Gastric Function Tests: Analysis & Stimulation
advertisement

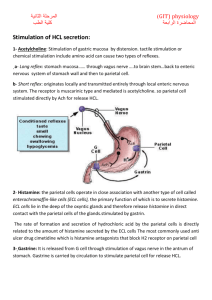
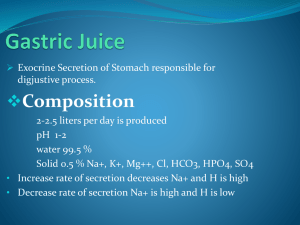
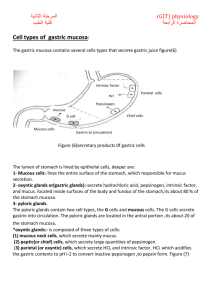
D-GASTRIC FUNCTION TESTS In some diseases of Stomach & Duodenum alterations in gastric secretion occurs, thereby chemical examination of gastric contents has limited but specific value in diagnosis & assessment of disorders of upper GIT. Hence to get complete data of gastric fn, the contents of stomach should be examined During resting period During digestion after meals After stimulation Gastric juice secreted in 24 hrs is about 1500 ml to 2000ml. N Chief constituents of Gastric juice HCl………Parietal cells / oxyntic cells - it activates the zymogen pepsinogen to pepsin by partial proteolysis, also helps in absorption of iron and calcium. Pepsinogen..........Chief cells - Pepsins act on proteins and polypeptides & cleave peptide bonds adjacent to aromatic amino acids Gastrin: hormone secreted by G cells, stimulates secretion of HCl. Intrinsic Factor: Parietal cells, is a glycoprotein required for absorption of Vit B 12 Gastric lipase: Chief cells. Act on Triglycerides, convert to Fatty acids and glycerol Rennin : is seen in infants but not in adults. Alkaline Mucus Indications of Gastric Function Tests To diagnose Gastric Ulcers To exclude the diagnosis of Pernicious Anaemia & Peptic ulcer in Pt with GU. For presumptive diagnosis of Zollinger Ellison Syndrome To determine the completeness of Surgical Vagotomy. CLASSIFICATION OF GFTs Analysis of Resting contents(Gastric Residuum) Fractional Test Meal Analysis Analysis after Stimulation # Alcohol stimulation # Caffeine stimulation # Histamine stimulation CONTD…… # Augmented Histamine test # Insulin stimulation # Pentagastrin test Tubeless Gastric Analysis Other relevant tests are estimation of Sr.Gastrin, Sr.Pepsinogen levels, Tests for Occult blood and Tests for H.Pylori Analysis 1)Volume of resting contents: : N20-50ml after a night fast > 100-120 ml….is abnormal Volume.. - Hypersecretion of Gastric juice - Retention due to delayed emptying - Regurgitation of duodenal contents. 2) Consistency : N Fluid, should not contain food residues. 3) Colour: N Clear/ Colourless/ slight yellow/green.. Bright red / dark red / brown…abnormal dark brown seen in bleeding gastric ulcer, coffee ground appearance seen in Ca stomach. 4) Bile: Small amounts are insignificant, but increased in Intestinal Obstruction / Ileal Stasis. 5) Mucus: N in small amounts, increased in gastritis , Ca Stomach. 6) Free & Total Acidity: determined by titrating a portion of the sample with a standard solution of NaOH. Free acidity measures only HCl, Topfer’s reagent is used as indicator. Total acidity includes HCl and other organic acids , Phenolphthalein is used as indicator Normal values - Free Acid : 0-30 mEq / L > 50 mEq / L indicates Hyperacidity - Total Acid : 10-40 mEq / L 7) Organic Acids: like lactic acid & butyric acid in large amounts indicate achlorhydria/hypochlorhydria. Fractional Test Meal Analysis Diff. meals used are -Ewald test meal (2 pieces toast+250 ml tea) -Oatmeal porridge -Riegel meal..not used normally Procedure: After removing residual contents, meal is given. With intervals of 15 minutes contents of stomach are removed ,strained & analysed. Normally free acid rises steadily from 15 min – ½ hr/45 min, and decreases. Abnormal responses are: 1) Hyperchlorhydria / Hyperacidity: when free acid is > 50mEq / L Seen in - Duodenal ulcer, Gastric ulcer, Gastric cell hyperplasia, After Gastroenterostomy, Contd….. Gastric Neurosis, Hyperirritability, Pylorospasm , Pyloric Stenosis , Chr. Cholecystitis, Zollinger Ellison Syndrome. 2) Hypochlorhydria / Hypoacidity: Seen in Ca Stomach , Atonic Dyspepsia 3) Achlorhydria: No HCl is seen but pepsin is present. Seen in Ca Stomach, Chr.Gastritis, Partial Gastrectomy, Pernicious Anaemia, Hyper thyroidism, Myxoedema. Fractional Test Meal ACHYLIA GASTRICA : is a condition where both enzymes and acids are absent Seen in – Advanced Ca Stomach -- Advanced cases of Gastritis -- Pernicious Anaemia -- Subacute combined degeneration of spinal cord. Analysis after Stimulation : 1)Alcohol Stimulation : -stimulant used is 7% ethyl alcohol. - the residual contents removed after overnight fasting, 100ml alcohol is given, samples are taken every 15 min & analysed for free, total acidity,peptic activity,blood, bile,mucus. Advantages : - more easy to administer - consumed better than porridge - gastric response is rapid - emptying of stomach is more rapid than porridge. Disadvantages: - stimulus with alcohol is not so strictly physiological as with oatmeal. - stimulus is more vigorous compared to oatmeal - rather high levels of free acidity seen. 2) Caffeine Stimulation : - Caffeine Sodium Benzoate,500mg dissolved in 200ml of water is given. - Advantages are similar to that of alcohol stimulation. 