SO_cyprus_-anterior_abdominal_wall_14
advertisement

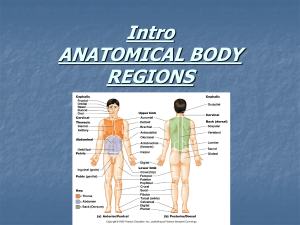
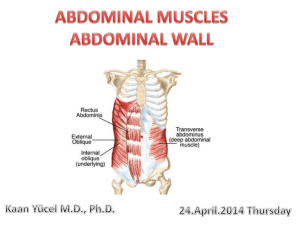
Anterior abdominal wall and the inguinal region Dr . Selda Önderoğlu ABDOMEN • The region between: Diaphragm and pelvis. • Boundaries: Roof: Diaphragm Posterior: Lumbar vertebrae+ Mm. Of the posterior abd. wall Infrerior: No boundary, continuous with the pelvic cavity, Superior Pelvic aperture Anterior and lateral: Anterior Abdominal Wall , Muscles Bony structures of the abdomen Posterior abdominal wall Topography of the Abdomen (PLANES) TRANSVERSE PLANES • Transpyloric plane : tip of 9th costal cartilages ; pylorus of stomach , L1 vertebra level. • Subcostal plane: tip of 10th costal cartilages , L3 vertebra. • Transtubercular plane: tubercles if iliac crests ; L5 vertebra level. • Interspinous plane: anterior superior iliac spines ; promontory of sacrum VERTICAL PLANES • Mid-clavicular plane: midpoint of clavicle- mid-point of inguinal ligament. • Semilunar line: lateral border of rectus abdominis muscle. Planes of abdomen Regions of the Abdomen • 9 regions: umbilical (around the umbilicus) epigastric;hypogastric L hypochondriac ; R hypochondriac L inguinal ; R inguinal L lumbar ; R lumbar region. Regions of abdomen Cutaneous nn. Of the anterior abdominal wall Skin innervation: lower 5 intercostal nerves+ subcostal nerve+ L1 spinal nerve (ilioinguinal+iliohypogastric nn.). Umbilical region skin inn.: T10. Anterior Abdominal Wall • Skin • Superficial fascia ( two layers) superficial fatty layer(CAMPER’S fascia) deep membranous layer(SCARPA’S fascia) • No deep fascia • External oblique muscle • Internal oblique muscle • Transversus abdominis muscle • Transversalis fascia • Lateral to midline(linea alba)- rectus abdominis muscle. • Extraperitoneal tissue layer- peritoneum. Superficial fascia two layers 1-superficial fatty layer (CAMPER’S fascia) 2-deep membranous layer (SCARPA’S fascia) – Muscles of the ant.abd.wall External oblique muscle (most superf.m) Internal oblique muscle Transversus abdominis muscle Those 3 mm are laterally located On both sides of the midline(linea alba) Rectus abdominis muscle inferiorly:Pyramidalis muscle External Oblique Muscle (M. Obliquus externus abdominis) • • • • Most superficial muscle. O: 5-12 ribs I: Linea alba+ inguinal ligament Parts of inguinal lig.: reflected part +lacunar ligament+ pectineal Lig. • Inn: lower 5 intercostal nn.+ subcostal n.+ L1. • Superficial inguinal ring: opening in the aponeurosis of external Oblique Muscle. has: Lateral crus-medial crus- intercrural fibres. inguinal ligament from anterior sup. iliac spine- to pubic symphsis lacunar ligament pectineal ligament Superficial inguinal Ring -Lat.crus -Medial crus -intercrural fibers Internal Oblique Muscle (Musculus Obliquus internus abdominis) • -middle layer muscle -fibers are 90 degrees to external oblique m.fibers • O:thoracolumbar fascia+iliac crest+inguinal lig. • I: linea alba+conjoint tendon ( common tendon with the transversus abdominis muscle)+ Pubic crest+pecten pubis. • Inn.:lower5 intercostal nn+subcostal n.+L1. (same with external oblique). TRANSVERSUS ABDOMINIS MUSCLE • located Innermost • O: inf. 6 Costal cartilages+Thoracolumbar fascia+inguinal ligament • I: conjoint tendon+linea alba. • Innerv.:lower5 intercostal nn.+ subcostal n.