Bonds
advertisement

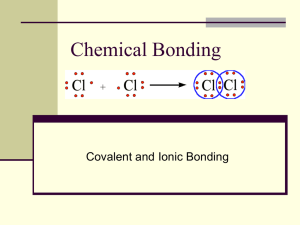
Bonding Lab Wrapping things up Checking results: station 5 check below- your solutions may have been contaminated! Compound Bond Type Conductivity C6H8O6 (ascorbic acid) Covalent 8 Glycerin Covalent 1-2 C12H22O11 (sucrose) Covalent 0-1 H2O (water) Covalent 0 C3H7OH (rubbing alcohol) Covalent 0-1 NaCl (salt) Ionic 9 Cu(NO3)2 (copper nitrate) Ionic 10 K2C2O4 (potassium oxalate) Ionic 8 Mg(NO3)2 (magnesium nitrate) 9 Ionic Station 7 Conclusion: Compounds w/ionic bonding contain metals & non-metals (ex: NaCl, Na=M, Cl=NM). Compounds w/metallic bonding contain only metals (ex: Zn=M). Compounds w/covalent or network covalent bonding are made of NMs (ex: Sugar=C6H12O6, C&H&O=NMs). 2.1.1 Bond Types Bonds • Bonds = the attraction that holds atoms together • Two or more atoms may form bonds in order to make a compound – Example: the elements hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) can form a bond to make the compound water (H2O) What am I doing here? 4 different types of bonds ionic Network covalent metallic Covalent (molecular) Ionic “ion” = a charged particle How these bonds form: • Metal atoms give up their valence electrons to the non-metals • Metals form positive ions (lose e-) • Non-metals form negative ions (gain e-) • Attraction due to opposite charges holds the atoms together Properties of Ionic Compounds • • • • • Made of metal & non-metal atoms Dissolve in water Conduct electricity when dissolved Do not conduct when solid Brittle Covalent (molecular) How these bonds form: • Valence electrons are shared between groups of atoms • These groups of atoms are called “molecules” Properties of Molecular Covalent Compounds • • • • Made of nonmetals Some dissolve in water, some don’t Do not conduct electricity Are liquids or gases or soft solids Network covalent How these bonds form: • Valence electrons connect atoms together in all directions- a giant network of connected atoms Properties of Covalent Network Compounds • • • • Made of nonmetal atoms Do not dissolve in water Do not conduct electricity Very hard solids Metallic How these bonds form: • Electrons move freely, not associated with any particular atom • “Sea of electrons” Properties of Metallic Compounds • • • • Made of metal atoms Do not dissolve in water Conduct electricity Are bendable solids Ionic Bonds • • • • Hold two ions together Anion = negative ion Cation = positive ion Opposite charges attract Na + cation Cl anion Why do ionic solutions conduct? • Crystal lattice dissolves in water to form individual ions • Movement of ions allows current to flow Why does tap water conduct electricity and not pure, de-ionized water? • Your tap water may have… – Chlorine – Dissolved minerals such as calcium and magnesium – Sodium – Fluoride H2O Na+ H2O Cl - Pure Water FMg2+ Tap Water Bonding Animations http://www.mhhe.com/physsci/chemistry/anim ations/chang_7e_esp/bom1s2_11.swf http://ithacasciencezone.com/chemzone/lesson s/03bonding/mleebonding/default.htm Check your work! (2.1.1) “step two” Ionic NaCl CuCl2 NaOH MgSO4 Covalent network C Si SiO2 Metallic Na Cu Hg Pt Molecular covalent H2O CH4 CH3CH2OH 1. Which model would you predict for the following substances? Explain your reasoning. C6H12O6 (sugar) Molecular Covalent, it is made of non-metals & dissolves in water. KI (potassium iodide) Ionic, it is made of a metal & a non-metal. MgO (magnesium oxide) Ionic, it is made of a metal & a non-metal. Au (gold) Metallic, it is made of only metal atoms. CO2 (carbon dioxide gas) Molecular Covalent, it is made of non-metals & is a gas. 2. In the ionic solid, Model 1, the non-metal atoms have a negative charge & the metal atoms have a positive charge. What do you think causes these charges? Gaining & losing electrons! Gaining electrons = negative charge Losing electrons = positive charge 3. In the metallic solid, Model 3, the “sea” of electrons has a negative charge. What charge would the spherical atoms have? Explain. Positive charge because they are attracting the “sea” of electrons. 4. In covalent substances electrons are shared between atoms. What differences do you see in Models 2 & 4? In Model 2, electrons are being shared between 4 atoms. In Model 4, electrons are only being shared between 2 atoms. 5. Use the models to explain the following evidence: a) Molecular covalent substances are often gases The atoms are not as connected so they can “fly away” as a gas. b) Ionic substances are brittle Because they don’t share electrons, they are not as connected & can break easily. 1. Compare & contrast each of the following pairs of bonding types with respect to i) the role of electrons in bonding and ii) physical properties of the bonded materials such as hardness: a) Ionic bonding & covalent bonding In ionic bonding, electrons are transferred from a metal to a non-metal. In covalent bonding, electrons are shared between 2 non-metals. Substances with ionic bonding are solids and substances with covalent bonding are liquids or gases. 1. Compare & contrast each of the following pairs of bonding types with respect to i) the role of electrons in bonding and ii) physical properties of the bonded materials such as hardness: a) Network covalent bonding & metallic bonding In network covalent bonding, electrons are shared between non-metals all around. In metallic bonding, atoms are surrounded by a sea of electrons. Substances with both of these types of bonding are hard solids. Only metals conduct electricity though. 2. You observed NO2(g) when you dissolved Cu(s) in nitric acid in the copper cycle lab. How would you classify the bonding in NO2 (g)? Explain. Molecular covalent because both N & O are nonmetals & it’s a gas. 3. Think about the physical properties of the following substances, and decide which type of bonding you would probably find in each substance. Explain your reasoning. a) hair gel Covalent—it’s a liquid. b) silver bracelet Metallic—it’s made of only metals. c) motor oil Covalent—it’s a liquid. d) sodium bicarbonate Ionic—it’s a solid (& has metals & nonmetals). 4. Look at the chemical makeup of the following substances & decide which type of bonding you would probably find in each substance. a) Zn (s) zinc Metallic b) C3H8 (l) propane Covalent c) CaCO3 (s) calcium carbonate Ionic