CHEMICAL EQUATIONS
advertisement

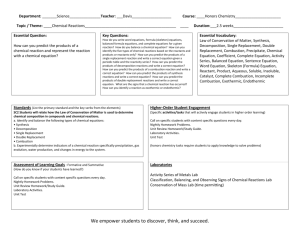
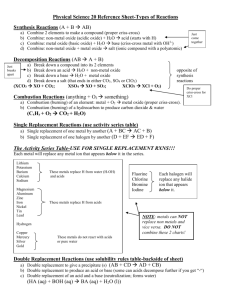
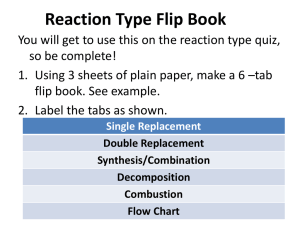
CHEMICAL REACTIONS The process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more different substances Word Equations To write a word equation, Write the names of the reactants to the left of the arrow separated by plus signs; 2. Write the names of the products to the right of the arrow, also separated by plus signs. 1. Reactant + Reactant Product + Product EXAMPLE Methane + Oxygen Carbon dioxide + Water EXAMPLE 2 Iron + Oxygen Iron(III) Oxide EXAMPLE 3 Hydrogen Peroxide Water and Oxygen Skeleton Equations Write the formulas of the reactants to the left of the yields sign (arrow) and the formulas of the products to the right. A skeleton equation is a chemical equation that does not indicate the relative amounts of the reactants and products. Here is the equation for rusting: Fe + O2 Fe2O3 Formula Writing Practice WS Catalyst A catalyst is a substance that speeds up the reaction but is not used up in the reaction Without catalyst With Catalyst Important Symbols Balancing Chemical Equations To write a balanced chemical equation, Write the skeleton equation 2. Use coefficients to balance the equation so that it obeys the law of conservation of mass. Remember you want the same number of atoms of each element on each side of the equation. 1. Example Example 2 Example 3 -- Try on your own!!! Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction in which sodium hydroxide and calcium bromide react to produce solid calcium hydroxide and sodium bromide. (The reaction occurs in water.) NaOH(aq)+CaBr2(aq) Ca(OH)2(s)+NaBr(aq) 2NaOH(aq)+CaBr2(aq) Ca(OH)2(s)+2NaBr(aq) Summary Write a skeleton equation Count atoms Add/adjust coefficients Reduce coefficients to lowest possible ratio Check your work Warm Up!! _____NaClO3 →____ NaCl + __O2 Chemical Equations from Names Magnesium and Hydrogen Chloride produce Hydrogen and Magnesium Chloride Calcium Hydroxide and Lithium Chloride produce Lithium Hydroxide and Calcium Chloride Decompose Copper (II) oxide into Copper and Oxygen Aluminum and Iron (III) oxide produce iron and aluminum oxide combustion of Butane (C4H10) in air to produce carbon dioxide and water Warm Up ___AgNO3 + __Ni __Ni(NO3)2 + __Ag The Five Types of Reactions Synthesis Combustion Decomposition Chemical Reactions Double Replacement Single Replacement Chemistry with Synthesis Reactions A + B AB 1. Synthesis Reactions (Combination) Two or more reactants produce one product Examples: NH3 + HCl NH4Cl H2 + O2 H2O Ag2S Al + Cl2 AlCl3 Ag + S Chemistry with Decomposition Reactions AB A + B 2. Decomposition One reactant produces two or more products Examples Ag2O Ag + O2 PCl5 PCl3 + Cl2 H2O2 H2O + O2 CuO Cu + O2 Chemistry with Single Replacement AB + C AC + B 3. Single Replacement One element replaces another element Must consult the activity series 3. Single Replacement One element and one compound producing a different element and compound Examples Fe + H3(PO4) H2 + Fe3(PO4)2 H2 + CuO Cu + H2O Zn + HCl H2 + ZnCl2 Cl2 + KBr Br2 + KCl Equations Activity Series Worksheet Chemistry with Double Replacement AB + CD AD + CB 4. Double Replacement A double-replacement reaction is a chemical change involving an exchange of positive ions between two compounds. Examples: Al(NO3)3 + NaOH Al(OH)3 + NaNO3 PbCl2 + Li2SO4 PbSO4 + LiCl ZnBr2 + AgNO3 Zn(NO3)2 + AgBr BaCl2 + KIO3 Ba(IO3)2 + KCl 4. Double replacement Three main products of a double replacement reaction Precipitate (solubility table) Water Gas 5. Combustion A combustion reaction Chemical change Element or a compound reacts with oxygen Producing energy in the form of heat and light 5. Combustion A hydrocarbon reacts with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water Examples: CH4 + O2 CO2 + H2O C6H12O6 + O2 CO2 + H2O