Pharmacology B
advertisement

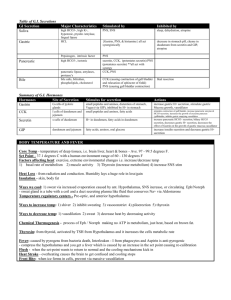
Pharmacology B Lin, I-Yao A 43y/o male CEO of a multinational company experienced severe burning pain one and a half hour after a sumptuous lunch. This is accompanied by mild nausea and vomiting. He was given a glass of milk and some cookies which apparently provided some relief. Diagnosis: Peptic ulcer of duodenum Ulcer of the distal stomach and proximal duodenum caused by gastric secretions (hydrochloric acid and pepsin) and impaired mucosal defenses. It’s associate with Helicobacter pylori which increased hydrochloric acid secretion, and inadequate mucosal defense against gastric acid. Cause: 1. Using aspirin medicine 2. Drinking alcohol excessively 3. Smoking cigarettes and using tobacco 4. Others. Sign and symptoms: 1. Nausea and vomiting. 2. Weight loss 3. Fatigue 4. Heartburn, indigestion, belching. 5. Vomiting blood 6. Bloody or dark tarry stools Lab examination: Gesophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) . Take biopsy to test for H, pylori. Stool guaiac to test for blood in the stool. Schilling test to check for anemia. Treatment approaches include: Eradicating the H. pylori infection. Reducing secretion of gastric acid or neutralizing the acid after it is released. Providing agents that protect the gastric mucosa from damage. Treatment - medication <Antacids> NaHCO3, Mg(OH)2, Al(OH)3. <Acid secretion reducers> Proton-Pump inhibitors: Omprazole, Lansoprazole. H2 – Antagonists: Cimetidine, Ranitidine. <Mucosal strengtheners> Sucralfate, Bismuth chelate, Prostaglandins <H. pylori eradication> Omprazole + Clarithromycin + Amoxillin/ Metronidazole <Antacids> -weak base that react with gastric HCl to form salt and water -reduce gastric acidity -reduce pepsin activity Side effect: NaHCO3-systemic alkalosis Mg(OH)2-diarrhea, hyper magmesemia Al(OH)3-constipation, hypophosphatemia <Acid secretion reducers> 1. Proton-Pump inhibitors: Omprazole, Lansoprazole. -inhibits gastric parietal cell proton pump H+/K+ ATPase, dercease gastric acid secretion. 2. H2 – Antagonists: -blocker H2-receptor and reduce cAMP which inhibit gastric acid secretion. Side effect: Cimetidine-confusion, reversible gynecomastia. Ranitidine-headache. The H2-receptor antagonist can’t combined with PPI inhibitor which the H2-receptor antagonist even inhibit omeprazole. <Mucosal strengtheners> 1. Sucralfate -selective binding to necrotic ulcer tissre and act as barrier to acid, pepsin, bile. -requires acid pH to be activated, there fore should not be used with antacid, H2 antagonist or proton pump inhibitors. 2. Bismuth chelate -binds and ulcer tissue, coat it and protectit from acid and pepsin. 3. Prostaglandins -inhibits secretion of HCl and stimulates secretion of mucus and bicarbonate (cytoprotective effect). Non pharmacology: Avoid food and drink that seems to cause more severe symptoms such as spicy foods, coffee and possibly alcohol. stop smoking. Should be lose excess weight if overweight.