Chem 20 Reference Sheet-Types of Reactions
advertisement

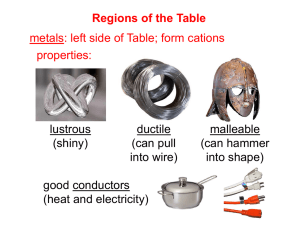
Physical Science 20 Reference Sheet-Types of Reactions Synthesis Reactions (A + B AB) a) b) c) d) Combine 2 elements to make a compound (proper criss-cross) Combine: non-metal oxide (acidic oxide) + H2O acid (starts with H) Combine: metal oxide (basic oxide) + H2O base (criss-cross metal with OH1-) Combine: non-metal oxide + metal oxide salt (ionic compound with a polyatomic) Just come together Decomposition Reactions (AB A + B) a) Break down a compound into its 2 elements b) Break down an acid H2O + non-metal oxide c) Break down a base H2O + metal oxide d) Break down a salt (that ends in either CO3, SO4 or ClO3) (XCO3 XO + CO2; XSO4 XO + SO3; XClO3 XCl + O2) Just breaks apart opposite of synthesis reactions Combustion Reactions (anything + O2 something) Do proper criss-cross for XCl a) Combustion (burning) of an element: metal + O2 metal oxide (proper criss-cross). b) Combustion (burning) of a hydrocarbon to produce carbon dioxide & water (CxHy + O2 CO2 + H2O) Single Replacement Reactions (use activity series table) a) Single replacement of one metal by another (A + BC AC + B) b) Single replacement of one halogen by another (D + EF ED + F) The Activity Series Table-USE FOR SINGLE REPLACEMENT RXNS!!! Each metal will replace any metal ion that appears below it in the series. Lithium Potassium Barium Calcium Sodium Magnesium Aluminum Zinc Iron Nickel Tin Lead These metals replace H from water (H-OH) and acids Each halogen will replace any halide ion that appears below it. These metals replace H from acids NOTE: metals can NOT replace non metals and vice versa. DO NOT combine these 2 charts! Hydrogen Copper Mercury Silver Gold Fluorine Chlorine Bromine Iodine These metals do not react with acids or pure water Double Replacement Reactions (use solubility rules table-backside of sheet) a) Double replacement to give a precipitate (s) (AB + CD AD + CB) b) Double replacement to produce an acid or base (some can acids decompose further if you get “-“) c) Double replacement of an acid and a base (neutralization; forms water) (HA (aq) + BOH (aq) BA (aq) + H2O (l))