The World of Late Antiquity
advertisement

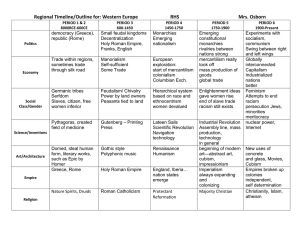
The World of Late Antiquity A Waning Empire Thesis: 1) The Roman Empire in the West gradually evolved into the Europe of the Germanic successor kingdoms. Although change was rapid in the fifth century, nowhere did a sharp break occur. 2) The “concept” of Rome was an important legacy which would be important to later generations, and in different periods the meaning and history of “Rome” would reflect the particular aims of those later generations. Hollingsworth’s argument: 1st & 2nd Century “Golden Age” 3rd&4th Centuries: “Anarchy & Recovery” The Crisis of the Third Century – leadership crisis – military crisis – economic crisis – social crisis – religious crisis. Strong Emperors Respond Diocletian (284-305 AD) Tetrarchy and division of the empire (Roman Provinces) “defense in depth” Edict of Prices Restoration of Civic Gods Constantine the Great (306-337 AD) Legitimating Ceremonial Christianity: “Ruler by the Grace of God.” Constantinople The Last Century of the Western Empire Germanic migrations Confusion of “public” and “private” Loss of an Army The Roman Heritage – – Towns Roman education and culture