Mitosis
advertisement

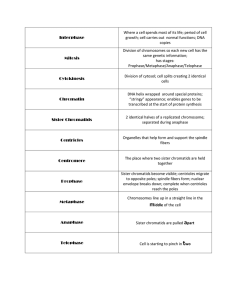
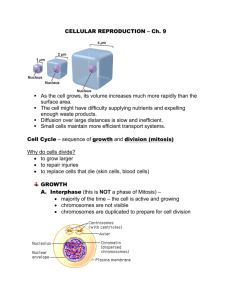
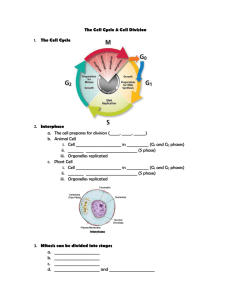
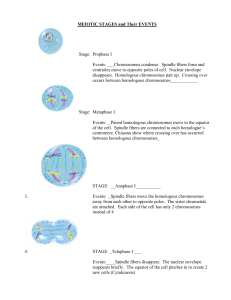
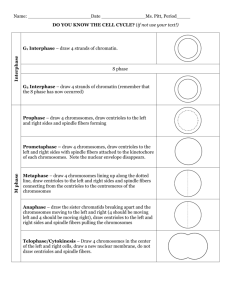
Why do cells need to divide? How do cells divide? What needs to happen to make an exact copy of this cell? • Does an organism grow because its cells get larger or because it increases the number of cells? • What limits the size that a cell can reach? • How does the surface area change when a large cell divides into smaller cells that have the same total volume? • Are cells dividing all the time? • Do all cells divide at the same rate? • What must duplicate/replicate before a cell divides? Types of Reproduction • Asexual Reproduction – Cloning of an individual cell – Produce genetically identical offspring – Occurs in bacteria, body cells • Sexual Reproduction – Occurs when two reproductive cells join – Make genetically diverse cells since the offspring get traits from both parents Vocabulary Chromatin- long strand of DNA Chromatid- each strand of a duplicated chromosome Centromere- the area where two chromatids are joined. Splits during anaphase. Kinetochore- a protein on chromosomes where spindle fibers attach. Centrioles- tiny structures in the cytoplasm of animal cells that help organize the spindles. (2 centrioles =centrosome) Spindle fiber- a fanlike microtubule structure that helps separate the chromatids • Spindle- a fanlike microtubule structure that helps separate the chromatids -composed of centrioles and spindle fibers Cell Cycle- Interphase • G1 – Cell Growth-increase in size, routine functions (longest) • S – DNA replication- Synthesis of new DNA/ chromosomes replicated • G2- Preparing for Cell Division- replication of organelles, microtubules and other molecules for cell division • http://iknow.net/cell_div_education.html M Phase (minutes to days) • Mitosis – – – – Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Pro=before Meta=after Ana=back Telo= end • Cytokinesis – Division of the cytoplasm and organelles Mitosis- phases • Prophase – Chromosomes become visible (coil) – nuclear membrane dissolves – Spindle forms – Nucleolus disappears Prophase Metaphase • Chromosomes line up along the equator • Spindle fibers connect centromeres (of chromatids) to opposite poles Anaphase • Centromeres divide • Chromosomes move toward opposite poles – Each Sr. Chromatid is pulled toward opposite pole • Spindle fibers shorten Telophase • Reverse of Prophase • Nuclear membrane forms at each pole • Chromosomes uncoil • Spindle fibers dissolve • Cytokinesis begins Cytokinesis • Cytoplasm divided in half • Cell membrane pinched by a belt of protein threads or contractile ring Plant vs Animal Cell Division Animals • Centrioles • Pinching or cleavage of cell membrane Both Equal sized offspring cells Identical copy of original cell’s chromosomes Plants • No centrioles • Vesicles fuse forming a cell plate • A new cell wall forms on either side of the cell plate Animal and Plant Cell Division • http://iknow.net/cell_div_education.html • • • • Prophase- a “pro” is #1 Metaphase- “M” middle Anaphase- Away Telephase – Two nuclei • http://glencoe.mcgrawhill.com/sites/dl/free/0078802849/164155/00 053413.html