Cell Boundaries: Diffusion, Osmosis & Transport
advertisement

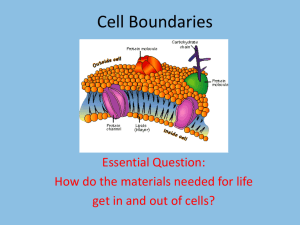
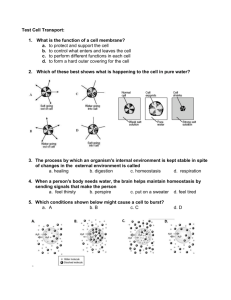
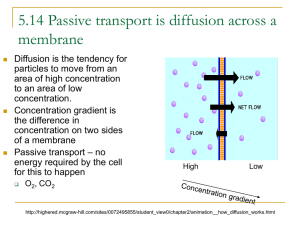
Cell Boundaries Essential Question: How do the materials needed for life get in and out of cells? Organelle Functions cell membrane Outer covering of cell, controls what goes in and out. Animal Cell Analogy Your skin Plant Cell Organelle Functions Thick outer wall of plant cells. Provides protection and support. cell wall Analogy Brick wall, Cereal box Cell wall Animal Cell Cell membrane Plant Cell Close-up of Cell Membrane What’s the difference between osmosis and diffusion? • Diffusion = movement of molecules from area of high concentration to low. Equilibrium (equally spread out) Red food coloring diffuses through a glass of water • Osmosis = diffusion of water across a membrane. Water moves by osmosis from left to right How does osmosis affect movement of water in and out of cells? • Water tends to move in or out of cells by osmosis in such a way as to reach equilibrium (equal concentrations inside and outside) 6. A red blood cell is 80% water. What would happen if red blood cells were put into each of the three beakers shown below? Label the appropriate solutions as hypotonic, hypertonic, or isotonic. Then describe how osmotic pressure would affect the blood cells placed in each. 80% 80% water water 100% water Hypotonic More water moves into cell than out, Making it swell 80% water 80% water 20% salt 65% water 35% salt Isotonic Hypertonic Water moves in & out of cell at same rate, So cell stays same size More water moves out of cell than in, Making it shrink Osmosis Animation http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animation_ _how_osmosis_works.html Which jar contains pure water? Salt water? Corn syrup? A corn syrup (hypertonic) More water diffused out of egg B C pure water (hypotonic) More water diffused into egg salt water (isotonic) Water diffused in and out of egg equally. 7. What is facilitated diffusion? Copy the diagram in Figure 7-17 and use it to explain how facilitated diffusion is used to move glucose into cells. Facilitated diffusion = Protein channels help molecules diffuse into or out of cell 8. Given that a starch molecule can be hundreds of times bigger than a glucose molecule, would it be easy or difficult for starch in your bloodstream to get inside your cells? Explain. Difficult, because starch molecule too big to get through holes in cell membrane. starch Glucose (sugar) 9. What’s the difference between active and passive transport in cells? • Passive requires no energy from cells, happens by itself. Moving materials from high concentration to low. • Active requires energy from cells. Moving materials from area of low concentration to high. 10. Apply what you’ve learned here to explain why you shouldn’t drink sea water if you’re stranded on a raft in the middle of the ocean. Cells will lose water and shrink, you will get dehydrated. What do you think caused the elodea cells to change as they did after adding salt water? • Cells became dehydrated, water moved out of cells. Cell membrane contracted around chloroplasts. Before adding salt water After Video: Active & Passive Transport http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kfy92hdaAH0 Questions? More videos • Passive and active transport http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JShwXBWGMyY • Diffusion, osmosis, active transport http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OXCKjhE1xco • Diffusion and osmosis http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qotIWgL7zFs A B C Which jar contains pure water? Salt water? Corn syrup?