Materials Move Across Cell*s Membranes
advertisement

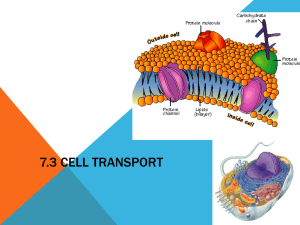
MATERIALS MOVE ACROSS CELL’S MEMBRANES Chapter 2.3C Review What is a cell membrane?? What is the purpose of a membrane? What are membranes primarily made up of? For the remainder of the powerpoint, copy words highlighted in ORANGE! Diffusion Molecules spread out from where there are many to where there are fewer They keep spreading until they are evenly distributed Examples: Smelling a scent Oxygen (needed for respiration) and carbon dioxide (produced by respiration) Concentration The number of particles of that substance in a specific volume Example: Dissolving 9 grams of sugar in 1 liter of water yields the concentration 9g/L Diffusion in Cells Materials are able to move into and out of the cell Example: Photosynthesis: produces oxygen inside the cell Concentration of oxygen is higher on the inside than the outside Oxygen cells move out of the cell by diffusion **What are some daily examples of diffusion? Types of Diffusion Passive transport Active transport Osmosis Endocytosis Exocytosis Passive Transport Materials move without using the cell’s energy (moving from high concentration to low concentration) Osmosis Diffusion of water through a membrane Example: Unwatered plants wither Water leaves the plant’s roots to go to the dry soil to even out the concentration of water molecules When the plant is watered, water molecules diffuse through the plant’s cell membranes to even out the concentration again Active Transport Process of using energy to move materials through a membrane (moving from low concentration to high concentration) Examples: Marine Kidneys iguanas Endocytosis Moving materials too large to pass through a membrane INTO the cell Membrane folds inward, creating a pocket Membrane closes around the material, forming a “package” “Package” breaks away from cell membrane, bringing the material into the cell Exocytosis Moving materials too large to pass through a membrane OUT OF the cell “Package” carries materials to cell membrane Attaches to membrane and merges together Materials are pushed out of membrane Cell Size (and shape) Affects Transport As cell grows, surface area is not large enough to allow resources to travel to all parts of cell As a result, the cell may: Stop growing Divide Shape Thin and flat cells (single-celled organisms) have increased surface area Long and skinny cells (nerve and muscle) have increased surface area