Region 13: Anterior Abdominal Wall and Inguinal Area Landmarks
advertisement

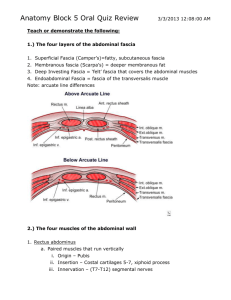
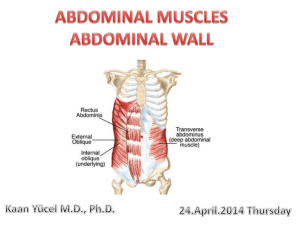
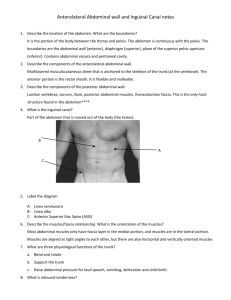
Region 13: Anterior Abdominal Wall and Inguinal Area Landmarks and Surface Anatomy --bony landmarks: ziphoid process, costal margin, pubic symphysis, pubic crest, pubic tubercle, ASIA, iliac crest, tubercle of crest, PSIS lumbar spine --Soft tissue landmarks: umbilicus, linea alba, linea semilunaris (lateral rectus line) --Planes in Abdominal region (divides into 9 regions) *2 horizontal lines a. transpyloric plane b. transtubercular plane *2 vertical lines a. right and left lateral line: drawn vertically through points halfway b/w ASIS and midline/umbilicus b. Subcostal zone: divided by R and L lateral lines into middle epigastric and 2 lateral hypochondriac regions c. Umbilical zone: divided into middle umbilical and 2 lateral lumbar regions d. Hypogastric zone: middle hypogastric and 2 lateral iliac/inguinal regions --Quadrants in Abdominal Region *vertical midsagittal line through umbilicus *horizontal line through umbilicus a. forms upper right and left quadrants b. and lower right and left quadrants Skin --dermatomes a. T6 goes over skin of xiphoid process b. T10 goes over region of umbilicus c. L1 goes over inguinal ligament Superficial Fascia --Layers: outer fatty/Camper’s layer and inner membranous/Scarpa’s layer *Scarpa’s fascia is continuous into perineum as Colles fascia --Blood vessels *superficial epigastric: parent vessel is in the femoral region -the vein communicates with lateral thoracic vein to form the thoracoepigastric vein that serves as collateral circulation for vena cava Muscles: external abdominal oblique, internal abdominal oblique, transversus abdominis, rectus abdominis External Abdominal Oblique Muscle O Lower eight ribs I Lower free margin of aponeurosis forms inguinal ligament Act. Flexes and rotates trunk as well as compresses and supports the abdominal viscera Internal Abdominal Oblique Muscle O Crest of ilium and inguinal ligament Fibers run upward, forward, and toward the midline, except those that help form I the falx inguinalis (conjoint tendon) Act. Flexes and rotates trunk as well as compresses and supports the abdominal viscera Transversus Abdominis Muscle Act. Compresses and supports the abdominal viscera Rectus Abdominis Muscle O On the pubic bone I 3 tendinous inscriptions Act. Flexes as well as compresses the abdominal viscera Rectus Sheath --Superior part a. anterior lamella of the rectus sheath *from the costal margin down to level of L4, consistes of the aponeurosis of the external oblique and half of the fibers of the aponeurosis of the interal oblique b. posterior lamella of the rectus sheath *consists of aponeurosis of half of the fibers of the internal oblique and the aponeurosis of the transversus abdominis *lower free margin of the posterior lamella is called the arcuate line/linea semicircularis at level of L4 --Inferior part a. below the level of L4 there is only an anterior lamella that consists of aponeuroses of all three abdominal muscles b. the aponeuroses in the interal oblique and the transversus abdominis fuse to form the conjoint tendon/falx inguinalis Posterior Surface of the Abdominal Wall --Deep Fascia *inner surface of muscular wall of abdomen is lined by deep fascia *Endoabdominal fascia: general term for this fascia -transversalis fascia: more specific, named for muscles it covers --Extraperitoneal Tissue *internal to transversalis fascia *median umbilical ligament, (obliterated urachus), forms medial umbilical fold *lateral to this are inferior epigastric vessels forming lateral umbilical fold --Parietal peritoneum: lines the peritoneal cavity Blood and Nerve Supply --Arteries a. superficial epigastric vessels: from femoral vessels b. superior epigastric vessels: from internal thoracic vessels c. inferior epigastric vessels: from external iliac arteries d. deep circumflex iliac vessels: from external iliac aa. e. musculophrenic vessels: from internal thoracic vessels f. superficial circumflex iliac vessels: from femoral vessels --Veins a. thoracoepigastric vein: important collateral route b/w vena cava b. paraumbilical veins: important collateral rout in portal hypertension --Nerves a. spinal nerves T6-L1: inn. both muscles and skin Inguinal Canal --space occupied by: spermatic cord or the round ligament of the uterus while they pass through abdominal wall --Walls of the inguinal Canal a. anterior: external obluqie aponeurosis reinforced by interal oblique muscle fibers b. posterior: transversalis fascia reinforced by the common tendon of the internal oblique and transversus abdominis muscles (the conjoint/falx inguinalis tendon) c. roof: arching fibers of internal oblique and transversus abdominis muscles d. floor: inguinal ligament reinforced by lacunar ligament medially *lacunar ligament: medially rolled fibers of the inguinal ligament *deep inguinal ring: located just above and about midway of the inguinal ligament, lateral to the inferior epigastric vessels -mouth of an evagination of the transversalis fascia: continues over the spermatic cord as the internal spermatic fascia (innermost covering of spermatic cord) *cremasteric muscle and fascia: second covering of spermatic cord, evagination of the internal oblique muscle *superficial inguinal ring: mouth of evagination of external oblique aponeurosis *external spermatic fascia: continuation of external abdominal oblique’s aponeurosis that continues over the inguinal canal’s contents --Contents of the Inguinal Canal in Females a. round ligament of the uterus --Contents of the Inguinal Canal in Males a. ductus deferens b. testicular a. c. pampiniform plexus of veins c. testicular autonomic nerves d. lymphatics drainging the testes --Processus vaginalis: evagination of peritoneum, accompanies testes through the canal and forms the tunica vaginalis of the testes Hernias (protrusions of an organ, part of an organ) --Inguinal Hernias a. indirect inguinal hernia *lateral to the inferior epigastric vessels b. direct inguinal hernia *enters inguinal canal through the inguinal triangle (Hesselbach’s triangle) *inguinal triangle is bounded by inguinal ligament, inferior epigastric vessels, and lateral border of the rectus abdominis c. umbilical hernias d. femoral hernias: pass under the inguinal ligament Scrotum --testes --epididymis --Walls of the sac consists of skin and superficial fascia (Dartos tunic) *continuation of Celles fascia containing smooth muscle that wrinkles the scrotal sac --Testis inaginates the tunica vaginalis *tunica albuginea: thick capsule *inside, CT septa form compartments of the seminiferous tubules --epididymus: consists of a head, body, and tail