pm) (kJ/mol) Length length (cm) (cm) H He Li Be B C N O F Ne Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar K Ca Ga Ge As Se Br Kr 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 31 32 33 34 35 36 32 50 155 112 98 91 92 73 72 71 190 160 143 132 128 127 99 98 235 197 141 137 139 140 114 112 1312 2372 520 900 801 1086 1402 1314 1681 2081 496 738 578 786 1012 1000 1251 1520 419 590 579 762 944 941 1140 1351 81 2.2 1.0 1.6 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 0.9 1.3 1.6 1.9 2.2 2.6 3.2 0.8 1.0 1.4 2.0 2.2 2.5 3.0 - DRAFT DOCUMENT LAB 12 PRE-LAB: PERIODIC TRENDS 1. Which groups of the periodic table contain the “representative elements”? Why do you think these elements are called “representative”? 2. What is a periodic trend? 3. Consult a chemistry textbook to find the definitions for the following properties, then restate the definition in your own words. Atomic radius Ionization energy Electronegativity 4. Read the procedure for this activity. What is the purpose for including drinking straws in the Materials list? 5. Follow the directions in Procedure 2 to calculate the straw length needed to represent The atomic radius of oxygen The ionization energy of neon The electronegativity of arsenic 82