Cell Transport
advertisement
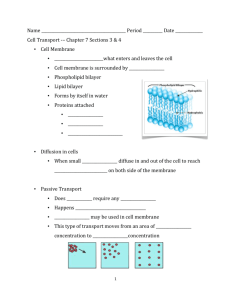
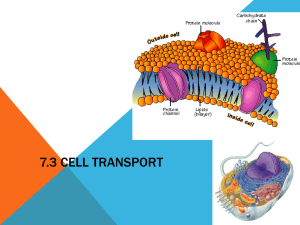
Cell Transport maintaining homeostasis Passive Transport Does NOT require any ATP or energy Happens automatically Channels may be used in cell membrane Passive Transport This type of transport moves from an area of high concentration to low concentration Diffusion Type of passive transport When molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration until equilibrium is met What affects the rate of diffusion? Concentration of the solution Temperature of the solution Pressure also speeds up particle motion Concentration The amount of dissolved solute in a solution Molecules will move to an area less concentrated Molecules diffuse through the cell membrane of cells Concentration gradient The difference in concentration in a solution between a cell and its surroundings Concentration Gradient No gradient - even distribution Concentration to the right Increase Rate of Diffusion Temperature Molecules move faster in higher temperatures Pressure Increasing pressure also increases rate of diffusion Equilibrium This occurs when there is no longer a concentration gradient Molecules are evenly dispersed but still continue to move randomly Cell Membrane Movement through membrane Cell membrane is surrounded by water Phospholipid bilayer Cell Membrane Forms by itself in water Proteins imbedded Markers Receptors Channels Diffusion in cells Small molecules diffuse in and out of the cell to reach equilibrium on both side of the membrane Osmosis Diffusion of water across a biological membrane From an area of high concentration to low concentration of WATER Comparing concentrations Osmosis in Cells Cells are surrounded by water and filled with water. Water can move freely through the membrane Direction of Osmosis Hypertonic Outside cell is more concentrated than cell ex: 20% salt solution 10% salt solution The solution with 20% salt is hypertonic compared to the 10% salt solution Hypotonic Outside the cell is less concentrated than cell ex: 10% salt solution 20% salt solution The solution with 10% salt is hypotonic compared to the 20% salt solution Isotonic Equal concentrations ex: 10% salt solution Equilibrium is reached 10% salt solution Osmotic Pressure Net movement of water into cells Determined by solute concentration Osmosis - hypertonic Higher concentration in solution Ex: a cell in salt water If molecules are too large to fit through cell membrane or protein channels Water will diffuse OUT of the cell to reach equilibrium Cell shrinks Osmosis - hypotonic Lower concentration in solution Ex: a cell in pure water If molecules are too large to fit through cell membrane or protein channels Water will diffuse INTO the cell to reach equilibrium Cell swells - may burst! Osmosis - Isotonic Equal concentration in solution If molecules are too large to fit through cell membrane or protein channels Water will diffuse IN AND OUT of the cell to maintain equilibrium Osmosis in Plant Cells Turgor Pressure Pressure on the walls of the plant cells due to vacuole filling Increase in turgor pressure is increase in water to cell Plasmolysis When a cell shrinks due to lack of water Red Onion Cells Isotonic Red Onion Cells Hypertonic Red Onion Cells Hypotonic Facilitated Diffusion When the cell membrane has protein channels (carrier proteins) where materials are transported in or out of cell NO energy needed for this process Active Transport Against concentration gradient From an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration Requires cell energy (ATP) because you’re going AGAINST concentration gradient 3 types of active transport Protein channels embedded in cell membrane Gated channels Need energy to open Protein changes shape when energy is used Sodium/Potassium Pump Step 1: 3 Na+ ions bind to carrier protein Step 2: ATP binds to carrier protein and changes shape allowing Na+ to move out of the cell Step 3: 2 K+ ions move into carrier protein Step 4: ATP binds to carrier protein and changes shape allowing K+ to move into the cell Movement in Vesicles Endocytosis - INTO the cell Cell membrane is used to create a vesicle around particles Phagocytosis Particle ingestion Pinocytosis Liquid ingestion Movement in Vesicles Exocytosis - OUT of the cell Vesicles created in the cell fuse with cell membrane and release particles/liquids Known as bulk transport