Handout - Study Reference
advertisement
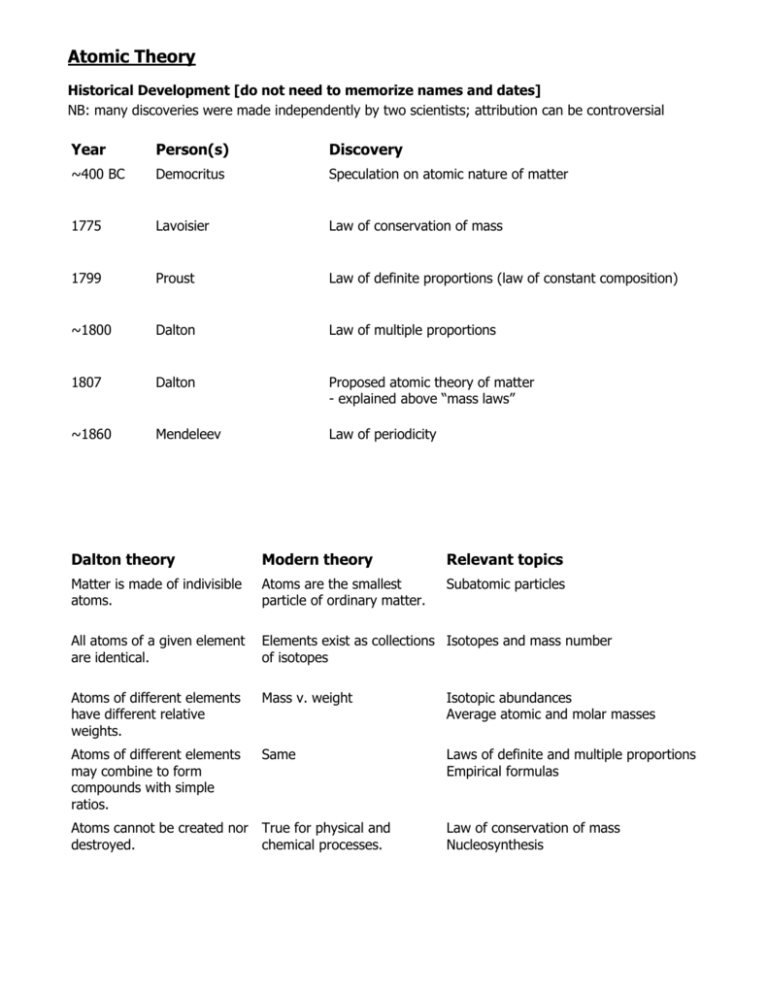
Atomic Theory Historical Development [do not need to memorize names and dates] NB: many discoveries were made independently by two scientists; attribution can be controversial Year Person(s) Discovery ~400 BC Democritus Speculation on atomic nature of matter 1775 Lavoisier Law of conservation of mass 1799 Proust Law of definite proportions (law of constant composition) ~1800 Dalton Law of multiple proportions 1807 Dalton Proposed atomic theory of matter - explained above “mass laws” ~1860 Mendeleev Law of periodicity Dalton theory Modern theory Relevant topics Matter is made of indivisible atoms. Atoms are the smallest particle of ordinary matter. Subatomic particles All atoms of a given element are identical. Elements exist as collections Isotopes and mass number of isotopes Atoms of different elements have different relative weights. Mass v. weight Isotopic abundances Average atomic and molar masses Atoms of different elements may combine to form compounds with simple ratios. Same Laws of definite and multiple proportions Empirical formulas Atoms cannot be created nor True for physical and destroyed. chemical processes. Law of conservation of mass Nucleosynthesis Atomic Theory Discoveries of subatomic particles and related advances During the 1800s, there was a gradual acceptance of a “billiard ball” model of an indivisible atom Year Person(s) Discovery 1675-1835 Gas discharge, arc, and incandescent lamp development 1857-1895 Geissler tube, Crookes tube (1875), X-ray tube ~1886 Thompson & Goldstein Proton discovered 1897 Thompson Electron discovered - same thing as cathode ray and beta ray - leads to “plum pudding” model of atom 1899 Rutherford Alpha (α) and beta (β) radiation discovered 1911 Rutherford Proposed “nuclear model” of atom 1913 Moseley Atomic number basis of periodicity not atomic mass Bohr Proposed “quantum model” of atom De Broglie Proposed dual wave-particle nature of matter 1927 Heisenberg Proposed uncertainty principle 1932 Chadwick Neutron discovered The modern quantum model of the atom is quite abstract and math provides the best description. Between wave-particle duality and the uncertainty principle, it is difficult to describe the nature of the atom without some strange analogies. In this course, when discussing “locations” of electrons what is meant is the probability density of the electron wavefunctions. Much more frequently we will discuss the energies of the electrons. No more of that situation need concern us for now. Atomic Theory Below is a summary of what you should know about the structure of the atom. Matter is composed of atoms. Atoms are composed of protons, electrons, and neutrons. Atom nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons. Nucleus is surrounded by “cloud of electrons”. Each element has a unique proton number. Neutral atoms have equal proton and electron numbers. Elements exist as collection of isotopes with varying neutron numbers. Subatomic Particles Z atomic number Z=P A mass number A=Z+N=P+N N=A-Z Q charge Q=P-E Q=0 Particle Symbol Charge (u) (for neutral atom) Charge (C) Mass (u) Mass (g) Mass (kg) Molar mass (g) Proton p+ +1 +1.602×10-19 1.007 1.673×10-24 1.673×10-27 1.007 Neutron n0 0 0 1.009 1.675×10-24 1.675×10-27 1.009 Electron e- -1 -1.602×10-19 0.000549 9.109×10-25 9.109×10-31 0.000549 Because the mass of the electron is ~1800 times smaller than the masses of the proton and neutron, the electron mass is generally neglected for most calculations. Thus, the mass of the atom is nearly the same as the mass of the nucleus. Also, because the masses of protons and neutrons are ~1 atomic mass unit, the mass of a particular isotope is approximately equal to the nucleon number. Atomic Theory Isotopes Isotope Symbol P N A Hydrogen-1 1 H 1 0 1 Hydrogen-2 2 H 1 1 2 Carbon-12 12 C 6 6 12 Carbon-13 Carbon-14 Average Atomic Mass Weighted average of the isotope masses Hydrogen three isotopes exist average mass = 1.008 g·mol -1 Carbon eight isotopes exist (only two are stable) average mass = 12.01 g·mol -1 12 13 C C 12.00 13.00 98.91 % 1.09 %











