Lecture about Gastric Juice By Dr. Muhammad Shahid Saeed
advertisement

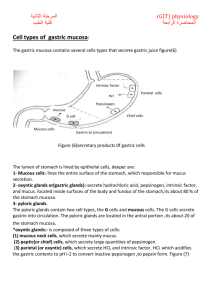
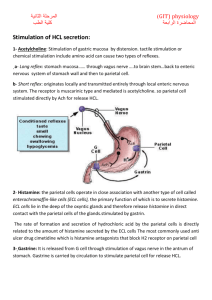
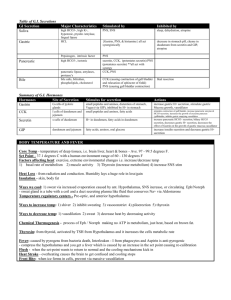
Exocrine Secretion of Stomach responsible for digjustive process. Composition 2-2.5 liters per day is produced pH 1-2 water 99.5 % Solid 0.5 % Na+, K+, Mg++, Cl, HCO3, HPO4, SO4 • Increase rate of secretion decreases Na+ and H is high • Decrease rate of secretion Na+ is high and H is low o Pepsin produced by of the chief cells of gastric glands in the form of pepsinogen. o Pepsinogen is converted to pepsin in the presence of HCL at pH of 2. o G. lipase split fat little role in digestion of fat. o G. Geletinase liquefy gelatin o G. Amylase CHO digestion o Lysozyme bactericidal o Carbonic anhydrase SOLUBLE MUCIN: Thin layer produced by pyloric and cardiac glands INSOLUBLE MUCIN: Produced by foveolar cells and covers the entire gastric mucosa INTRINSIC FACTOR: Produced by Parital cells responsible for B12 absorption. Parietal Cell is fine network of intercellular canaliculi it increases hydrogen ions will increase in HCL secretion which may go up to 155 meq/L which is 3 million time more than plasma. Secretion is in two steps i. Secretion of Hydrogen Ions ii. Secretion of Chloride Ion In P Cells following reaction occur. CO2+ H2O ↔H2CO3 ↔H+ HCO3 Hydrogen Ion is secreted in the lumen of canalculi in K ion exchange by Na+ - K+ ATPase pump. HCO3 enters into the blood in exchange of cl HCO3 is responsible for Post perendial alkeline tide characterized by alkaline urine and increase PCO2 and decrease breathing. HCO3 enters into pancreatic secretion in small intestine to neutralize its acidity Cl channel are present on apical membrane of P cell Cl channel are activated by CAMP H+ Cl → HCL All this process is done by active transportation and energy is provided by the mitochondria which are scattered in P.cells Vegal Stimulation, Gastrin Histamine increase the HCL production. Low pH in Stomach, smatostatin, postaglandins (PGE, PGI), Epithelial growth factor transforming growth factor will decrease the HCL production. Functions: i. Breakdown of Protein ii. Provide Environment Pepsin action iii. Inhibits bacterial growth Chief Cell Produce it mainly and small amount is produced by pyloric cell Chief cell produce pepsinogen I and pyloric cell produce pepsinogen II Stored as zymogen granules at epical region of chief cell Pepsinogen is converted to pepsin in the presence of HCL and pepsin further potentiate the conversion of pepsinogen in pepsin Splits Proteins in proteases, peptones and polypeptides Optimal pH for action is to so HCL is most important factors for the action of Pepsin Mucus Secretion: Insoluble mucus is produced mucus secreted cell of gastric mucosa it is a gel like coat over mucosa which protect the stomach from the attack of HCL. Soluble Mucus is produced by mucus cell of pyloric and cardiac glands Intrinsic Factor It is a glycoprotein produced by the P cells of the mucosa Specially in the fundus region by cyclic AMP Intrinsic factor combines with vitamin B 12 and complex is formed which absorb the Vitamin B 12 in small intestine Neural Vagal stimulation will increase HCL production by accting on P Cell which causes through release of Ach. Ach potentiate the effect of histamine on H2 receptors. GRP ( Gastric Release Peptide) is produced which causes release of HCL Somatostatin is inhibited by vagal stimulation Ach acts on enterochromoffin like cell which acts on histamine which increases H ions by acting on H2 receptors Gastrin • G cell produce it and it goes into the blood and then reaches to stomach and causes increase production of pepsin and HCL by acting on P cell and chief cell. • Gastrin is produced in progastrin from which is inactive and activated by HCL and digestive enzyme. • Gastrin of three types. i. G14 ii. G17 iii. G34 G17 is the main type with half life of two to three minutes and it is inactivated by kidney and small intestine Mechanism of action : Gastrin acts on CCk- β/ gastrin receptors on P cells and open calcium channel this increase in H ion by opening of Ca++ channels under the effect of Na+, K+ ATPase pimp. Gastrin increase histamine which causes increase in HCL Vagal Stimulation distension pyloric entrum, Product of digestion, Ca+ and epinephrine increases the production of gastrin. While low pH of gastric Juice, somatostatin, secretin, gastrin inhibitory peptide, VIP, glucagon and calcitonin decrease the production of gastrin. Cephalic Phase By smell sight and thought gastric juice is produce. about 500 ml/h of gastric juice is produce by this phase. 1. 2. Gastric phase 200 ml/h of gastric juice is produce by the presence of food in the stomach due to distention of stomach , products of digestion and low pH will produce gastrin release and ultimately gastric juice production is increase. Distention of small intestine, presence of acidic food in the intestine inhibits gastric secretion by intarogastric reflex release of secretin GIP, VIP CCK inhibits the gastrin release.