- U
advertisement

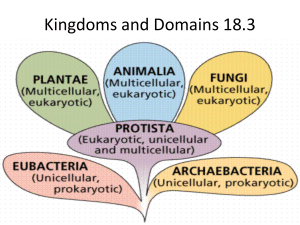
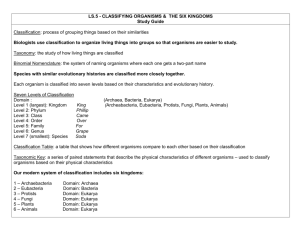
Classification Classification Scheme How many kingdoms? Lumpers v. Splitters 5 Kingdoms: Monera (now archaebacteria & eubacteria), Protista, Plantae, Fungi, Animalia 6 Kingdoms: Eubacteria, Archaebacteria, Protista, Plantae, Fungi, Animalia 8 Kingdoms: Eubacteria, Archaebacteria, Archenzoa, Chromista, Protista, Plantae, Fungi, Animalia Virus? Where does it fit in? A Virus treads the fine line that separates living and nonliving things Viruses need a host cell (bacteria, plant or animal) to live in and reproduce Ex: AIDS, Herpes, Hepatitis C, Smallpox, West Nile Virus, Ebola. SARS, Flu, Foot & Mouth Disease Archaebacteria Domain: Archaea Prokaryotes Unicellular Have Cell Walls Autotrophic or Heterotrophic Anaerobic (does not require oxygen) EX: Halophiles/ Thermophiles/ Methanogens Eubacteria Domain: Bacteria Prokaryote Unicellular Has Cell Walls Autotroph or Heterotroph Aerobic or anaerobic Examples: e coli, strep, cyanobacteria, Treated with antibiotics Protists Domain: Eukarya Eukaryotic Both Unicellular and Multicellular Some have cell walls Both Heterotrophic and Autotrophic Aerobic Examples: Amoeba, Euglena, Volvox, Algae FUNGUS Decomposers Domain: Eukarya Eukaryotic Both Unicellular and Multicellular Cell walls made of chitin Heterotrophic Aerobic Examples: Next page FUNGUS Decomposers Common Molds: Mildew, Bread mold Sac Fungi: Yeast, Powdery Mildew Club Fungi: Mushrooms Imperfect Fungi: Athletes Foot, Ringworm Plant Kingdom general characteristics Domain: Eukarya Eukaryotic Mutlicellular Cell walls made of cellulose Autotrophic Aerobic Plant Kingdom general characteristics Has 12 major DIVISIONS The plant kingdom uses divisions rather than phyla Plants have three main parts Roots: anchor plant Stems: transport materials Leaves: site of photosynthesis (in chloroplasts) MAKES THE FOOD!! Examples: next page Non-vascular Divisions Liverwarts Hornwarts Mosses Small, low to the ground MUST have moisture to reproduce Decomposer Vascular W/O seeds Whisk Ferns Club Mosses Horse Tails Ferns Largest group of vascular plants Alternation of generations Vascular With Seeds Gnetae Cycads Ginkgoes Have male and female trees Conifers (gymnosperms) Grow very large & old Have needles and cones flowering plants Have flowers Produce Fruit Large variety The Animal Kingdom Domain: Eukarya Eukaryotic Multicellular NO cell walls Heterotrophic Aerobic Examples: Next pages Porifera/Sponges Sponges Lack Specialized Tissues Filter Feeders Sessile (cannot move) Asymmetry Environmental Indicators Cnidarians Stinging Cells Radial Symmetry Examples: Coral, hydra, sea anemone, jelly fish Platyhelminthes-Flatworms Bilateral Symmetry Unsegmented/Flat EX: Planarians, Tapeworms & Flukes Nematoda-Roundworms Round, Unsegmented bodies Ex: ascaris(hookworms & pinworms), wuchereria bancrofti Mollusks EX: Snails, slugs, Scallops & Squids Soft body protected by a hard shell Mantle, Foot & Visceral Mass Annelids-Segmented Worms EX; Earthworms, leeches & polychaetes Segments, true coelomates Most are hermaphroditic Arthropods--- So many!!!!!! MOST DIVERSE ANIMAL PHYLUM Segmented bodies Jointed Appendages Exoskeleton made of Chiton Crustaceans 2 body parts EX: Crayfish, Crabs, Lobsters, Pillbugs & Shrimp Arachnids 8 legs & pedipalps No antennae Compound eyes Spiders & Scorpions -Insects---- Antennae 6 legs Diverse Echinoderms Spiny Skin Water Vascular System Radial Symmetry EX: Seastars, Sea Cucumbers, Brittle Stars, Sand Dollars Chondrichthes Cartilage Fish Sharks & Rays Osteichthyes Bony Fish Puffer fish, carp, salmon Amphibians Lives on water & Land 3 Chamber heart Eggs must stay damp Reptiles Rough Skin Amniotic Egg Ex: Snakes, Lizards & Crocodiles Birds Warm Blooded Flight Feathers? Marsupials Pouches Monotremes Duck-Billed Platypus & Spiny Ant Eater Egg-Laying Mammals Placental Mammals •Carry young in utero TaDa The End