Mitosis - Wayne County Public Schools
advertisement

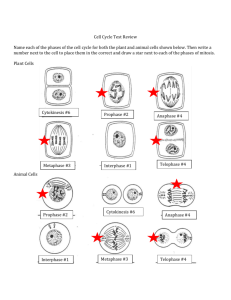
Mitosis By: Ann Benning Asexual Reproduction • Asexual Reproduction: One parent, the offspring is a clone of the parent/organism because of no exchange of genetic material • Four types of Asexual Reproduction : – – – – Mitosis Bidding Binary Fission Regeneration • There is only 1 parent involved and the offspring is identical (nothing is different) to the parent What is Mitosis? • Mitosis is a process where a single a single cell divides resulting in two genetically identical cells • Before Mitosis begins Interphase occurs • Mitosis has 4 steps (PMAT) – – – – Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase • New cells are produced by the power of mitosis Interphase • Interphase has to happen before anything can happen in mitosis • Interphase has an appearance a normal cell • Chromosomes are not visible at the time and are long, skinny things called chromatins – Chromatins are made of 40% DNA and 60% Protein • DNA is replicated • Interphase is important to the cell because it prepares the cell for mitosis Prophase (Pmat) • Prophase is the first step in mitosis • Prophase is when the chromosome’s replicates are visible and they attach themselves to centrioles • Centrioles then move to opposite ends of the cell • The nucleolus disappears and the nuclear envelope breaks down • Prophase is important to the cell because it forms all the needed things/items they need to split the cell like – Spindle Fibers Metaphase (pMat) • Metaphase is the 2nd step in Mitosis • During Metaphase, chromosomes line up around the equator of the cell • The spindle fibers attach themselves to centrioles • Metaphase is important to the cell because it starts to allow the cell to divide into two Anaphase (pmAt) • Anaphase is the 3rd step in Mitosis • The centromeres split into 2 • Spindle Fibers pull centromeres to opposite poles(ends) of the cell • The chromosomes split into 2 chromatids – These are also pulled to the opposite ends of the cell • Anaphase is important to the cell because it pulls the chromosomes to the “new cells” Telophase (pmaT) • • • • Telophase is the 4th step of Mitosis Chromatids unravel and form chromatids Centrioles replicate themselves The nuclear membrane comes and reforms around the chromosome – To make the 2 “new cells” • Telophase is important to the cell because allows the cell to divide into 2 new cells Cytokinesis • Cytokinesis is a step of cell cycle but not a step in Mitosis • Cytokinesis is the physical division of cytoplasm to daughter cells Ways to Remember •Mitosis –PMAT (Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase and Telophase) •Cell Cycle: –IPMATC (Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase and Cytokinesis) Quick Review #14 1. What step does the centrioles replicate themselves? a. Telophase b. Prophase c. Anaphase 2. What step does the cell look the same like nothing will happen or nothing has happened? a. Prophase b. Anaphase c. Interphase 3. What step does centromeres get pulled to opposite ends of the cell? a. Anaphase b. Cytokinesis c. Metaphase 4. What step do centrioles move to opposite ends of the cell? a. Metaphase b. Prophase c. Telophase Quick Review #2 5. How many parents does asexual reproduction need? a. 10 b. 1 c. 2 6. When does the cell become 2 “new cells”? a. Cytokinesis b. Prophase c. Telopahse