The Abdomen

The Abdomen
Xiaoming Zhang
Department of Human Anatom
School of Medicine of Zhejiang University
Introduction
Formation: Abdominal wall, Abdominal cavity and contents
Boundaries
Superior boundary
Inferior boundary
Abdominal wall
Anterior Abdominal Wall
posterior abdominal wall
Abdominal cavity
Division
4 abdominal quadrants
right epigastric region left epigastric region right hypogastric region left hypogastric region
9 abdominal regions
hypogastric region
Abdominal Wall
Anterior Abdominal Wall
Ⅲ.The abdominal wall
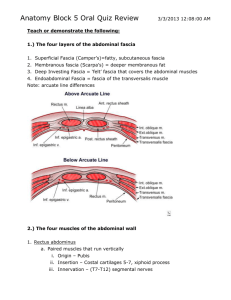
The layers of the anterior abdominal wall: skin superficial fascia muscles transverse fascia extraperitoneal fascia parietal peritoneum
I
Anterior Abdominal Wall
Layers and structures
Superficial structures
1.skin
2.superficial fascia
superficial layer — Camper‘s fascia
deep layer — Scarpa‘s fascia, Colles’ fascia
3.superficial vessels and cutaneous nerves
Superficial structures
superficial arteries : three groups
•
The branches of posterior intercostal A., subcostal A., and lumbar A.
;
•
Superior and inferior epigastric A.
;
•
Superficial epigastric A. and superfical iliac circumflex.
Superficial structures
the superficial veins:
—umbilical venous network
above the umbilicus
below the umbilicus
Superficial lymphatic vessels:
upper → axillary lymph nodes
lower → superficial inguinal lymph nodes
anastomise with the lymphatics of the liver the cutaneous nerves
I
Anterior Abdominal Wall
Deep Structures
Deep fascia
Muscular layers
rectus abdominis
the sheath of rectus abdominis
anterior layer of the sheath is formed by the aponeurosis of the obliquus externus and the ant. layer of the aponeurosis of the obliquus internus.
The linea alba is extending between the xiphoid process and the pubic symphysis, formed by the decussating of the aponeuroses of the three flat muscles.
The posterior layer of the sheath is formed by the aponeurosis of the transversus and the post. Layer of the aponeurosis of the obliquus internus.
The posterior layer of the sheath is lack of at the arcuate line (about 4cm below the omphalo )
I
Anterior Abdominal Wall
Deep Structures
Muscular layers
linea alba)
superficial inguinal ring
reflected ligament
external spermatic fascia
Inguinal ligament
lacunar ligament
)
( 3) The internus abdominis
—arises from the lateral 2/3 of the inguinal lig.,the iliac crest and the thoracolumbar fascia.The
muscular fibers is replace by the aponeurosis(ant. And post. layers) at the lateral margin of the rectus.
—cremaster
—inguinal falx
(4) The transverse abdominis
—arises from the lateral 1/3 of the inguinal lig.,the iliac crest and the thoracolumbar fascia and internal aspect of lower 6 costal cartilage.
—cremaster
—inguinal falx
— inguinal canal
1. position — parallel to,and above the inguinal lig.
Immediately.
About 4cm long.
2. Structures
— two orifices
(1) the deep inguinal ring lies a transverse finger breadth(2cm)above the midpoint of inguinal lig.
formed by the transverse fascia.
(2)sup. Inguinal ring formed by the aponeurosis of the obliquus externus.
triangular defect in shape.
medial and lateral crus
—four walls
(1) ant. wall is mainly formed by aponeurosis of the obliquus ext.,and laterally is reinforced by the beginning part of the obliquus internus.
(2) inf. wall is formed by the inguinal ligament
(3) Post.wall is formed by the transverse fascia, inguinal falx and the reflected lig..
(4) Sup. wall is formed by the arched fibers of the obliquus internus and transverse abdominis
The contents male spermetic cord, ilioinguinal nerve female round ligament and ilioinguinal nerve
The inguinal triangle
—boundaries inf. boundary medial half of the inguinal ligament medial boundary lateral border of the rectus abdominis lateral boundary inf. epigastric a..
**direct inguinal hernia
I Anterior Abdominal Wall
Deep Structures
extraperitoneal fascia
parietal peritoneum
Five longitudinal folds
Median umbilical fold
Medial umbilical fold
Lateral umbilical fold
inguinal medial fossa and inguinal lateral fossa
Summary of anterior abdominal wall
Superficial structures
skin
superficial fascia : Camper and Scarpa
superficial vessels and cutaneous nerves
Deep Structures
Deep fascia
Muscular layers
The vessels and nerves
transversalis fascia
extraperitoneal fascia
parietal peritoneum
II Inguinal region
Boundaries
Superior boundary—from anterior iliac spine to lateral margin of rectus
Medial boundary—lateral margin of rectus
Inferior boundary—inguinal ligament inguinal trangle(Hesselbach trangle )
laterally —inferior epigastric A.
medially —the lateral border of the rectus abdominis
inferiorly —medial half of the inguinal ligament
III The incisions of anterolateral wall of abdomen
Rectus incision
Median incision
Inferior median incision
McBurney’s incision