File - History with Mr. Bayne
advertisement

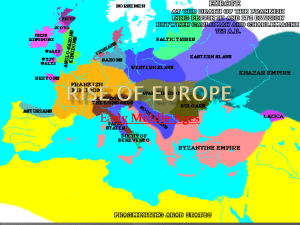
Early Middle Ages 500 to 1000 A.D. • • • • • Day 1 Warm up Greece/Rome Test: Turn in packets Textbook worksheet Begin notes Early Middle Ages notes on invaders and Charlemagne • Finish worksheet Daily Objective The student will demonstrate knowledge of Western Europe during the Middle Ages from about 500 to 1000 A.D. (C.E.) in terms of its impact on Western civilization by sequencing events related to the invasions, settlements, and influence of migratory groups, including Angles, Saxons, Magyars, and Vikings. explaining the rise of Frankish kings, the Age of Charlemagne, and the revival of the idea of the Roman Empire on a textbook worksheet. Warm-up 1(Test Day) Give the letter of 1. Capital of the Roman Empire 2. Gaul 3. Britain 4. Birthplace of Judaism and Christianity F 5. First Democracy E 6. Destroyed by Rome in Punic Wars H 7. The wars that united Athens and Sparta against an empire were the Persian or Peloponnesian Wars? 8. The type of government in Sparta was a democracy or oligarchy? 9. The first emperor of Rome was Julius or Augustus? 10. The Roman emperor who moved the capital and legalized Christianity was Constantine or Nero? 11. The Roman Empire fell in 476 AD or 476 BC? Warm-up 2 (2 slides) 1. The Angles and Saxons settled in England or France? 2. The Franks settled in Gaul or Carthage? 3. The Frankish King who conquered an empire and was crowned “Holy Roman Emperor” by the Pope was Clovis or Charlemagne? 4. Charlemagne’s empire combined Roman, Christian, and English or German traditions? CENTRAL ASIA Russia Hungary North Africa 3. The invaders depicted in orange are the Vikings or Muslims? 4. The invaders in purple are the Angles and Saxons or Magyars? 5. The Muslim Empire (in green) was stopped from expanding further into western Europe at the Battle of Tours or Isis? Day 2 • • • • • • • Warm up Terms Invaders map (SmartBoard-together) Invaders chart Feudalism Notes Terms Study for quiz tomorrow! Daily Objective The student will demonstrate knowledge of Western Europe during the Middle Ages from about 500 to 1000 A.D. (C.E.) in terms of its impact on Western civilization by b) explaining the structure of feudal society and its economic, social, and political effects on a terms list and chart Warm-up 3 1. Which change was a result of the rise of the feudal system? A. Major cities were established. B. Local lords had the most political power. 2. Self-sufficient communities ruled by lords were called city-states or manors? 3. In return for farming the lord’s land a serf received protection or land? A __________ would pledge his loyalty and military service in exchange for a grant of land. serf or vassal? 4. The grant of land given to a vassal was called a fief or lord? Day 3 • • • • • Warm up Quiz Notes on Church Finish Terms Review 26-32 Daily Objective The student will demonstrate knowledge of Western Europe during the Middle Ages from about 500 to 1000 A.D. (C.E.) in terms of its impact on Western civilization by a) sequencing events related to the spread and influence of Christianity and the Catholic Church throughout Europe on a terms list and review. Warm-up 4 1. Which factor strengthened both the Christian Church and the empire of Charlemagne? A. Unity between politics and religion B. Respect for elders and ancestors 2. This illuminated manuscript was probably created in a monastery or palace? 3. Missionaries carried Christianity and Latin or Greek alphabet to Germanic tribes. 4. Who anointed Charlemagne Emperor: Patriarch or Pope 5. Who served the religious and social needs of the people. Lords or parish priests 6. Who could read and write: the serfs or the clergy (priests, monks, nuns, bishops, etc.) Day 4 1. Warm up questions 2. Finish Review/packets 3. MANOR PROJECT: Design your own manor. Include everything needed to be self-sufficient: • farmland • manor house • serf’s cottages • church • defenses (walls) • water source • fuel source • name the manor • Study for TEST tomorrow! Objective: SWBAT describe the characteristics of Early Medieval Society on a Quiz ,Test Review, and project Warm-up 5 1. Scandinavians who invaded Europe and settled in Russia were called — Vikings or Aryans 2. Feudal relationships defined land ownership and protection agreements between — A. serfs and peasants B. lords and vassals 3. The Frankish kings expanded their territory most often through — conquest or inheritance 4. What was the main role of serfs in the feudal system? soldiers or laborers 5. The Battle of Tours was significant because it marked the — A. end of Muslim expansion into Western Europe B. end of the Crusades in the Middle East 6. Where did the Magyars settle Hungary or Gaul? Day 5 • • • • Warm up Turn in packets Early Middle Ages