Chapter 5 Review - Belle Vernon Area School District
advertisement

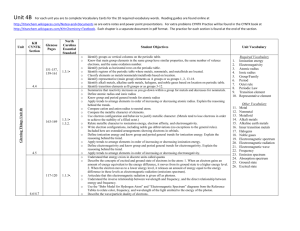
Chapter 5 Review • Play slide show. • Correct answer appears in blue. Which has a higher Ionization Energy? • • • • • • • Al Ca Ba Pt Nd F Ne Cl Ba Cs Pd Gd Br Xe Which has a larger Atomic Radius? • • • • • • • Al Ca Ba Pt Nd F Ne Cl Ba Cs Pd Gd Br Xe Which has a smaller radius? • • • • • • • • Na K F Br Mg F Cs Ag Nb S O Se Al B Pt Ne Which has a lower electronegativity? • • • • • • • • Na K F Br Mg F Cs Ag Nb S O Se Al B Pt Ne Example 1-Try to arrange the following in order of increasing atomic Radius. • Try this: Be, Ba, Sr, Answer • Be, Sr, Ba Example 2-Try to arrange the following in order of decreasing atomic Radius. • Try this: • Co, Cu, Se, Cs Answer • Cs, Co, Cu, Se Example 3-Put the following in order of decreasing ionization energy • As, Se, Cl, Br Answer • Cl, Br, Se, As Example 4- Put the following in order of increasing electronegativity • Cd, P, S, F, O Answer • Cd, P, S, O,F Example 5-Please arrange the following in order of increasing electron affinity. • Al, B, Ga, C, F, N Answer • Ga, Al, B, C, N, F Shielding and Nuclear Charge • Shielding explains family trends. As you move down a family, there are more energy levels. More energy levels means the valence electrons are further away from the nucleus. With more energy levels, the radius is larger and the electrons are more easily removed, meaning a lower Ionization energy. • Example: Li has a smaller radius and larger ionization energy than Na. • Nuclear charge explains period trends. As you move across a period, the energy level stays the same, what changes is the number of protons and electrons. With more protons, the electrons are pulled in closer, resulting in a smaller nucleus, making it more difficult to remove an electron (thus a higher IE). • Example: Li has a larger radius and lower ionization energy than Be. Questions on whiteboards • How did Mendeleev demonstrate that his periodic table was valid or useful? He was able to predict properties of unknown elements • What did Moseley’s work contribute to the development of the periodic table? He used atomic number to organize the periodic table • Why do elements in a group have similar properties? They have the same number of valence electrons. • Sketch the general shape of the periodic table and label the s-, p-, d-, and f- blocks. • A chemistry experiment calls for a compound that supplies ions of bromine, but unfortunately this compound is not available. Ruth substitutes a compound that supplies ions of chlorine. Betsy uses a compound that contains selenium. From what you know about the periodic table, who will have a more successful experiment? Why? Ruth can use chlorine because it is in the same family as bromine, and therefore will have similar properties. • The energy change from an added electron is called ______________. Electron affinity • Why does atomic radius decrease as you move from left to right across a period? The elements are in the same energy level, but are adding one proton as you move from left to right. The greater the number of protons, the greater the positive charge. With a greater positive nuclear charge, there is more attraction between the electrons and protons, pulling the electrons in closer. • Why do atoms become smaller as positive ions? They lose electrons (usually valence electrons). • Why do atoms get bigger as negative ions? They gain electrons. • Why are there no electronegativity values for noble gases? Electronegativity is the tendency of atoms to attract electrons in a bond. Since noble gases do not react and do not form bonds, we cannot measure electronegativity. • Distinguish between a cation and an anion. Cations are positive and become smaller. Anions are negative and become bigger. • Identify the least and most electronegative atoms on the periodic table. Francium (#87) is the least electronegative. Fluorine (#9) is the most electronegative. (He is a noble gas and therefore has no electronegativity value) • In the modern periodic table, elements are arranged according to _________. Atomic number • Why are Group 17 elements, the halogens, the most reactive nonmetals? They only need one electron to have a full set of valence electrons and become stable like the noble gases. • As you move from left to right across period 3 from Mg to Cl, the energy needed to remove an electron from an atom ____________. increases • In which family is Ca? Alkaline earth metals • In which family is At? halogens • In which family is Xe? Noble gases • In which family is Cs? Alkali metals