Cardiovascular MRI Techniques in Heart Diseases
advertisement

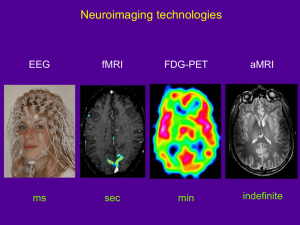
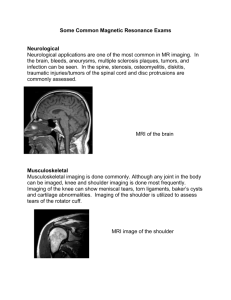
Cardiovascular MRI Techniques in Heart Diseases Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) technique enables us to achieve any dimensional (even functional) images with any orientation without potential harmful effects. Beside its high soft-tissue contrast discrimination, different data acquisition protocols could be applied via MRI scanners in order to purify interested areas or enhance contrast of MR images. Additional safe contrast agents, such as gadolinium, are also used for these purposes (in Perfusion Analysis for functional maps). Capabilities of MRI in detection of anatomic or functional disorders is indispensable. Coronary diseases can be excluded with high confidence. Cardiac MRI is a useful noninvasive method for the early diagnosis and follow-up of cardiac Sarcoiditis. Wall Thickening (ex. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy) of myocardium is a sensitive indicator of dysfunctional contraction of heart and it is possible to identify it thanks to MRI. Terminology Angiography: The imaging of arteries or veins. Atherosclerosis: Degenerative disease of the arteries resulting in plaques consisting of necrotic cells, lipids, and cholesterol crystals. Cardiomyopathy: A disease of the heart muscle that leads to generalized deterioration of the muscle and its pumping ability Fibrosis: An abnormal thickening. Myocarditis: Inflammation or degeneration of the heart muscle. Idiopathic: Without a known cause. Ablation: The erosive process. Stress tests: Standard stress tests, such as treadmill exercise tests, is used to measure how well a person's heart handles exertion. Stenosis: Narrowing of arteries or veins. Cine MRI: Type of MRI which can show blood flow. Perfusion Analysis: Analysis of a dynamic MRI scan results, while a contrast agent injection. Tagged MRI: Labeled dark lines of MR images, emerged because of regional perturbation of magnetization. Ali BAYRAM 28/11/2005