Cell Cycle and Mitosis
advertisement
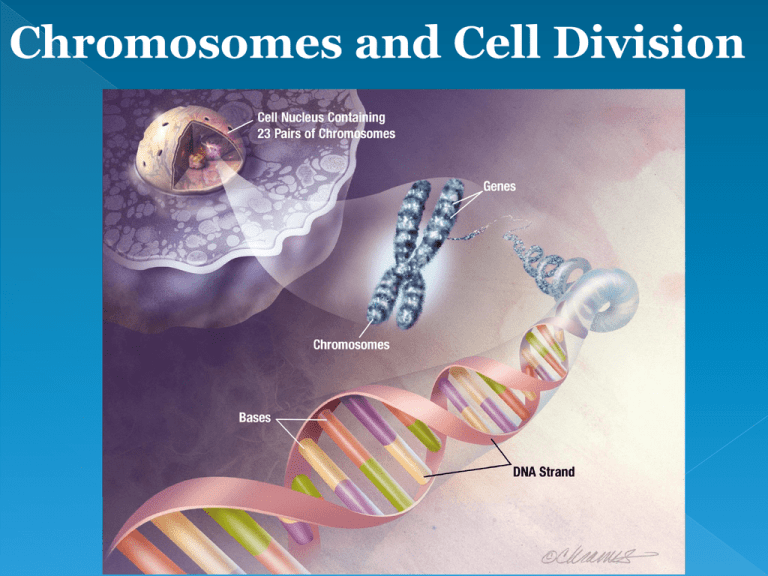
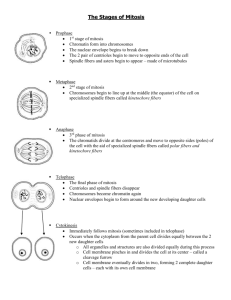
Chromosomes and Cell Division DNA Negatively charged Double stranded Wraps around histones CHROMOSOME=chromatid + kinetochore 46 chromosomes in humans DNA Limits Cell Size Cell cannot survive unless there is enough DNA to support the protein needs of the cell Some really large cells are multinucleated › More nuclei = › more DNA = › quick protein making Cell Reproduction Cell Division= making 2 daughter cells from one parent cell AKA : Asexual Reproduction Happens in all cells New cells are genetically identical! Prokaryote Cell Division Bacteria Circular DNA Produce 2 daughter cells by BINARY FISSION DNA copied Know steps! How do little elephants grow up to be BIG elephants? The process of mitosis begins after a sperm fertilizes an egg. Only happens in eukaryotes. Only happens in somatic cells. Cells reproduce constantly. Skin cancer - the abnormal growth of skin cells - most often develops on skin exposed to the sun. Animated Mitosis Cycle http://www.cellsalive.com/mitosis.htm • Interphase • Prophase • Metaphase • Anaphase • Telophase & Cytokinesis Chromosomes are copied (# doubles) • Chromosomes appear as threadlike coils (chromatin) at the start, but each chromosome and its copy(sister chromosome) change to sister chromatids at end of this phase • Nucleus CELL MEMBRANE Cytoplasm Animal Cell Plant Cell Photographs from: http://www.bioweb.uncc.edu/biol1110/Stages.htm • • • • Mitosis begins (cell begins to divide) Centrioles appear and begin to move to opposite end of the cell. Spindle fibers form between the poles. Nuclear membrane breaks down. Centrioles Sister chromatids Spindle fibers Animal Cell Plant Cell Spindle fibers Centrioles Photographs from: http://www.bioweb.uncc.edu/biol1110/Stages.htm • • • • Meta = Middle Centromere/Kinetochore replicate Sister Chromatids (or pairs of chromosomes) attach to the spindle fibers. Chromosomes line up along the equator Centrioles Spindle fibers Animal Cell Plant Cell Photographs from: http://www.bioweb.uncc.edu/biol1110/Stages.htm Chromatids (or pairs of chromosomes) separate and are pulled to the poles • Pulled by spindle fibers. • Centrioles Spindle fibers Animal Cell Plant Cell Photographs from: http://www.bioweb.uncc.edu/biol1110/Stages.htm Two new nuclei form. • Nuclear Membrane reforms • Spindle Fibers fall apart • Chromosomes uncoil into chromatin (thread) • Cleavage: membrane pinches to make 2 identical cells (Cytokinesis) • Nuclei Chromatin Nuclei Animal Cell Plant Cell Photographs from: http://www.bioweb.uncc.edu/biol1110/Stages.htm • Cell membrane moves inward to create two daughter cells – each with its own nucleus with identical chromosomes. Plant Mitosis -- Review Interphase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis Animal Mitosis -- Review Interphase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis 24 - Cell Division 25 25 Why is mitosis important? Growth and replacement of dead, lost, or damaged cells Ensures each daughter cell gets a complete and exact copy of the genetic material from the parent cell in the quickest, most efficient way http://www.cellsalive.com/mitosis.htm Means division of the cytoplasm Division of cell into two, identical halves called daughter cells In plant cells, cell plate forms at the equator to divide cell In animal cells, cleavage furrow forms to split cell copyright cmassengale 28 Cleavage furrow in animal cell copyright cmassengale Cell plate in plant cell 29 Two identical daughter cells Parent Cell copyright cmassengale 30 If mitosis is not controlled, unlimited cell division occurs causing cancerous tumors Oncogenes are special proteins that increase the chance that a normal cell develops into a tumor cell Cancer cells 31 copyright cmassengale