DISORDERS OF POTASSIUM HOMEOSTASIS
advertisement

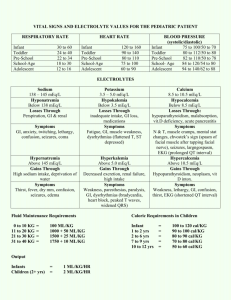
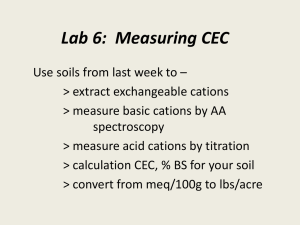
DISORDERS OF POTASSIUM HOMEOSTASIS Informal Academic in Service Overview Hypokalemia Hyperkalemia Case Discussion HYPOKALEMIA Serum potassium < 3.5 mEq/L Pathophysiology Total body potassium deficit Shifting of serum potassium into the intracellular compartment Causes Drugs (loop and thiazide diuretics) Diarrhea Vomiting Hypomagnesemia Principal cell Lumen - Blood Na+ Na+ K+ K+ Hypo Mg + Aldosterone เพิ่มการดูดเกลือ กลับขับ K+ ออก Loop VS Thiazide Principal cell Thaizide Blood Lumen - Na+ Na+ K+ K+ ความต่างศักย์ไฟฟ้าคือ = 9 กรณีได้ HCTZ + + + + + + Principal cell Loop Lumen - Blood Na+ Na+ K+ K+ Ca2+ Ca2+ Ca2+ ความต่างศักย์ไฟฟ้า คือ 3 กรณีได้ furosemide + + + + + + ดังนั้น HCTZ จึง lost K มากกว่า Furosemide Clinical Presentation Nonspecific signs and symptoms Cardiovascular Hypertension Cardiac arrhythmias: heart block, atrial flutter, paroxysmal atrial tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, and digitalisinduced arrhythmias ECG effects (serum K <2.5 mEq/L): ST-segment depression or flattening, T-wave inversion and U-wave elevation Neuromuscular symptoms Muscle weakness, cramping, malaise and myalgias Treatment Every 1 mEq/L fall of K below 3.5 mEq/L Total body deficit of 100-400 mEq Chronic used of loop or thiazide diuretics generally need 40-100 mEq of K K supplementation Oral: KCl IV: severe hypokalemia signs and symptoms of hypokalemia Inability to tolerate oral therapy Treatment K administration Dilute in saline because dextrose can stimulate insulin secretion and worsen intracellular shifting of K 10-20 mEq of K in 100 ml of NSS through a peripheral vein over 1 hr ECG monitoring (If infusion rates > 10 mEq/hr) HYPERKALEMIA Serum potassium > 5.5 mEq/L Pathophysiology Kintake > Kexcretion Transcellular distribution of K is disturbed Causes Increased K intake Decreased K excretion Tubular unresponsiveness to aldosterone Redistribution of K to the extracellular space Drugs: ACEI, ARB, K-sparing diuretics Clinical Presentation Frequently asymptomatic Heart palpitations or skipped heartbeats ECG change (serum K 5.5-6 mEq/L) Peaked T waves Widening of the PR interval Loss of the P wave Widening of the QRS complex Merging of the QRS complex with the T wave resulting in a sine-wave pattern Treatment Dialysis Calcium administration Insulin and dextrose, sodium bicarbonate, or albuterol Sodium polystyrene sulfonate/Calcium polystyrene sulfonate Treatment algorithm for hyperkalemia Treatment Dialysis Most rapid lowering serum K Calcium Rapidly reverses ECG & arrhythmias Not lower serum K Short acting Must be repeated if signs or symptoms recur Insulin & dextrose/sodium bicarbonate/albuterol Rapid shift potassium intracellularly Treatment Sodium polystyrene sulfonate (kayexalate) Mild to moderate hyperkalemia (K 5-7 mEq/L) Each gram of resin exchanges 1 mEq of Na for 1 mEq of K Sorbitol promotes excretion of K (by diarrhea) Tolerated & effective: oral > rectal Calcium polystyrene sulfonate Same kayexalate used For patient who restriction of Na Therapeutic Alternatives for the Management of Hyperkalemia Medication Dose Calcium 1 g (1 ampule) Route of Administration IV over 5–10 min Onset/Duration