Organic Chem~ Macromolecules
advertisement

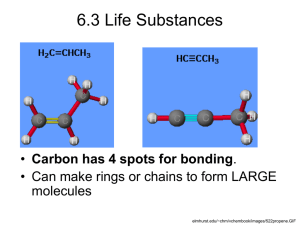
Biochemistry Macromolecules (large molecules): Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids These are Polymers (many parts) constructed of Monomers (single part) polymer polymer monomer How to Connect Monomers- Hydrolysis Breaking apart polymer Adding water molecule Connecting MonomersDehydration reaction Hydrolysis Breaking apart polymer Adding water molecule Connecting MonomersDehydration reaction joining monomers loss of water molecule Hydrolysis Breaking apart polymer Adding water molecule Connecting MonomersDehydration reaction joining monomers loss of water molecule Hydrolysis Breaking apart polymer Adding water molecule Connecting MonomersDehydration reaction this takes energy Hydrolysis Breaking apart polymer Adding water molecule Connecting MonomersDehydration reaction this means energy must be added in order for the reaction to occur Putting together HydrolysisBreaking apart polymers Breaking apart polymer Hydrolysis(break w/ water) Adding water molecule Adding water molecule HydrolysisBreaking apart polymers Breaking apart polymer Hydrolysis(break w/ water) Adding water molecule Adding water molecule HydrolysisBreaking apart polymers Breaking apart polymer Hydrolysis(break w/ water) Adding water molecule Adding water molecule HydrolysisBreaking apart polymers Breaking apart polymer Hydrolysis(break w/ water) Adding water molecule Adding water molecule Creating MonomersHydrolysis reaction this gives off energy when this happens breaking up explain to your partner what is Hydrolysishappening Breaking apart polymer Adding water molecule Macromolecules (large molecules): Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Carbohydratesfunctions: Fuel - stores energy Building material - > in plants = cellulose (cell wall) in animals = chitin (insect/ lobster covering) Carbohydrates- types: 1)Monosaccharides Single Sugar Monosaccharides Structure: Single Sugar Function: Fuel for cell work ex. glucose - blood sugar fructose - fruit sugar lactose - ?? Monosaccharides structure: multiple of CH2O ex. glucose C6H12O6 Disaccharides Two sugar monomers joined by dehydration synthesis Disaccharides Two sugar monomers joined by dehydration synthesis JOIN / SPIT OH- Disaccharides Two sugar monomers joined by dehydration synthesis ex. sucrose - table sugar Polysaccharides Many monomers Polysaccharides Many monomers Functions: •1) Energy storage= •starch (plant) •glycogen (animal) Polysaccharides Many monomers Functions: •1) Energy storage= 2) Structural support = cellulose Polysaccharides 2) Structural support = cellulose Macromolecules (large molecules): Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids LipidsTypes: 1) Fat~ triglyceride 2) Phospholipid~ cell membranes 3) Steriod 4) Wax LipidsStructure = have a higher ratio of C & H than Oxygen Therefore, are they polar or nonpolar? They HATE water Lipids- (hydrophobic) 1) Fats (triglyceride) functions: -energy storage -cushion internal organs -insulation Types of Lipids: Fats- structure 1 Glycerol Fatty acid chain = hydrophobic •Energy storage •Cushion Types of Lipids: Fats- structure +3 fatty acid Glycerol chains Fatty acid chain = hydrophobic •Energy storage •Cushion http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Eu5j_Us8uI&safe=active 2)Phospholipids- structure 1 hydrophilic head 2 hydrophobic tails 2)Phospholipids- structure 1 hydrophilic head 2 hydrophobic tails 3) Steroids4 Fused (connected) “rings” cholesterol, testosterone, estrogen 4) WaxLong CH2 chain Macromolecules (large molecules): Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids ProteinsMonomer = amino acid Polymer of amino acids = polypeptides- Proteinsfunction depends on shape: 1) support 2) structure 3) enzymes Amino Acids = monomer 20 types Amino Acids H amino group C NH2 Carboxyl COOH R (VARIABLE) 20 types Amino Acids H amino group 20 varying molecules C R carboxyl 20 types Proteins- precise sequence of amino acids. amino - - carboxyl group group Sequence of amino acids determines HOW the protein works Shape determine s how the protein works Macromolecules (large molecules): Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Nucleic AcidsDNA RNA Programs ALL organism function Nucleic AcidsComposed of: nitrogen base, sugar, phosphate group = NUCLEOTIDE DNA RNA