Kingdoms and Domains 18.3
Kingdoms and Domains 18.3
• Most inclusive taxonomic category; larger than a kingdom.
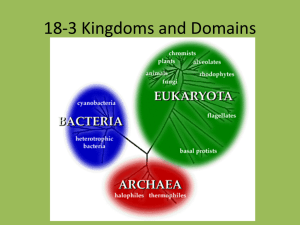
Domain
Bacteria
• Domain of unicellular prokaryotes that have cell walls containing peptidoglycan.
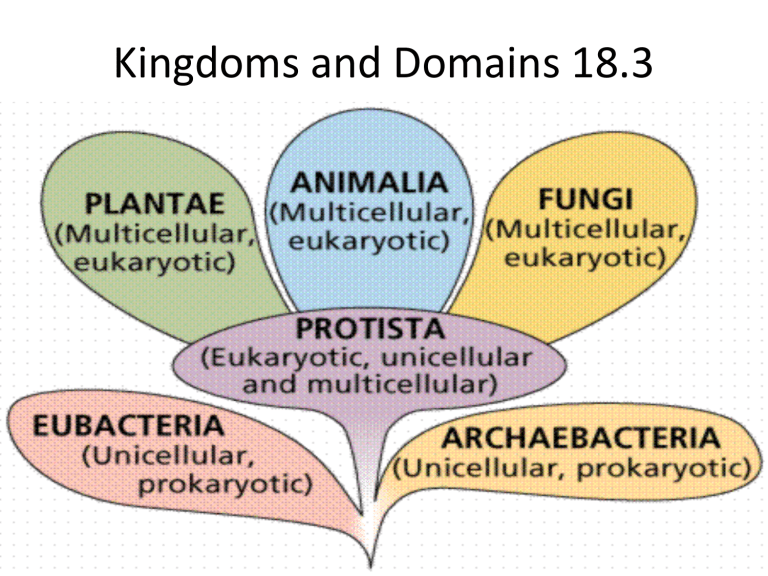
Eubacteria
• Kingdom of unicellular prokaryotes whose cell walls are made up of peptidoglycan.
Archaea
• Domain of unicellular prokaryotes that have cell walls that do not contain peptidoglycan.
Archaebacteria
• Kingdom of unicellular prokaryotes whose cell walls that do not contain peptidoglycan.
Eukarya
• Domain of all organisms whose cells have nuclei, including protists, plants, fungi, and animals.
Protista
• Kingdom composed of eukaryotes that are not classified as plants, animals, or fungi.
Fungi
• Kingdom composed of heterotrophs; many obtain energy and nutrients from dead organic matter.
Plantae
• Kingdom of multicellular photosynthetic autotrophs that have cell walls containing cellulose.
Animalia
• Kingdom of multicellular eukaryotic heterotrophs whose cells do not have cell walls.
Key Concept
• What are the six kingdoms of life as they are now identified?
– The six-kingdom system of classification includes the kingdoms
Eubacteria, Archaebacteria, Protista,
Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia.
Key Concept
• What is the three-domain system of classification?
– The three domains are the domain
Eukarya, Which is composed of protists, fungi, plants, and animals; the domain Bacteria, which corresponds to the kingdom Eubacteria; and the domain Archaea, which corresponds to the kingdom Archaebacteria.