biomolecule ppt
advertisement

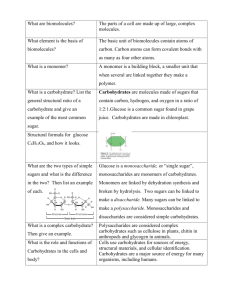
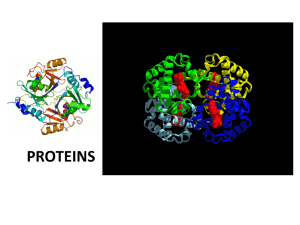
BIOMOLECULES LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION… We will be repeating these ALL year! Yesterday: Atoms Molecules Macromolecules… Today we will dig into the four macromolecules that are essential for life to exist. What are the 4 biomolecules? • • • • Carbohydrates Lipids Nucleic Acids Proteins TODAY TOMORROW WE TYPICALLY GET BIOMOLECULES FROM FOOD… THIS IS WHY WE MUST EAT IN THE FIRST PLACE! THE BIOMOLECULES SERVE TO KEEP ORGANISMS ALIVE. #1: CARBOHYDRATES ARE SUGARS! We get 4 kilocalories per gram of carb that we eat! What are Carbohydrates? Most common organic molecule Function: Primary energy source our body needs IMPORTANT! Elements present: C, H, O (1:2:1 ratio) Monomer (building block): Monosaccharides (Glucose is most common) Polymer: Polysaccharides (starch, Glycogen, Cellulose, Chitin) Examples: Chocolate, Bread, Pasta, Fruits, Vegetables (ALL FROM PLANTS!!!) Sugars that make up Carbs Single sugar: monosaccharide 2 monosaccharides: disaccharide Ex: glucose , fructose (in fruits) Ex: maltose, sucrose 3+ monosaccharides: polysaccharide Ex: Starch, Glycogen, Cellulose, and Chitin I am a polysaccharide! Types of polysaccharides Starch: Used for energy storage in plants Potatoes, pasta and rice are starches They provide a quick form of energy for the body Glycogen: • I am formed in the Liver! Used for energy storage in animals More Polysaccharides Cellulose: • Provides structural support in plants (found in the cell wall) GIVES US FIBER!!! Chitin: Found in exoskeletens of arthropods (insects, spiders) • Found in cell wall of some fungi • Structure of Carbohydrates • • Remember: Elements are C, H, and O Primarily in a Ring shape (but not always) Take a minute to find the word that does NOT belong. Raise your hand, do not shout out! #2: LIPIDS ARE FATS We get 9 kcals per gram Of fat that we consume. Lipids Function: Store energy, Insulates your body, and make up the cell membrane! Elements: C-H-O Monomer (Building blocks): glycerol & 3 fatty acids Polymer: Phospholipids, triglycerides Example: Steroids, cholesterol, fats, Oils, Nuts, Waxes, and make up part of the cell membrane! Lipids Lipids are Hydrophobic (water fearing) and do not dissolve in water! • Lipids can be: Important! • Saturated: The bonds between all the carbons are single bonds. •Solid at room temperature •Mainly animal fats (bacon grease, lard) • Unsaturated: There is at least one double or triple bond between carbons present. •Liquid at room temperature •Mainly plant based fats (olive oil, peanut oil) as well as oily fish (Tuna, Sardines) Lipid Structure Remember: Elements present are C, H, O Long strands of Carbon and Hydrogen CALLED HYDROCARBONS! Saturated Fats Unsaturated Fats Take a minute to find the word that does NOT belong. Raise your hand, do not shout out! BIOMOLECULES PART 2 PROTEINS AND NUCLEIC ACIDS! #3: PROTEINS BUILD US We get 4 kcals per gram Of protein that we consume. Proteins • Function of proteins • • • Transport molecules in and out of the cell Control the speed of chemical reactions Used for growth and repair Proteins make up the structure of living things… Hair, nails, skin, bones, muscle, etc are all built by protein! Proteins NITROGEN IS PRESENT, NOW! Elements: C-H-O-N Monomer (Building Block): amino acids (20 different ones!) Polymer: proteins (tons) Examples of proteins: hemoglobin in red blood cells, albumin in eggs, enzymes that control reactions in the body, and antibodies Found in: fish, eggs, meat Protein Structure Remember: Elements are C, H, O, and N “R” groups represent one of the 20 Amino Acids! (so, each amino acid has something different in that spot) Why are amino acids important? • When groups of amino acids are joined together a protein is formed • There are 20 kinds of amino acids • They consist of a carboxyl group (COOH) and an amino group NH2 • Peptide bonds form between amino acids (polypeptide = many peptide bonds = protein!) Take a minute to find the word that does NOT belong. Raise your hand, do not shout out! #4: NUCLEIC ACIDS These biomolecules are not necessarily from food Nucleic acids Function: • Provide our genetic information • Holds the instructions to make proteins. Elements: C-H-O-N-P Monomer : nucleotides • A nucleotide is made up of: • Sugar • Phosphate • Nitrogen Base: A, T, G, C, or U Polymer: DNA, RNA and ATP Genetic code! Recipe for proteins Energy carrier Structure of Nucleic Acid Take a minute to find the word that does NOT belong. Raise your hand, do not shout out!