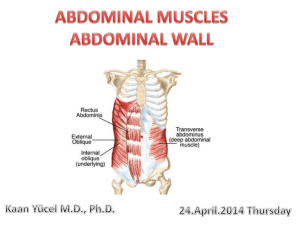
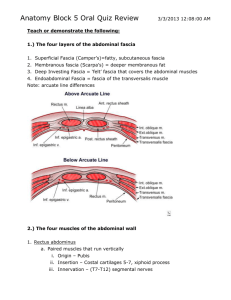
Words in bold The Abdomen: Superficial epigastric arteries and veins: the superior epigastric vein anastomoses with lateral thoracic vein in the superficial fascia collateral venous channel from the femoral vein to the axillary . If obstruction of inferior vena cava or hepatic portal vein caput medusae. Anterior cutaneous nerves : are branchings of the intercostal nerves :T7(below 7 and 8 rib),subcostal(T12),iliohypogastric L1(below L1 ) Lateral cutaneous nerves: from the intercostal and subcostal nerves T6 innervates the skin superficial to the xiphoid process T10 innervates the skin of the umbilicus T12 innervates the skin superior to the pubic symphysis L1 innervates the skin overlying the pubic symphysis External Oblique : superolateral to inferomedial Insertions: proximal : 5-12 rib distal: linea alba, pubic crest and tubercle anterior half of the iliac crest Innervation : Thoracoabdominal nerves (T7-T11)+ subcostal nerve (T12) compresses and supports the abdominal viscera , flexes and rotates the trunk External spermatic Fascia and superficial inguinal ring are made by the aponeurosis of the External oblique muscle . ilioinguinal nerve is anterior to the spermatic cord : sensory sensation to the anterior of the external genitalia and medial thigh . It is between the external and internal oblique . Inferior and parallel to iliohypogastric. Inguinal canal has a medial and a lateral crus +intercrural fibers (prevent the crura from spreading apart ) Inguinal ligament: from the ASIS to the pubic tubercle Lacunar ligament : form at the medial end of the inguinal ligament , with fibers that turn posteriorly and attach to the pecten pubis Internal Oblique Muscle: superomedial to inferolateral Proximal attachment :Iliac crest , thoracolumbar fascia , lateral half of the inguinal ligament Distal attachment: linea alba , ribs 10-12, pubic crest and pecten pubic via conjoint tendon Innervation:T17-T11 + subcostal and L1 Action: Compresses and supports the abdominal viscera + flexes and rotates the abdominal trunk Aponeurosisconjoint tendon posterior to inguinal canal Arching fibers roof of inguinal canal Cremaster muscle: from the internal oblique to the spermatic cord Ilioinguinal nerve: between the internal and external oblique , parallel and inferior to the iliohypogastric The conjoint tendon :aponeurosis of the internal oblique and transvers abdominis Transversus abdominus: horizontal Proximal attachment: Thoracolumbar fascia, Iliac crest internal surface of costal cartilage(7 to 12) Distal attachment: linea alba ,pubic crest ,pecten pubis via conjoint tendon Innervation:T7-T11,T12,L1 Action: compresses and supports the abdominal viscera, flexes and rotates the abdominal trunk The arching fibers of the transversus abdominis forms the roof of the inguinal canal and its aponeurosis forms part of the posterior abdominal wall Inguinal hernias: the inguinal canal is a weak point in which the abdominal viscera can protrude Direct: through the hesselbach triangle , medial to the inferior epigastric artery Indirect (congenital): through the deep inguinal canal , lateral to the inferior epigastric artery Hesselbach’s triangle: Bound : Laterally by : the inferior epigastric vessel Medially by : the rectus abdominis Inferiorly by: the inguinal ligament The Rectus Sheath : Rectus abdominus ,superior and inferior epigastric vessels(on the posterior side of the rectus abdominus, within the extraperitoneal fascia) , pyramidalis muscle , ventral terminal of rami of T7-T11anterior cutaneous nerves Rectus abdominus : from the fifth rib to pubic symphysis Proximal attachment : Xiphoid process , costal cartilage 5 to 7 Distal attachment: pubic symphysis and pubic crest Innervation:T7-T11 and subcostal T12 Action: compresses abdominal viscera , flexes trunk , pelvic tilt Has tendinous intersections Pyramidalis muscle: attaches to the anterior surface of the pubis and linea alba tension on the linea alba Linea Alba: because there are no bones in the anterior abdominal wall , the linea alba serves as a muscle attachment Rectus Sheath: Above arcuate line : anteriorly and posteriorly : aponeurosis of the three muscles Below arcuate line: only anteriorly The inferior epigastric vessels are much larger than the posterior , they enter the rectus sheath at the level of the arcuate line Epigastric anastomosis: The superior and inferior epigastric anastomosis together , if the IVC is obstructed they go to the PVC. If the aorta is obstructed, they take its place. External iliac and internal thoracic Transversalis fascia: lines the inner surface of the transverse abdominus. The deep inguinal ring : the point at which the gubernaculum passed through the transversalis fascia during development . Inguinal canal : Anterior: External Oblique Posterior: Transversalis fascia laterally and conjoint tendon medially Superior: the arching of the oblique and transvers Inferior: Inguinal ligament and lacunar ligament Falciform ligament : connects the anterior wall to the anterior surface of the liver Umbilical folds: Medial: remnant of the umbilical artery Median: urachus(remnant of the allantois) Lateral: epigastric vessels The lesser omentum :composed of the hepatogastric ligament and hepatoduodenal ligament . The Greater omentum: composed of the gastrophrenic gastrosplenic and gastrocolic ligaments. Made of two double layers of peritoneum . Continuous with the lesser omentum which links the liver to the stomach. The rectum is located partly in the abdomen , partly in the pelvis The round ligament at the inferior edge of the falciform ligament , contains remnant of left umbilical veins from development . The coronary ligament is around the liver and joins at left and right triangular ligaments. Omental bursa=lesser sac The transverse mesocolon: attaches from the transverse colon to the anterior surface of the duodenum and pancreas Phrenicocolic ligament : attaches the left colic flexure to the diaphragm Mesentery: suspends the ileum and jejunum to the posterior abdominal wall Mesoappendix: Attaches the appendix to the distal ileum and cecum and contains the appendicular artery Sigmoid mesocolon: Suspends the sigmoid to the posterior abdominal wall Omental foramen lies posterior to the hepatoduodenal ligament Boundaries of omental foramen: Anterior: hepatoduodenal ligament Posterior: The parietal peritoneum overlying the IVC and the right crus of the diaphragm Superior: liver Inferiorly : first part of duodenum Superior and inferior recesses of the lesser peritoneal sac Intraperitoneal organs: Stomach , liver , spleen , rectum(1/3),sigmoid colon , tail of pancreas , first part of duodenum , ileum, jejunum , cecum the transverse colon Retroperitoneal organs: Suprarenal glands, aorta and IVC ,duodenum(except first part) secondary ,Pancreas (except tail) secondary ,ureters, colon(ascending descending)secondary ,kidneys,esophagus,rectum(2/3) Liver in the right upper quadrant (the ligaments are made of peritoneum) right kidney lower than left The spleen is in the upper left , next tol the stomach The stomach is deep to the liver Gastrosphrenic ligament :greater curvature of the stomach to diaphragm Gastrosplenic: greater curvature of the stomach to the spleen Splenorenal: spleen to the wall anterior to the left kidney