Medical and Molecular Genetics - U
advertisement

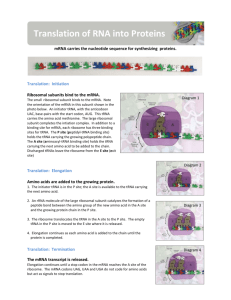
Medical and Molecular Genetics Lecture 6 Protein Synthesis & Maturation 1) Define the terms: genetic code, codon, anticodon, degeneracy, wobble, open reading frame charged tRNA, translation, and polysome. Genetic code – a system of specific base sequences that specifies which amino acids are to be used for the synthesis of a protein molecule during translation. Codon – specifies a specific amino acid and consists of a triplet of bases, there are 64. Anticodon – a sequence of three bases on the tRNA which binds to its complimentary codon on the mRNA when translating the code. Degeneracy – many codons specify the same amino acid (synonyms) and they generally differ at the third base. Wobble – base pairing is not strict for the last nucleotide of the codon anticodon pair so that one tRNA can recognize codons that specify the same amino acid. Open reading frame – the string of codons contained within the mRNA and translated into protein. Charged tRNA – a tRNA molecule that has been linked to an amino acid. Translocation – moving the ribosome three nucleotides in the 5’ to 3’ along the mRNA so that a new codon occupies the A site. Polysome – an mRNA that is bound by multiple ribosomes. 2) List the types of the types of RNA used in translation and state their functions. tRNA – recognizes codons on mRNA, carries amino acids specified for those codons, and places them in the protein that is being translated. mRNA – is the transcribed code from a DNA template, which binds to ribosomes and directs translation. rRNA – makes up parts of the ribosomal subunits along with proteins, which allow it to bind mRNA and tRNA as the protein is being built. 3) State the function of the ribosome in translation and list its major components. Ribosomes are the sites of translation and are composed of RNA and protein. They have a sedimentation coefficient of 80S and consist of two subunits: a 60S large subunit and a 40S small subunit. The 60S subunit consists of 45 proteins and three rRNAs having sedimentation coefficients of 5.8S, and 28S. The 40S subunit consists of 33 proteins and an 18S rRNA. 4) Describe the major steps of translation. Translation occurs in three major steps: initiation, elongation, and termination. Initiation ahs four major steps: 1) dissociation of the ribosome into 40S and 60S subunits, 2) formation of a preinitiation complex which consists of met-tRNA, eukaryotic initiation factor 2 (eIF-2), GTP, and the 40S subunit, 3) binding of mRNA, 4) association of the 60S subunit. Elongation occurs in three major steps: 1) binding of charged aminoacyl-tRNA at the A site along with GTP and an elongation factor called eEF-1α, 2) peptide bond formation catalyzed by peptidyl transferase binding the peptidyl-tRNA at the P site with the AA at the A site, 3) translocation of the growing peptide chain moves in the 5’ to 3’ direction so that a new codon occupies the A site as the P site dissociates and this is catalyzed by elongation factor 2 (eEF-2) at the expense of GTP. Termination occurs when a stop codon appears at the A site and releasing factors recognize the stop codon to hydrolyze the bond between the polypeptide and tRNA to dissociate from the P site.