orientation(1)
advertisement

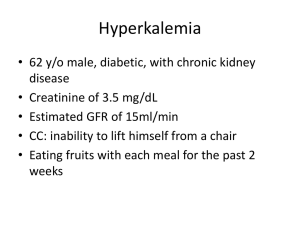
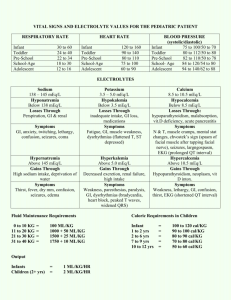
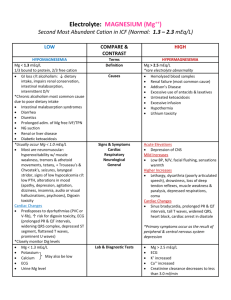
SPECIAL RESUSCITATION SITUATIONS 特殊情況下的復甦術 致命的電解質異常 1 40歲女性 Sudden collapse 經心臟電擊術後 40歲女性 12導程心電圖 40歲女性 血中鉀離子濃度過高 (K=7.0meq/L) 致命的電解質異常 造成心臟停止或降低急救成效 在檢驗數值出來前即採取急救措施 以高血鉀最易致命 5 高血鉀 血鉀 > 5.0 mEq/L pH 0.1 U serum K+ 0.3 mEq/L 6 高血鉀原因 Drugs (K+-sparing diuretics, ACEI, NSAIDs, K supplements) ESRD Muscle breakdown (rhabdomyolysis) Metabolic acidosis Pseudohyperkalemia Hemolysis Tumor lysis syndrome Diet (rarely sole cause) Hypoaldosteronism (Addison disease, hyporeninemia) Type 4 renal tubular acidosis Other: hyperkalemic periodic paralysis 7 高血鉀 症狀:全身無力(由下肢往上漸進式發生) ,呼吸衰竭 心電圖變化 T波變高 P波變平 PR延長 QRS波變寬 – S波變深 – idioventricular rhythm – sine waves – VF、心跳停止 8 Hyperkalemia Etiology – renal failure, transcellular shifts, cell death, drugs, pseudohyperkalemia Manifestations – cardiac, neuromuscular 9 高血鉀症的症狀 Hyperkalemia Treatment Stop potassium ! Get an ECG Hyperkalemia with ECG changes is a medical emergency Hyperkalemia Treatment First phase is emergency treatment to counteract the effects of hyperkalemia IV Calcium Temporizing treatment to drive the potassium into the cells glucose plus insulin Beta2 agonist NaHCO3 Therapy directed at actual removal of potassium from the body sodium polystyrene sulfonate (Kayexalate) dialysis Determine and correct the underlying cause 低血鉀 血鉀 < 3.5 mEq/L 原因 攝取減少 流失過多(腸胃道及腎臟為主) 由細胞外移至細胞內 13 低血鉀 症狀: 無力、疲累、麻痺 呼吸困難 便秘、麻痺性腸阻塞 小腿痙攣 肌肉崩解 14 低血鉀 心電圖變化 U波 T波變平 ST改變 心律不整(服用digoxin者尤甚) PEA or Asystole 15 低血鉀症的症狀 心率不整 (Arrhythmia) Atrial or ventricular tachyarrhythmia Decreased amplitude of P wave U wave. Conjoined T-U wave: "camel's hump" 處置 減少流失及補充鉀 心律不整或 K+ <2.5 IV K + 最大量10-20 mEq/h + ECG 心跳停止(VF/VT): 2 mEq/min 10 mEq /5-10 min 血鉀1mEq須補充150-400 mEq 17 高血鈉 血鈉 > 145 mEq/L 症狀: 口渴、意識不清、無力、躁動、 局部神經症狀、抽搐、昏迷 18 處置 減少水份流失、補水 低血容:補生理食鹽水 缺水量 =體重 x 0.5 x (血鈉 - 140) /140 ♂ 體重 x 0.4 x (血鈉 - 140) /140 ♀ 70公斤男性,血鈉160,缺水量 ? L 血鈉 0.5-1.0 mEq/h (< 12 / 24 hrs) Daily supply: Water deficit x 10 / (血鈉 - 140) Rate: Daily supply/24 + ongoing demand 19 低血鈉 血鈉 < 135 mEq/L 症狀:急性或 <120 才有症狀 噁心、嘔吐、頭痛、躁動、疲累、 抽搐、昏迷或死亡 20 處置 補鈉排水 SIADH: 限水 ( 50 - 66% ) Na+ deficit= (desired [Na+] - current [Na+]) x 0.5 x body wt (kg) (* 0.5 for men, 0.4 for women.) 3% saline = 513 mEq Na+/L Na+ 0.5 -1/hr (max. 10-12/24h) 補充太快 pontine myelinolysis 21 鎂 Na, K, Ca之移動所必需 低血鎂細胞內鉀無法補齊 穩定細胞膜作用: 可治療心律不整 22 高血鎂 血鎂 > 2.2 mEq/L 最常見原因: 腎衰竭 其它原因: 攝取過多 內臟破裂仍持續進食 23 高血鎂 神經症狀 : 肌無力、麻痺、運動失調、 嗜睡、意識混亂 腸胃症狀:噁心、嘔吐 心血管症狀:血管擴張、緩脈、換氣不 足、心肺停止 24 高血鎂 心電圖變化 PR、 QT 延長 QRS 變寬 P波電位變小 T波變高 Complete AV block、Asystole 25 處置 補鈣離子 CaCl2 ( 5 to 10 mEq IV ) 可避免致命性心律不整 移除血鎂 血液透析 腎及心血管功能正常 IV N /S + furosemide 減少攝取 26 低血鎂 血鎂 < 1.3 mEq/L 比高血鎂症常見 吸收減少、流失增加所致 PTH或某些藥物 (eg, pentamidine, diuretics, alcohol) 