3) Histamine Stimulation Test: - it is a powerful stimulant for secretion of HCl, acts on oxyntic cells(specific H2receptors ) Indications : To differentiate “ True “ Achlorhydria from “ False “ Achlorhydria Types of Histamine test - Standard Histamine test - Augmented histamine test (Kays test). Standard Histamine test: SC injection of Histamine 0.01mg/kg bwt , is given. # Results - Absence of HCl…true achlorhydria, seen in pernicious anemia. - Increase in HCl…Duodenal Ulcer Augmented Histamine test (Kays) : larger dose, 0.04mg/kg b wt of histamine acid phosphate, SC. Indications: -to show inability to secrete acid as in pernicious anemia & subacute combined degeneration of cord. - to assess max possible acid secretion in diagnosis & Surg.Rx of Duodenal ulcer. Disadv : larger dose causes severe allergic reactions,hence another antihistaminic given to prevent. Procedure: After overnight fast, residual contents are analysed and contents are collected every 20 min for an hr. Halfway through this period 4ml of mepyramine maleate (anthisan), given IM, to block H1 receptors. At the end of hr histamine acid phosphate,0.04mg / kg bwt, SC given.and contents removed every 15 min for 1 hr. Recently, histamine analogue,called “Histalog”(3 beta-amino ethyl pyrazole) is used instead of histamine recommended dose –10-50mg No side effects seen hence no need to use an antihistamine to block H1 receptors. Insulin Stimulation test (Hollander’s test): Hypoglycemia produced by insulin is a potent stimulus of gastric acid secretion. Indications: to see the effectiveness of vagotomy in pts with duodenal ulcer. 15units of soluble insulin given IV Disadv: Hypoglycemia 4) Results: in pts with DU , before operation there is marked & prolonged output of acid in response to insulin. After successful vagotomy, there is no response and acid level is very low. 5) Pentagastrin test: Pentagastrin, synthetic peptide, having biologically active sequence of gastrin.It is “Butyl oxy carbonyl- beta alanine Trp-Met-Asp-Phe CONH2” Dose— 6 microgram/kg bwt. SC It is a potent stimulator, causing max stimulation after assessing basal secretion rate, hence it is a measure of Total Parietal Mass. Procedure: after removing the residual contents , the gastric juice secreted for next 1 hr is collected as a single sample, which is called BASAL SECRETION. Then pentagastrin is given & 4 samples are collected with 15 min intervals. Basal Acid Output (BAO) is output in mmol / hr, in basal secretion. Maximal Acid Output(MAO) is output in mmol/hr, given by sum of the 15 min acid output after stimulation. Peak Acid output (PAO) is output of 2 Consecutive 15 min samples having highest acid content and the value is multiplied by 2. Result: N basal secretion rate is 1-2.5mEq/hr, after pentagastrin stimulus..it is 20-40mEq/hr. - in DU…. 15-83mEq/hr - in ZE syndrome..basal secretion is > 10 mEq / hr Tube Less Gastric Analysis : it avoids discomfort of naso gastric tube Used only as a screening test. Fasting secretion is stimulated by histalogue , after 1 hr dye bound resin “Diagnex Blue” with “ Azure A” is given orally. In the presence of HCl resin releases dye,which is absorbed & later excreted in urine The quantity of dye in urine provides indication of presence /absence of HCl. It is not reliable in pts with renal diseases, urinary retention,malabsorption,pyloric obstruction etc. OTHER TESTS: Serum Gastrin : is estimated by Radio Immuno Assay. level is < 10 pico moles/L, N in Zollinger Ellison Syndrome it is > 100 pmol/L. Serum Pepsinogen : level is 30-160units/ml - in pernicious anaemia…very low/absent N - in DU…> 200 units/ml CONCLUSION Gastric Function tests are of limited but specific value in diagnosing and assessing some disorders of Upper GIT.