Six Kingdoms PP
advertisement

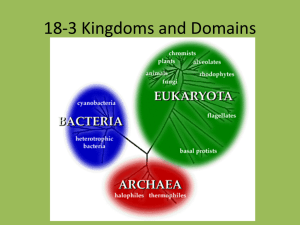
Notes Three Domains Six Kingdoms Domains Archae Bacteria Eukarya Six Kingdoms The system of classification consists of six kingdoms: Archaebacteria Eubacteria Protists Fungi Plants Animals How do we decide? Organisms are placed into kingdoms based on: their type of cells how they get food the number of cells in their bodies Domain Archae Archaebacteria The name archaebacteria means “ancient bacteria.”Archaebacteria can be either autotrophic or heterotrophic and live only in places without oxygen. Archaebacteria are prokaryotes, organisms whose cells do not have a nucleus. Single-celled or unicellular. Some are known as Extremophiles- can survive in extreme conditions Domain Bacteria - Eubacteria Bacteria belong to the kingdom known as Eubacteria. Eubacteria are unicellular prokaryotes. Can be found in soil, water, and surfaces. Can be beneficial (helpful) or harmful. Are used in the production of certain foods and also help us to break down foods in the intestines. Domain Eukarya - Protists The protist kingdom is sometimes called the “odds and ends” kingdom because its members are so different from one another. Protists can be autotrophs or heterotrophs. Although many protists are unicellular, some are multicellular. However, all protists are eukaryotes— organisms with cells that contain nuclei. Domain Eukarya - Fungi Mushrooms, molds, mildew, and yeast are all fungi. Most fungi are multicellular eukaryotes. A few, such as yeast, are unicellular eukaryotes. Fungi are found almost everywhere on land, but only a few live in fresh water. All fungi are heterotrophs-they feed on other things and are not capable of making their own food. Most fungi feed on dead or decaying organisms. Domain Eukarya - Plants Plants are all multicellular eukaryotes. The plant kingdom includes a wide variety of organisms. Found on land and in water. All plants are autotrophs. Plants feed almost all of the heterotrophs on Earth. Domain Eukarya - Animals All animals are multicellular eukaryotes. All animals are heterotrophs. Animals have different adaptations that allow them to find food, capture it, eat it, and digest it. Members of the animal kingdom are found in diverse environments on earth.