The Halogens - Chemistry stuff
advertisement
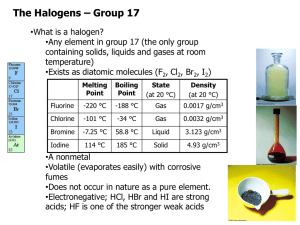
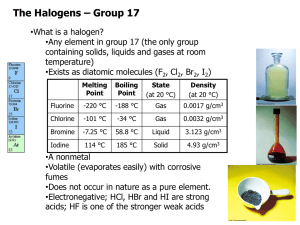
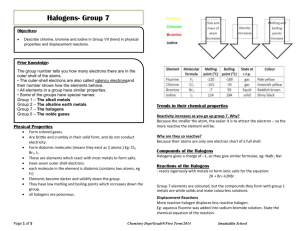
The Halogens Group VII Group VII • Known as halogens – Derived from Greek, Salt maker – React with metals to form salts • Astatine doesn’t really exist for a long enough time to explore its chemistry – we predict its reactions by observing trends VII F Cl Br I At At RTP • Fluorine – Pale yellow gas • Chlorine – Pale green gas – Bleaches damp litmus • Bromine – Brown Liquid (evaporates easily to a brown gas) – Does nasty things to skin! • Iodine – Dark grey / black crystals – Sublimes to a violet vapour on gentle heating VII F Cl Br I At Properties • Electron configuration – 5 p electrons. • Atomic Radius – Increases down the group • Ionic radius – Increases down the group VII F Cl • First Ionisation energy – Decreases down group Br • First Electron Affinity – Decreases down group I • Electronegativity. – Decreases from F - I At Compounds • Solubility – – – – – – – – Chlorine and Bromine are fairly soluble in water They react reversibly Cl2 +H2O HCl + HOCl Aqueous solutions are called Chlorine or Bromine water Chlorine water is (just about) pale green Bromine water is orangey brown – red Iodine is only slightly soluble in water Halogens are much more soluble in hexane. VII F Cl Br I At Bonding in halogens • Ionic Bonding – All the Halogens form X- ions – With group I & II • Ionic bonding – With group III • Aluminium fluoride – Ionic • Aluminium chloride varies depending on whether it is anhydrous or not. – With d-block metals • Covelant when anhydrous • Ionic with water. Bonding in halogens • Covalent Bonding – Polar covalent bonds with almost all non metals – Fluorine is always in the -1 oxidation state – Chlorine is in the -1 oxidation state unless bonded with fluorine or oxygen • Halogens other than fluorine have empty d-orbitals so it is possible to promote electrons from the p-orbital into the energetically similar d-orbital • This allows more than one covalent bond to be formed. – This only happens when bonded to a small very electronegative atom such as oxygen. Reactions of the Halogens • Reactions with Metals Reactions of the Halogens • Reactions with phosphorus Reactions of the Halogens • Reactions with solutions of other halides Reactions of the Halogens • Reactions with water Reactions of the Halogens • Reactions with alkali Reactions of the Halogens • Reactions with reducing agents Reactions of the Halogens • Reactions with sodium thiosulphate Hydrogen Halides