Hesselbach's triangle
advertisement

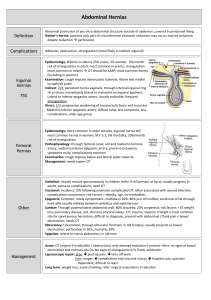
ABDOMEN Lu Xiaoli Regional Anatomy & Operative Surgery China Medical University BOUNDARIES Abdominopelvic Cavity Abdominal Cavity Pelvic Cavity P242-fig.4.21 DIVISIONS P242-fig.4.22 P243-fig.4.23 P243-fig.4.23 Which one of the following is not one of the 9 regions of the abdomen? A. Right hypochondriac B. Left inguinal or iliac C. Epigastric D. Right upper E. Left lumbar Which of the following is NOT true concerning the peritoneal cavity? A. The peritoneal cavity is a potential space. B. The peritoneal cavity contains organs inside of it. C. The peritoneal cavity is filled with fluid that lubricates its contents. D. The parietal and visceral peritoneum are linings of the peritoneal cavity. The usual location for an appendectomy incision is the: A. left lower quadrant B. left upper quadrant C. right lower quadrant D. right upper quadrant You were asked to assist in a surgical operation on a young patient to treat an ulcer in the first part of the duodenum. You would expect that the surgeon will approach the ulcer by doing an anterior abdominal wall incision in the following region: A. Epigastric B. Left inguinal C. Left lumbar D. Right hypochondrial E. Hypogastric ABDOMINAL WALL Abdominal wall Anterolateral abdominal wall Posterior abdominal wall LAYERS Skin Superficial fascia Deep fascia Muscles Transversalis fascia Extraperitoneal fascia Peritoneum Superficial fascia Camper’s fascia Scarpa's fascia P245-fig.4.25~4.26 SUPERFICIAL ARTERIES Lateral Median Posterior intercostal a. Subcostal a. Lumbar a. Epigastric a. hypogastric a. Inferior Superficial epigastric a. Superficial iliac a. P255-fig.4.39 Superficial veins lateral thoracic thoracoepigastric paraumbilical S epigastric S circumflex iliac subclavian portal femoral Caput Medusae (Medusa Head ) INNERVATIONS Intercostal Nerve T7-T12 10th Intercostal Nerve MUSCLES Anterior Group •Rectus Abdominis •Pyramidalis Lateral Group •External Oblique •Internal Oblique •Transversus RECTUS ABDOMINIS Tendinous Intersection (3) Linea Semilunaris Rectus Sheath Arcuate line PYRAMIDALIS LINEA ALBA External Oblique Abdominis Oblique Internal Abdominis Transversus Abdominis Arteries 5 intercostal arteries subcostal arteries 4 lumbar arteries Superior epigastric artery—internal thoracic artery Inferior epigastric artery -external iliac artery Deep iliac circumflex artery- external iliac artery Inferior epigastric artery Lymphatic Drainage Intercostal Lymphatic Nodes Anterior → Parasternal Lymphatic Nodes Middle → Lumbar Lymphatic Nodes Lower → External Iliac Lymphatic Nodes Innervations Intercostal n. Anterior cutaneous branch Lateral cutaneous branch T7-12 thoracic n. Iliohypogastric n. Ilioinguinal n. Genitofemoral n. Transversalis Fascia Extraperitoneal Fascia Parietal Peritoneum Umbilical Folds Median -- median umbilical lig. Medial -- chorda arteriae umbilicalis Lateral -- inferior epigastric a. & v. INCISIONS Longitudinal Midline Paramedian Transrectal Oblique Subcostal McBurney’s Transverse Pfannenstiel Combined Thoracal-abdominal The inferior border of the rectus sheath posteriorly is called the: A. Falx inguinalis B. Inguinal ligament C. Internal inguinal ring D. Arcuate line E. Linea alba Following an emergency appendectomy your patient complained of having paresthesia (numbness) of the skin at the pubic region. The most likely nerve that has been injured during the operation is: A. Genitofemoral B. Iliohypogastric C. Subcostal D. Spinal nerve T10 E. Spinal nerve T9 An obstetrician decides to do a Caesarean section on a 25-yearold pregnant woman. A transverse suprapubic incision is chosen for that purpose. All of the following abdominal wall layers will be encountered during the incision EXCEPT the: A. Anterior rectus sheath B. Posterior rectus sheath C. Rectus abdominis muscle D. Skin and subcutaneous tissue E. Transversalis fascia, extraperitoneal fat, and peritoneum Surgical approaches to the abdomen sometimes necessitate a midline incision between the two rectus sheaths, i.e., through the: A. Linea aspera B. Arcuate line C. Semilunar line D. Iliopectineal line E. Linea alba The internal thoracic artery is sometimes surgically cut near the caudal end of the sternum and used to supply blood to a region of the heart. In these cases, maintenance of adequate blood flow to the rectus abdominis may be dependent on increased flow through which artery? A. Superficial epigastric B. Inferior epigastric C. Umbilical D. Superficial circumflex iliac E. Deep circumflex iliac INGUINAL REGION Boundaries LAYERS Skin Superficial Camper’s Scarpa’s layer External Oblique Abdominis Inguinal Lig. Lacunar Lig. Pectineal Lig. (cooper’s Lig.) Reflected Ligament Lateral Crus Superficial Inguinal Ring Intercrural Fibers Medial Crus Internal oblique abdominis transverse abdominis Conjoint Tendon Cremaster Cremaster Conjoint Tendon Transverse Abdominal Fascia abdominal inguinal ring (deep inguinal ring) Extraperitoneal fascia Parietal peritoneum Medial inguinal fossa lateral inguinal fossa Descent Of Testis 4 lunar month 11 weeks 8 lunar month Inguinal Canal Roof internal oblique abdominis transversus abdominis Floor inguinal ligament lacunar ligament anterior wall external abdominal oblique aponeurosis internal abdominal oblique aponeurosis posterior