Review Sheet – Chemistry – Ch
advertisement

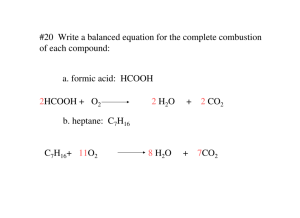
Review Sheet – Chemistry, Level 3 – Ch. 9: Chemical Reactions Name: ____________________ Date:___________ Period:___ This test covers materials in the textbook in Chapters 9 (pp. 279-297). You are always responsible for the topics on the previous tests. . Test Expectations The student should be able: Write balanced chemical equations starting from word equations, formula equations, or just reactants. Classify chemical reactions as one of the five common types of reactions. 1. Define each of the following terms clearly and completely. (a) product – (f) balanced chemical equation– (b) reactant – (g) word equation – (c) coefficients – (h) diatomic element – (d) chemical reaction – (i) conservation of mass – (e) combustion – (j) precipitation – a) b) c) d) Product – A substance that is produced during a chemical change. Reactant – A substance that is consumed during a chemical change. Coefficients – A numerical prefix indicating the number of each reactant or product in a chemical equation. Chemical Reaction – Change that takes place when two or more substances (reactants) interact to form new substances (products). e) Combustion – A chemical reaction between a fuel and an oxidizing agent that produces heat (and usually, light). f) Balanced Chemical Equation – A description of a chemical reaction that gives the chemical formulas of the reactants and the products of the reaction, with coefficients introduced so that the number of each type of atom and the total charge is unchanged by the reaction. g) Word Equation – An equation in which the reactants and products in a chemical reaction are represented by words. h) Diatomic Element – A molecule that contains only two atoms. i) Conservation of Mass – The principle stating that matter is not created or destroyed during a chemical reaction. j) Precipitation – Precipitation is the formation of a solid in a solution during a chemical reaction. 2. Balance each of the following chemical equations. Then write the name of the type of chemical reaction on the line provided. A. 2 O2 + N2 N2O4 _____synthesis_________________ B. 2 NaF 2 Na + F2 _____decomposition______________ C. 2 NaI + Pb(NO3)2 2 NaNO3 + PbI2 2 F2 D. CS2 + E. Li3PO4 3 Li F. C8H16 + 12 O2 G. 2 Al + CF4 + + P 2S + H. C6H12 + 9 O2 _____single replacement_________ 2 O2 8 CO2 + 8 H2O 3 FeO Al2O3 + ______double replacement_____ 3 Fe 6 CO2 + 6 H2O _____ decomposition _______ _____combustion_______________ ______ single replacement ________ ______ combustion _____________ 3. Write the balanced chemical equation for the chemical reaction between water and calcium. The reaction produces calcium hydroxide and hydrogen. Ca + 2 H2O Ca(OH)2 + H2 4. Bromine combines with nitrogen to produce gaseous nitrogen tribromide. Write the balanced chemical equation for this reaction. N2 + 3 Br2 2 NBr3 5. Write the balanced chemical equation for the direct combination (synthesis) reaction that occurs when ammonia vapor and hydrogen sulfide gas react to produce solid ammonium sulfide ((NH4)2S). 2 NH3 + H2S (NH4)2S 6. For the following reactions: I. Determine the type of reaction II. Complete the word equation III. Write correct formulas and balance the equations. A. Mg + Cu(NO3)2 Mg(NO3)2 + Cu (single replacement) B. BaBr2 + Na2CO3 BaCO3 + 2 NaBr (double replacement) C. C6H8 + 8 O2 6 CO2 + 4 H2O (combustion) D. calcium chloride + gold (I) oxide calcium oxide + gold (I) chloride CaCl2 + Au2O CaO + 2 AuCl (double replacement) E. potassium carbonate carbon dioxide + potassium oxide K2CO3 CO2 + K2O (decomposition) F. chlorine + potassium bromide bromine + potassium chloride Cl2 + 2 KBr Br2 + 2 KCl (single replacement) G. iron (III) oxide + potassium carbonate iron(III) carbonate + potassium oxide Fe2O3 + 3 K2CO3 Fe2(CO3)3 + 3 K2O (double replacement) H. potassium + nitrogen potassium nitride 6 K + N2 2 K3N (synthesis) I. iron (III) hydroxide water + iron (III) oxide 2 Fe(OH)3 3 H2O + Fe2O3 (decomposition) J. gold + potassium chloride No Rxn. (single replacement) K. aluminum + silver nitrate silver + aluminum nitrate Al + 3 AgNO3 3 Ag + Al(NO3)3 (single replacement) L. calcium hydroxide + nitric acid water + calcium nitrate Ca(OH)2 + 2 HNO3 2 H2O + Ca(NO3)2 (double replacement)