6 Combined spectral analysis
advertisement

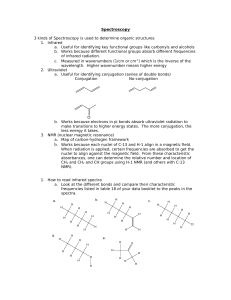
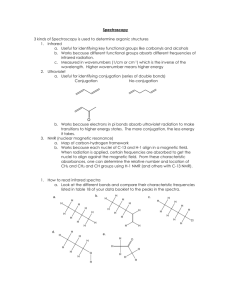
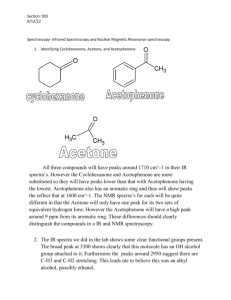
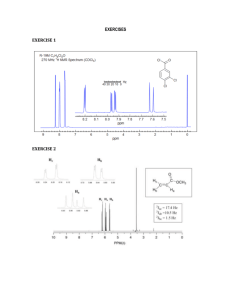
In carbon-13 NMR, what do the number of peaks represent? The number of chemically different carbon atoms present What are the two main factors to look for in the analysis of carbon-13 NMR spectra? The number of peaks present & the chemical shift of the peak Which two features are present in proton NMR spectra, but not in carbon-13 NMR spectra? The relative peak area (integration value) and the splitting of the peak What does the splitting of the proton NMR peak tell you? The number of protons on the carbon (or other) atom adjacent to a particular type of proton Which solvent is used in proton NMR? TMS (Tetramethylsilane) What does the area under the peak represent in proton NMR? The number of protons responsible for the peak What splitting pattern will be shown by a group adjacent to a methyl (CH3) group? A quartet Combined spectral analysis Aim • Use mass spectrometry, Infra-red and NMR spectra to deduce the structure of a compound. Combined spectral analysis A compound containing 58.8% carbon, 9.8% hydrogen and 31.4% oxygen is subjected to mass spectrometry and found to give intense peaks at m/z = 43 and m/z = 71, in addition to a molecular ion peak at m/z = 102. Infra-red analysis of the molecule showed a sharp peak at m/z = 1710 cm-1. A proton nmr spectrum of the molecule yielded the following peaks: Chemical shift Splitting Integration factor 0.8 Triplet 3 1.1 Sextet 2 2.3 Triplet 2 3.7 Singlet 3 Deduce the structure of the molecule and account for the formation of all the peaks the spectra. Answer • Molecular formula = C5H10O2 • mass spectrum: peak at 43 from: CH3CH2CH2COOCH3+. CH3CH2CH2+ + .COOCH3 peak at 71 from: CH3CH2CH2COOCH3+. CH3CH2CH2CO+ + .OCH3 • infra-red spectrum: peak at 1710 cm-1 indicates a carbonyl • • • • • proton nmr spectrum: peak at 0.8 is CH3- adjacent to -CH2peak at 1.1 is -CH2- adjacent to CH3- and -CH2peak at 2.3 is -CH2CO- adjacent to -CH2peak at 3.7 is CH3O- • so molecule is methyl butanoate, CH3CH2CH2COOCH3 Past exam questions