wall transversalis fascia conjoint tendon (falx inguinalis) Contents (male) spermatic cord arteries: testicular artery, deferential artery, cremasteric artery nerves: genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve, nerve to cremaster, sympathetic nerves vas deferens pampiniform plexus lymphatic vessels ilioinguinal nerve Contents (female) round ligament of the uterus ilioinguinal nerve Spermatic Fascia Internal spermatic fascia Transversalis fascia Middle cremaster External aponeurosis abdominis of external oblique HERNIA Inguinal hernia Indirect Direct Inguinal Triangle (Hesselbach's triangle ) Direct Hernia A medical student was asked by her preceptor to palpate the margin of the superficial inguinal ring of a healthy male patient. After passing her finger down the edge of the medial crus of the superficial inguinal ring, she felt a bony protuberance deep to the lateral edge of the spermatic cord, which she correctly identified as the : A. pecten pubis B. pubic symphysis C. pubic tubercle D. iliopubic eminence E. iliopectineal line In order to reduce a hernia (return it to the abdominal cavity), a surgeon finds it necessary to ligate an artery in the extraperitoneal connective tissue (preperitoneal fat) running vertically just medial to the bowel as the bowel passes through the abdominal wall. This artery is the: A. Deep circumflex iliac B. Inferior epigastric C. Superficial circumflex iliac D. Superficial epigastric E. Superficial external pudendal During a laparoscopic examination of the deep surface of the lower anterior abdominal wall (using a lighted scope on a thin tube inserted through the wall), the attending physician noted something of interest and asked the young resident to look at the medial inguinal fossa. To do so, the young doctor would have to look at the area between the: A. inferior epigastric artery and urachus B. medial umbilical ligament and urachus C. inferior epigastric artery and lateral umbilical fold D. medial umbilical ligament and inferior epigastric artery E. median umbilical ligament and medial umbilical ligament If one were to make an incision parallel to and 2 inches above the inguinal ligament, one would find the inferior epigastric vessels between which layers of the abdominal wall? A. Camper's and Scarpa's fascias B. External abdominal oblique and internal abdominal oblique muscles C. Internal abdominal oblique and transversus abdominis muscles D. Skin and deep fascia of the abdominal wall E. Tranversus abdominis muscle and peritoneum Which structure passes through the deep inguinal ring? A. Iliohypogastric nerve B. Ilioinguinal nerve C. Inferior epigastric artery D. Medial umbilical ligament E. Round ligament of the uterus A loop of bowel protrudes through the abdominal wall to form a direct inguinal hernia; viewed from the abdominal side, the hernial sac would be found in which region? A. Deep inguinal ring B. Lateral inguinal fossa C. Medial inguinal fossa D. Superficial inguinal ring E. Supravesical fossa In a female with an indirect inguinal hernia, the herniated mass lies along side of which structure as it traverses the inguinal canal? A. Iliohypogastric nerve B. Inferior epigastric artery C. Ovarian artery and vein D. Pectineal ligament E. Round ligament of the uterus The skin of the mons pubis is supplied by which nerve? A. Anterior scrotal B. Anterior labial C. Femoral branch of the genitofemoral D. Iliohypogastric nerve E. Subcostal nerve During your peer presentation of the inguinal region dissection, you would indicate the position of the deep inguinal ring to be: A. B. Above the anterior superior iliac spine Above the midpoint of the inguinal ligament C. Above the pubic tubercle D. In the supravesical fossa E. Medial to the inferior epigastric artery A 45-year-old porter develops a direct inguinal hernia. If the hernia extended through the superficial inguinal ring, it would be surrounded by all of the abdominal wall layers EXCEPT the: A. External spermatic fascia B. Internal spermatic fascia C. Peritoneum and extraperitoneal connective tissue D. Weak fascia of the transversus abdominis muscle lateral to the falx The boundaries of the triangle include all except: A. Arcuate line B. Inferior epigastric vessels C. Inguinal ligament D. inguinal Lateral border of rectus abdominus muscle The superficial inguinal ring is an opening in which structure? A. External abdominal oblique aponeurosis B. Falx inguinalis C. Internal abdominal oblique muscle D. Scarpa's fascia E. Transversalis fascia Which nerve passes through the superficial inguinal ring and may therefore be endangered during inguinal hernia repair? A. Femoral branch of the genitofemoral B. Ilioinguinal C. Iliohypogastric D. Obturator E. Subcostal During exploratory surgery of the abdomen, an incidental finding was a herniation of bowel between the lateral edge of the rectus abdominis muscle, the inguinal ligament and the inferior epigastric vessels. These boundaries defined the hernia as a(n): A. Congenital inguinal hernia B. Direct inguinal hernia C. Femoral hernia D. Indirect inguinal hernia E. Umbilical hernia Superficial layers Skin Superficial skin Muscles Anterolateral Transversalis fascia abdominal wall Deep layers Subperitoneal fascia Parietal peritoneum 4 walls Inguinal canal 2 openings Inguinal region triangle Contens