Chapter 6
advertisement

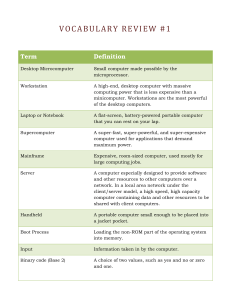
Chapter 6 Storage Professor Michael J. Losacco CIS 1110 – Using Computers Overview Chapter 6 List Capacities Describe Hard Disk Characteristics Explain Cloud Storage Advantages Differentiate Between CDs & DVDs Explain Miniature Storage Use Identify the Uses for Tape 2/29 Storage Chapter 6 Holds Data, Instructions, & Information For Future Use 3/29 Capacity Chapter 6 Number of Bytes Medium can Hold Average Fortune 1000 Capacity is 1PB computerworld.com 3/07 4/29 Volatility Chapter 6 Storage is Non-volatile Contents Retained when Power is Off Device Reading Transfer Item from Storage Media to Memory Writing Transfer Item from Memory to Storage Media Media Physical Material Stores Data, Instructions, & Information 5/29 Disk References Chapter 6 A: — Always Primary Floppy Drive B: — Secondary Floppy If It Exists C: — Always Primary Hard Drive D:, E:, F:, Etc. — Next Available Drive Hard drive CD-ROM DVD USB Network 6/29 Access Time Chapter 6 Time to Locate & Read Data on Media Time to Deliver Data from RAM to CPU 7/29 Hard Disk Chapter 6 Main Storage for System Unit Internal Consists of Several Inflexible Platters Enclosed in Airtight, Sealed Case Uses Magnetic Particles to Represent Data 8/29 Hard Disk Chapter 6 Mechanics 9/29 Hard Disk Chapter 6 Formatting Prepares Disk for Reading & Writing 10/29 Hard Disk Chapter 6 Formatting Track Circular Band Sector Pie-shaped Cluster Group of Sectors Cylinder Single Track Through All Platters 11/29 Hard Disk Chapter 6 Head Crash Spinning Creates Air Cushion Floats Read / Write Head Above Platter Crash Head Touches Platter Surface Clearance = Two-millionths of an Inch 12/29 Hard Disk Chapter 6 External Freestanding Removable Insert & Remove Miniature Used to Back Up or Transfer Files 13/29 Cloud Chapter 6 Internet Service Provides Storage to Computer Users Benefits Access Files From Any Computer Allow Others to Access Their Files View Time-critical Data Immediately Store Offsite Backups 14/29 Cloud Chapter 6 Examples Digital Photos Flickr, Picasa Digital Videos YouTube SocNet Content Facebook, MySpace Email Gmail, Hotmail, Yahoo Mail 15/29 Optical Disk Chapter 6 Flat, Round, Portable Disc Made of Metal, Plastic, Lacquer Stores Software Data Digital Photos Movies Music 16/29 Optical Disk Chapter 6 Mechanics 17/29 Optical Disk Chapter 6 CD (Compact Disc) CD-ROM Cannot Erase or Modify Contents CD-R (Recordable) Cannot Erase Contents Once Written CD-RW (Rewritable) Can be Erased Stores About 700 MB Writing Requires Burner & Software 18/29 Optical Disk Chapter 6 DVD (Digital Video Disc) DVD Drive & Software Required High Capacity CD Used for Movies, Music, Software 12.5MB per Frame 24 Frames per Second 3+ GB per Movie Compressed 19/29 Optical Disk Chapter 6 DVD DVD-ROM Cannot Erase or Modify Contents DVD-R & DVD+R Recordable DVD-RW, DVD+RW, & DVD-RAM Rewritable 20/29 Optical Disk Chapter 6 DVD Storage Two Layers of Pits Can be Used Lower Layer is Semitransparent Laser Can Read Through it to Upper Layer 21/29 Flash Chapter 6 Solid State Media Contain No Moving Parts Solid State Drive (SSD) Benefits Faster Access Time Faster Transfer Rates Generate Less Heat Consume Less Power Last Longer 22/29 Flash Chapter 6 Types 23/29 Flash Chapter 6 Uses 24/29 Flash Chapter 6 USB Drive Plugs into USB Port ExpressCard Module Developed by PCMCIA Used in Notebooks 25/29 Tape Chapter 6 Magnetically Coated Plastic Ribbon Stores Large Amounts of Data Low Cost Used for Backup Purposes Storage Sequential Access Reads / Writes Data Consecutively Similar to Audio Tape 26/29 Other Storage Chapter 6 Magnetic Stripe Card Contains Mag Stripe That Stores Data Smart Card Stores Data On Microprocessor Embedded In Card Prepaid Dollar Amounts Updated When Card is Used Healthcare Information Tracking Information 27/29 Other Storage Chapter 6 Microfilm 100-215-foot Roll of Film Microfiche Small Sheet of Film Usually 4” x 6” Store Microscopic Images of Docs 28/29 Media Life Expectancies Chapter 6 29/29