Lab: Conductivity of Solutions
advertisement

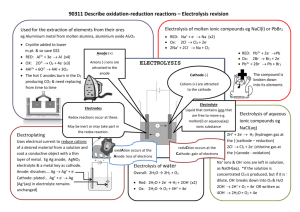
Lab: Conductivity of Solutions Electricity is "created" when certain chemicals react together. We use chemically- made electricity to power many machines from flashlights to a watch or even cars! The devices that store electricity are called batteries. Electricity can also be used to produce chemical changes. Water is a simple chemical made from two gases -- hydrogen and oxygen. Every molecule of water has two atoms of hydrogen for every atom of oxygen. H2O is the chemical formula for a molecule of water. If an electrical current is passed through water between electrodes (the positive and negative poles of a battery), the water is split into its two parts: oxygen and hydrogen. You can use electricity to split hydrogen gas out of the water similar to the process called electrolysis. If an ionic compound is dissolved in water, it dissociates into ions and the resulting solution will conduct electricity. Dissolving solid sodium chloride in water releases ions according to the equation: NaCl(s) --> Na+(aq) + Cl–(aq) When you pass an electric current through a solution, ions (charged particles) migrate towards the electrode of the opposite charge. In a salt solution (NaCl) the dominant species of ions are sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl-), because only a tiny amount of water (H2O) is ionised (to H+ and OH-) at pH 7, and that's why pure water is very difficult to electrolyse. So when you apply a current to the solution using copper electrodes, the chloride ions (Cl-), termed anions, will move towards the positive electrode (the anode), whilst the positively-charged sodium ions (the cations) will migrate towards the negative electrode (the cathode). The migrating ions carry charge through the solution and hence help to complete the circuit. At the anode, 2 chloride ions (Cl-) will each surrender an electron to the anode (which likes electrons because it is positively charged) to form a molecule of chlorine gas, which you see fizzing off : 2Cl-(aq) -> Cl2(g) + 2eAt the same time, the copper (Cu) forming the electrode will also try to donate electrons : Cu(s) -> 2e- + Cu2+(aq). When the copper (Cu) gives up 2 electrons it forms a copper ion (Cu2+) which then goes into solution, turning the electrolyte blue / green, as you have observed. At the negative electode (cathode) hydrogen ions (H+) from water pick up electrons to form hydrogen : 2H+(aq) + 2e- -> H2(g) ...and the copper ions (Cu2+) which were sent from the anode also pick up electrons to form metallic copper which is deposited on the cathode : Cu2+(aq) + 2e- -> Cu(s). So if you weighed the 2 electrodes before and after the experiment, you should be able to demonstrate that the anode (the positive electrode) gets lighter, and the cathode (the negative electrode) gets heavier. In this lab, you will study the effect of adding an ionic compound to distilled water to observe the effects on conductivity. Conductivity is present if there are bubbles present at the cathode and anode. Questions for you to answer as you do this lab. 1. Will deionized water conduct electricity? Why or why not? What do you observe when you do the experiment? Does it support your hypothesis? 2. When the solution bubbles, what are the bubbles? What gases do you think are bubbling out of the solution? 3. What would happen if we let this solution continue to bubble? What is left? What will this do to the pH of the solution? To the ion concentration of the solution? 4. Determine the conductivity of each of the following compounds. Dissolve about a teaspoon of each compound in 100 mL of distilled water. Keep your data on this sheet. Hypothesize about which ones you think will conduct electricity and which ones won’t. Compound/Solution Formula Distilled water Tap Water NaCl Sugar Hypothesis- Is it ionic? Polar? Conducts Electricity? Results and Observations 5. Draw the complete set up you used and label the cathode, anode, battery, solution, and gas (be specific!). Explain what exactly you are doing in the experiment. Include an explanation about what the cathode and anode are, and what is happening at each.