Radioactivity-1 - Science at NESS
advertisement

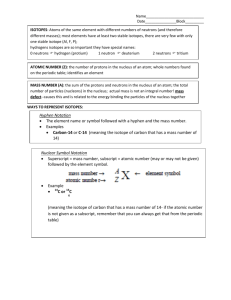
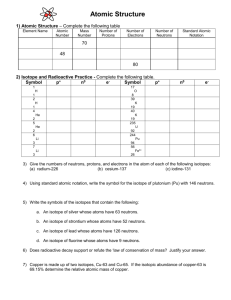
Radioactivity Isotopes and the Atomic theory Radioactivity • The release of high-energy particles and rays of energy from a substance caused by changes in the nuclei of the atom Uses • Medical diagnostic equipment and treatment, • Electricity Natural Background Radiation • Fast moving particles or waves that are found in the natural environment Radiation • High-energy rays and particles emitted by radioactive sources – eg,. Microwave, radio waves, X-rays, Gamma rays Isotopes and Mass Number Isotopes: Atoms that have the same number of protons but different number of neutrons Eg. Na with 12 neutrons or Na with 11 neutrons How do we determine if an atom is an isotope • We must be able to calculate the number of neutrons Remember atomic mass = protons + neutrons neutrons = atomic mass – atomic number Representing isotopes You will need to write a standard atomic symbol: • Symbol (K) • Atomic number (19) • Atomic mass (39) Eg 39K 19 Writing out names of isotopes • Write out atom name then a dash and then the atomic mass given (may be different then one on the periodic table) Eg Carbon-12, or Carbon-14 Assignment Questions 1-4