Test Begin High Middle Ages Intro to the Middle Ages A Life of Treachery Germanic Kingdoms Invasions by Germanic tribes shattered Roman protection over Western Europe. Population, trade, and learning declined. Eventually, Germanic tribes carved up Western Europe into small kingdoms. Anglo-Saxon Invaders •The Angles and Saxons were tribes that came from continental Europe and invaded Britain which became known as England (Angles Land). Franks •The Franks were the most successful of the Germanic kingdoms. Clovis • Clovis became king of the Franks, conquered the former Roman province of Gaul, and converted to Christianity Islamic Empire • The Islamic Empire emerged in 622 AD. Over the next 100 years, Muslims conquered the Middle East and all of North Africa. In 711 Muslims from North Africa (Moors) took over Spain. •The Franks stopped the Muslims from advancing further into Europe at the Battle of Tours (732 AD). Germanic Invaders Charlemagne •Charlemagne became king of the Franks and built an empire that included most of Western Europe (France, Germany, and a part of Italy). •He united the empire by building roads, schools and churches. • Pope Leo III crowned Charlemagne as Emperor in 800 CE. This formed an alliance between the Frankish Kings and the Christian Church, reviving Roman culture in Western Europe. •Charlemagne’s empire blended German, Roman, and Christian traditions throughout Western Europe. •Upon his death, Charlemagne’s Empire was divided. Medieval Culture New Invasions in Western Europe New Invasions by the Vikings and Magyars disrupted order in Europe. Vikings • Vikings were expert sailors and ferocious fighters who originated in Scandinavia and looted and burned communities from Ireland to Russia. • Scandinavian countries include: Norway, Finland, Sweden, and Denmark. The Vikings settled in Russia Russia Magyars •Magyars were nomadic people that overran Central Asia and then plundered parts of Germany and France. • After 50 years they were turned back and settled into what is present day Hungary. ASIA Magyar invasions Hungary Viking Invasions and Early Norman Manors Influence of these invasions: •Towns emptied and trade was disrupted. • People fled to manors with castles that provided protection from invaders. • They entered into feudal agreements with the lords of the manors who promised them protection. Manorial System During the Middle Ages • A manors was the lord’s estate. •Manors were selfsufficient agricultural communities. Everything one needed was made on the manor. From crops, clothing, fuel, to a water source. • Manors had a rigid class structure: Nobles were at the top (king, lords, and knights) and serfs were at the bottom. King Lords Knights Vassals Serfs (peasants) Feudalism • A loosely organized system of government based on the exchange of land for protection and services . • A lord would give a grant of land called a fief to a knight. In return the knight would fight for the lord. The knight who received the fief became the lord’s vassal. The vassal would pledge his loyalty and military service to the greater lord. In turn he would become lord of his own smaller manor (fief). Manors and the Feudal System • The lords held most of the power in feudal society because they had complete control over their manors and the people who lived there. • Kings had very little direct control over the people. They had high social status, but little power. Weak Kings and Strong Nobles •Knights were mounted warriors who pledged to defend their lords’ lands. Knights • Serfs were peasants who were bound to the land. The serfs farmed the land for the lords in return for protection from invaders. Serfs made up most of the population. Serfs How did Church grow in importance? The Church grew in importance as the authority of the government declined. The Church gained political influence by crowning of Charlemagne. The clergy (priests, monks, nuns, bishops, etc.) were among the few who could read or write. Charlemagne sent out missionaries, spreading Christianity and the Latin alphabet to Germanic tribes. • Local parish priests served the needs of the people • Priests performed sacraments – important religious ceremonies like baptism and marriage. • Clergy, which consisted of Priest and Nuns, assisted the people in many of their needs. Such as aiding the sick and the poor. • Monasteries preserved GrecoRoman cultural achievements by copying ancient texts. • The Church and the Monarchs competed for power. Vs. •The Pope would often threaten excommunication banishment from the church - to gain power from the monarchs. The Roman Catholic Church Review Video Quiz The Battle of Tours was significant because it marked the end of — 1. the Muslim expansion into Western Europe 2. the Crusades in the Middle East 1. The Angles and Saxons?