補乳婦女:高危險 27 低血鎂 - 原因 • GI loss: bowel resection, pancreatitis, diarrhea • Renal disease • Starvation • Drugs: diuretics, pentamidine, gentamicin, digoxin • Alcohol • Hypothermia • Hypercalcemia • Diabetic ketoacidosis • Hyperthyroidism/hypothyroidism • Phosphate deficiency • Burns • Sepsis • Lactation 28 低血鎂 - 症狀 肌肉震顫、束顫或強直 眼球震顫 意識改變、運動失調、眩暈、抽搐、吞 嚥困難 低血鈣、低血鉀 29 低血鎂 - 心電圖變化 QT延長 末段T波倒置 Heart blocks VF 30 處置 Severe or symptomatic hypoMg 1 to 2 g IV MgSO4 over 15’ Torsades de pointes 2 g of MgSO4 over 1 - 2’ Seizures 2 g IV MgSO4 over 10’ Calcium gluconate (1 g) 大部分有 hypoCa 腎功能不全者小心補 31 鈣 1/2 Ca in the ECF: bound to alb Alkalosis: Ca-alb binding Ca2+ Acidosis Ca2+ serum alb 1 g/dL total serum Ca 0.8 mg/dL (Ca = Serum Ca + 0.8 * (4 - Albumin)) In hypoalb., Ca2+ may be normal Ca antagonizes K and Mg at the cell mem. Ca regulated by PTH and vit. D 32 高血鈣 serum Ca > 10.5 mEq/L or Ca2+ > 4.8 mg/dL Primary hyperparathyroidism and malignancy account for >90% cases. 33 高血鈣 -症狀 Total serum Ca ≧12 to 15 mg/dL Neuro. S/S: depression, weakness, fatigue, ,confusion (at lower levels) hallucination, disorientation, hypotonicity, coma (at higher levels) Renal concentration of urine 34 高血鈣 -症狀 CV S/S: variable < 15 to 20 : myocardial contractility > 15 to 20 : myocardial depression Automaticity and ventricular systole is shortened Arrhythmias ( refractory period ) Digitalis toxicity is worsened Hypertension Many patients with hyperCa develop hypoK 35 高血鈣 -症狀 GI S/S: dysphagia constipation peptic ulcers pancreatitis Renal S/S: ability to concentrate urine dehydration diuresis (loss of Na, K, Mg, and P vicious circle of Ca reabsorption) 36 高血鈣 -心電圖變化 QT變短 PR and QRS 延長 QRS voltage 變大 T-wave變平、變寬 Notching of QRS AV block 37 處置 Symptomatic or >15 mg/dL NS at 300 to 500 mL/h --維持尿量200 to 300 mL/h After adequate rehydration: NS at 100 to 200 mL/h Closely monitor K & Mg Heart F. or Renal I.: hemodialysis Extreme conditions: chelating agents PO4 50 mmol/8-12 h or EDTA 10 to 50 mg/kg/4 h 38 處置(II) Lasix (1 mg/kg IV) controversial heart failure: required reuptake of Ca from bone Reduce bone resorption calcitonin Glucocorticoids (prednisolone 20~40 mg/day) 39 低血鈣 serum Ca < 8.5 mEq/L or Ca2+ < 4.2 mg/dL Causes: toxic shock syndrome abnormalities in Mg tumor lysis syndrome rapid cell turnover hyperK, hyperP, and hypoCa 40 低血鈣 - 症狀 Occur when Ca2+ < 2.5 mg/dL Paraesthesia Muscle cramps, carpopedal spasm Stridor Tetany Seizures Hyperreflexia Chvostek and Trousseau signs Cardiac contractility, heart failure 41 處置 急性,有症狀 10% Ca gluconate IV 10’ IV drip 0.5 to 2.0 mg/kg/hr in D5W 檢測血鈣 Q4-6H 維持血鈣 7-9 mg/dL 矯正 Mg, K, and pH 42 43




![Effective osmolality: 2 x ([Na] + [K])](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008663387_1-590320e85e31378083d542e43b1837df-300x300.png)



