Osmosis
advertisement

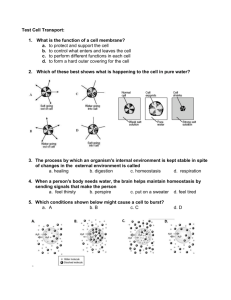
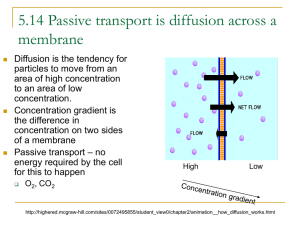
Osmosis Osmosis • When the diffusing substance is water, and when the diffusion takes place through a semi permeable membrane the process is called osmosis. • Also the movement of water down a concentration gradient from an area of high solvent concentration (weak solution) to an area of low solvent concentration (stronger solution.) Osmosis • Consider 2 salt solutions, (one dilute and the other concentrated) separate by a semi permeable membrane. • The 2 solutions will tend to equalize in concentration. i.e. the dilute one will tend to become more concentrated whereas the concentrated one will tend to become more dilute they do this by for example a process called osmosis. • Diffusion is movement of substances from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Isotonic solutions. • Two solutions with the same solute concentrations are said to be isotonic • The normal salt concentration of blood in the body is approximately 0.9% NaCl. • This is also known as physiologic saline. • Therefore blood and physiologic saline solutions are isotonic i.e. they have the same salt concentration. • Also a 5.5% glucose solution is isotonic with body fluids. Osmosis • Suppose a Red blood cell were placed in a small amount of physiologic saline? What will happen? Hypotonic solution • A hypotonic solution is one that contains a lower solute concentration than that of another solution • Distilled water and tap water are hypotonic compared to blood. • Suppose a red blood cell is placed in water (hypotonic) the salt concentration of blood is greater than that of water. Therefore osmosis will take place. • Water moves into the cells • Leading to Hemolysis. • Thus hypotonic solutions are not used for blood transfusion. Hypertonic solution • Is one that contains a higher solute concentration than that of another solution. • For example 5% NaCl is an example of hypertonic solution when compared with blood. • Suppose a red blood cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, what will happen ? • It would shrink because water moves out of the cell • Saline cathartics such as magnesium sulfate, milk of magnesia, and magnesium citrate are absorbed slowly and incompletely. • When ingested they form a hypertonic solution and water moves out from tissue spaces. Reverse osmosis • When water and a salt solution are separated by a semi permeable membrane, If the pressure greater than the osmotic pressure is applied to the salt solution side of the membrane, the entire process will be reversed • This process is called Reverse Osmosis. Osmosis • This continues until the solution is isotonic with body fluids. • The additional water in large intestine produces watery stool that is easily evacuated. Diffusion • Also known as passive transport • Is process whereby a substance moves from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. • The greater the difference in concentration the faster the rate of diffusion. • No external source of energy is needed. Diffusion • Gases will diffuse into one another. • When a bottle of ether is opened, the odor can soon be detected from a distance • Diffusion of gases takes place faster than liquids. • Another example is in loss of perspiration in the body. • Here the moisture flows from an area of high concentration (skin) to one of lower concentration (the air ) • The higher the moisture content of the air, the slower the rate of evaporation of moisture from the skin Diffusion across the cell membrane Factors affecting diffusion across a plasma membrane. • The greater the lipid solubility of the diffusing particle the more permeable the membrane will be. • Smaller particles will generally diffuse faster than large ones. • O2, H20 and CO2 will rapidly diffuse across the lipid bilayer Facilitated diffusion. • Allows diffusion of large , membrane – insoluble compounds such as sugars, amino acids. • Is also a passive process. • Substances bind to transport proteins • Rate of movement depends on the number of available transporter. Facilitated diffusion