+ L1. (same with external oblique) • TRANSVERSALIS FASCIA • Located post to transv. Abd. m. deep inguinal ring. • CONJOINT TENDON ( FALX INGUINALIS): common tendon of internal oblique+ transversus abdominis mm. Functions of anterior Abdominal muscles • support+protection+movements of trunk ( external oblique- turns the trunk to the other side); internal oblique( turns the trunk to the same side). • During coughing,sneezing, vomiting, parturition ( during birth of a child) all of these muscles contract( increase intraabdominal pressure.) Rectus Abdominis Muscle • • • • Located on both sides of midline(linea alba) O: Xiphoid process I: symphysis pubis Inn: lower 5 intercostal nn.+ subcostal nn!! ( different from the previous 3 Mm.) • F: flexes the trunk. • Has tendinous intersections:3-4 in number • enveloped by a sheath:RECTUS SHEATH. • Lat. Border: semilunar line Rectus abdominis muscle Rectus sheath RECTUS SHEATH • 4-5cm below UMBILICUS -ARCUATE LINE (SEMICIRCULAR LINE) : ABOVE this line: Anterior layer : external oblique apon. + anterior lamina of internal oblique’s aponeurosis.) Posterior layer: Posterior lamina of internal oblique apon.+ transversus abdominis apon. BELOW this line: Anterior layer : external oblique apon.+internal oblique apon.+transversus abdominis aponeurosis. Posterior layer: Only Transversalis fascia. • Structures within the rectus sheath: rectus abdominis muscle+ superior epigastric artery+ inferior epigastric artery+ lower 5 intercostal nn.+ subcostal n. Rectus sheath Arteries of anterior Abdominal wall -musculophrenic -Sup epigastric -İnferior epigastric -Deep circumflex iliac -Superficial circ.iliac INGUINAL CANAL • Surgically an important canal because it is the site of inguinal hernias • obliquely located;tubelike • 3-4cm. in length. • Has two openings : • Superficial inguinal ring external oblique apon. -medial • Deep ingunal ring: transversalis fascia - Lateral inguinal canal • • • • • • superficial inguinal ring Anterior wall Post. Wall Superior wall inferior wall deep inguinal ring 4-6 cm INGUINAL CANAL • WALLS: • anterior wall: skin+ superficial fascia+external oblique (medially)+ internal oblique ( laterally). • Posterior wall: Reflected ingunal lig.+ conjoint tendon+ transversalis fascia. • Inferior wall: inguinal lig.+ lacunar lig. • Superior wall: inferior margins of internal oblique+ transversus abdominis mm. Structures passing through Ingunal Canal • • • • Spermatic cord in male Round ligament of uterus in female. Ilioinguinal n.. Genital branch of genitofemoral n. Superficial inguinal ring INGUINAL HERNIA • Indirect Inguinal hernia: piece of organ passes through deep ing. ring- courses in inguinal canal – passes through superficial inguinal ring- protrudes outwards. • Direct inguinal hernia: piece of organ pushes directly ant. Abd. wall passes through supeficial inguinal ring – protrudes outwards. • How to differentiate direct and indirect ingunal hernia? reference is the inferior epigastric artery. • If it is lateral to this a. :Indirect inguinal hernia • If it is medial to this a.: Direct inguinal hernia. Femoral canal Femoral hernia (saphenus opening) Folds of the ant. Abd. wallperitoneum • When looked from inside the anterior abdominal wall there are some folds of parietal peritoneum : • Median umbilical fold : under which lies the urachus • Medial umbilical fold: under which umbilical artery lies. • Lateral umbilical fold: inferior epigastric vessels lie. ARTERIES, VEINS and LYMPH OF THE ANT. ABD. WALL • Arteries: Sup. Epigastric. A.+ ınferior epigastric a.+ superficial circumflex iliac a.+ deep circumflex iliac a.+ superficial epigastric a.+musculophrenic • Veıns: SAME NAMED. • IMPORTANT ANASTOMOSIS: supeficial epigastric vein- lateral thoracic vein- unite the veins of the superior and inf. Halves of the body. • Lymph: Axillary-above the umbilical region Inguinal- below the umbilical region. Lymphatics of the abdominal wall