of Action 1–2 min/10–30 min Furosemide 20–40 mg IV 5–15 min/4–6 hr Regular insulin 5–10 units IV or SC 30 min/2–6 hr Dextrose 10% 1,000 mL (100 g) IV over 1–2 hr 30 min/2–6 hr Dextrose 50% 50 mL (25 g) IV over 5 min 30 min/2–6 hr Sodium bicarbonate 50–100 mEq IV over 2–5 min 30 min/2–6 hr Albuterol 10–20 mg Nebulized over 10 min 30 min/1–2 hr Hemodialysis 4 hours N/A Immediate/variable Sodium polystyrene sulfonate 15–60 g Oral or rectal 1 hour/variable Case Discussion Warfarin clinic Case 1 ผูป้ ่ วยชายไทยอายุ 57 ปี Supraventricular tachycardia, DM, HT แพทย์ให้ Warfarin dose 15 mg/wk ปรับเพิ่ม enalapril จาก 5 mg/day เป็ น 10 mg/day แพทย์ไม่ได้สงั ่ spironolactone ต่อ consult ไม่พบแพทย์ มียาเดิมเหลือ (spironolactone) จึงให้ทานยาเดิมก่อน Advice sign of bleed/embolism แพทย์นัด 12/01/54 LAB INR 2.1 Hb 12.3 Na 137 BUN 22 PT 22.7 Hct 35.1 K 5.0 Cr 1.9 WBC 5360 Plate 229000 Cl 103 CO2 28 FBS 124 Subjective data ผูป้ ่ วยชายไทยอายุ 57 ปี Hx: Supraventricular tachycardia, DM, HT Warfarin dose 15 mg/wk (dose เดิม) แพทย์ปรับเพิ่ม enalapril จาก 5 mg/day เป็ น 10 mg/day แพทย์ไม่ได้สงั ่ spironolactone และไม่ได้สงั ่ off มียาเดิมเหลือ จึงให้ รับประทานยาเดิมก่อน Objective data INR 2.1 PT 22.7 K 5.0 BUN 22 Cr 1.9 FBS 124 แพทย์นัด 12/01/54 Assessment Spironolactone Dose: 25-50 mg/day in 1-2 divide dose Contraindication: hyperkalemia, acute renal insufficiency ADR: gynecomastia, hyperkalemia, metabolic acidosis Assessment Enalapril: Dose: 2.5-5.0 mg/day then increase as require at 1-2 wk (Max 40 mg/day) Contraindication: angioedema ADR: hyperkalemia (1% to 3.8% ) Assessment K 5.0 High potassium Cr 1.9 mg/dl ClCr = 36 ml/min Spironolactone ไม่แนะนำให้ใช้ถำ้ ClCr < 10 ml/min ดังนั้น จึงยังไม่จาเป็ นต้องหยุด spironolactone Management สำมำรถให้ยำ enalapril ร่วมกับ spironolactone ต่อไปได้ โดยติดตำม serum K, renal function และ ECG change Plan Goal Electrolyte balance Therapeutic plan RM Enalapril 5 mg Spironolactone 25 mg 1x2 pc 1x1 pc Plan Efficacy monitoring K 3.5-5.0 mEq/L BUN, Scr Toxicity monitoring Hyperkalemia Renal insufficiency Plan Education plan ติดตามอาการอ่อนเพลีย อัมพาต และ ภาวะการหายใจล้มเหลว ใช้ยาตามที่แพทย์สงั ่ Future plan ติดตามการใช้ยาในครั้งต่อไป ติดตามการเปลี่ยนแปลงของคลื่นหัวใจ Case 2 ผูป้ ่ วยหญิงไทย อายุ 47 ปี มารับยาวาร์ฟารินตามแพทย์นัด INR 2.37 K 3.4 แพทย์สงั ่ KCl elixir 10% ปริมาตร 15 ml PO stat แพทย์สงั ่ KCl elixir 10% 15 ml คิดว่า เหมาะสมหรือไม่? Potassium Chloride KCl 1 g ให้ Approximate K+ 13 mEq 10% KCl elixir มี KCl 10 g/100 ml ผูป้ ่ วยได้ 10% KCl elixir 15 ml = KCl 1.5 g แสดงว่า ผูป้ ่ วยได้ K+ 19.5 mEq Total + K replecement K+ 40 mEq oral เพิ่ม K+ ในเลือด ~ 1 mEq/L K+ 19.5 mEq oral เพิ่ม K+ ในเลือด ~ 0.5 mEq/L ดังนั้น คาดว่า จะเพิ่ม serum K = 3.4+0.5 = 3.9 mEq/L KNormal range = 3.5-5.0 mEq/L References Charles F Lacy, et al. Drug Information Handbook 2008-2009. 17th edition: 2008. Barbara G Wells, et al. Pharmacotherapy Handbook. 7th edition: 2009. สมาคมโรคเบาหวานแห่งประเทศไทยในพระราชูปถัมภ์สมเด็จพระเทพ รัตนราชสุดาฯ สยามบรมราชกุมารี, สมาคมโรคต่อมไร้ท่อแห่งประเทศไทย สานักงานหลักประกันสุขภาพแห่งชาติ. แนวทางเวชปฏิบตั ิสาหรับโรคเบาหวาน พ.ศ. ๒๕๕๑: 2552. Mancia G, et al. 2007 ESH-ESC Practice Guidelines for the Management of Arterial Hypertension. Journal of Hypertension: 25 (9), 2007. http://www.thomsonhc.com ขอบคุณครับ