Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
advertisement
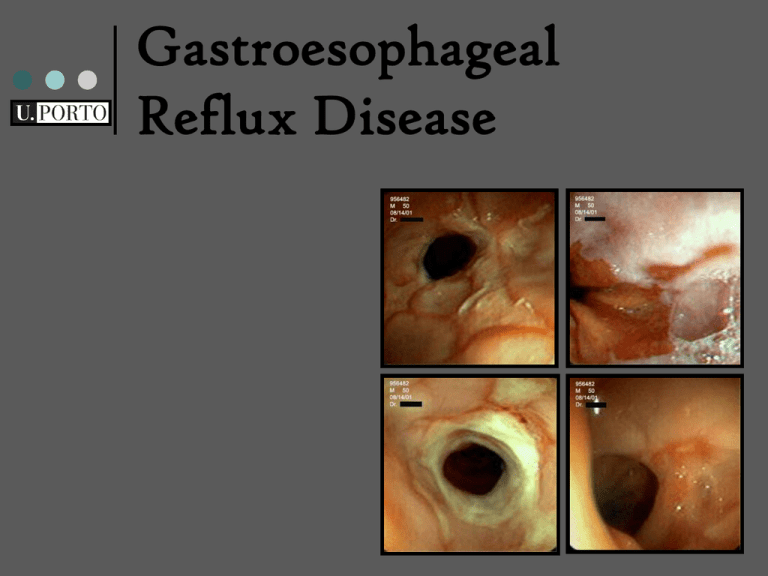
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) “a prevalent and chronic condition in which reflux of the stomach contents into the oesophagus causes a range of troublesome symptoms (including heartburn, acid regurgitation and epigastric pain) and complications” Vakil et al. The Montreal definition and classification of GERD: a global evidence-based consensus. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006 GERD causes disruption of physical, social and emotional wellbeing, reflux oesophagitis, haemorrhage, stricture, Barrett’s oesophagus and adenocarcinoma of the distal oesophagus; Prevalence: 20% of USA adult population (Sonnenberg et al, 1999) and similar results in Europe (Nazi et al 2006). Sintomatology Typical symptoms: heartburn regurgitation Others symptoms: chronic cough wheezing hoarseness chest pain Proton Pumps Inhibitors (PPIs) it primary function is the inhibition of acid production in the final common metabolic pathway of gastric parietal cells; It has an anti-secretory and anti-ulcer activities; It accelerates the spontaneous healing of acetic acid-induced gastric ulcers; When combined with two or three antibiotics, are used for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori (Hp). Proton Pumps Inhibitors (PPIs) All PPIs dose-dependently inhibit gastric acid secretion and raise intragastric pH for 24–48 h; Intragastric pH should be maintained above 3.5 to heal peptic ulcer and above 4 to heal gastroesophageal reflux disease. These findings suggest that therapeutic efficacy depends on drug dose and dosing interval. Proton Pumps Inhibitors (PPIs) The area under the plasma concentration-vs.-time curve (AUC) is closely related to the inhibition of gastric secretion. Omeprazole (20 mg) Omeprazole exerts a prolonged anti-secretory effect. “Twice daily dosing of Omeprazole 20mg b.d. appears to be significantly more effective than Lanzoprazole 30mg b.d. in controlling gastric acidity.” Katz PO, Hatlebakk JG, Castell DO. LANZOprazole (30 mg) Side effects: Headache Diarrhea Dizziness Nausea Lanzoprazole tends to relief symptoms more rapidly than Omeprazole, although initial healing is similar; It is an important alternative to Omeprazole. RABEprazole (20 mg) Rabeprazole can achieve more than 90% of eradication rates; It is as effective as Omeprazole and Lansoprazole when included as part of a triple-therapy regimen; Side effects: Diarrhea Headache Rhinitis Nausea Pharyngitis Abdominal pain. PANTOprazole (40 mg) Side effects: diarrhea headache stomach pain gas or bloating ESOMEprazole (40 mg) Decreases the chance of getting an ulcer in people who are taking nonsteroidal antiinflammatory medications (NSAIDs); Treats and prevents the return of stomach ulcers caused by a certain type of bacteria (H. pylori), with other medications; More including than pantoprazole ; Esomeprazole has more side effects than the others PPIs, and some of them are also much more serious. ESOMEprazole (40 mg) difficulty breathing or swallowing; swelling of the face, throat, tongue, lips, eyes, hands, feet, ankles, or lower legs; hoarseness headache diarrhea nausea gas stomach pain constipation dry mouth blisters or peeling skin hives rash itching Aims To compare efficacy and tolerability of five proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) commonly used in the longterm therapy of GERD, namely omeprazole, lansoprazole, rabeprazole, pantoprazole, and esomeprazole; To determine which PPI is more effective in enduring symptom relief, improving quality of life as well as in healing and preventing mucosal injury. Study design Synthesis studies: Metanalysis study Bibliographic databases: • Medline (http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/) Pubmed (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez) Embase(http://www.elsevier.com/wps/find/bibliographicdataba • sedescription.cws_home/523328/description#description) … • • Ana Lopes Andreia Pinto Catarina Melo Diogo Dias Isabel Saavedra João Matias Mariana Ferreira Mariana Mangas Paula Neves Rita Sapage Rui Coelho Teresa Caridade Teresa Tavares Turma 16 1º Ano Disciplina de IntroMed I FMUP 19 de Outubro de 2007