COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright Regulations 1969
advertisement

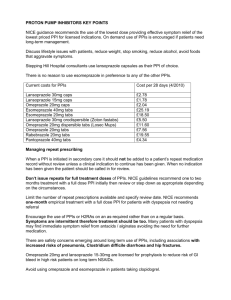
COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright Regulations 1969 WARNING This material has been copied and communicated to you by or on behalf of the University of Sydney pursuant to Part VB of the Copyright Act 1968. (The Act). The material in this communication may be subject to copyright under the Act. Any further copying or communication of this material by you may be the subject of copyright protection under the Act. Do not remove this notice. Dyspepsia Case Summary • Mr Milton (47 y.o.), has used Mylanta regularly. However, over time his dyspepsia has become more frequent www.images.com/.../male-tennis-player-serving/ Tutorial Scenario • Mr Milton, a regular patient at your pharmacy, has purchased Mylanta off and on for the past few years. • You have noticed that his purchase have recently become more frequent. • He is in his late 40’s, slightly over weight he drinks socially and at weekends and takes Perindopril for hypertension, but is otherwise healthy and plays tennis weekly. • For the past 4 days he has also been taking Voltaren Rapid 25 for a muscle injury. • As a biology and chemistry teacher he is always interested in how his medications work. Lectures to Support this Case • • • • Gut Drugs on Dyspepsia ‐ Dr Hilary Lloyd Histamines and Antihistamines ‐ A/Prof Jane Hanrahan Proton Pump Inhibitors 1 & 2 ‐ A/Prof Jane Hanrahan Dyspepsia 1 & 2 – Dr Beata Bajorek References to Support this Case • Lecture notes on H2 antiagonists and PPIs, gastrointestinal drugs and gastrointestinal disorders • NPS Prescribing Practice Review 25 – Proton Pump Inhibitors: Too much of a good thing? • NPS Prescribing Practice Review 45 – Proton pump inhibitors: step‐down to symptom control • L. Olbe, E.Carlsson & P. Lindberg, A Proton‐Pump Inhibitor Expedition: The Case Histories Of Omeprazole And Esomeprazole. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2003, 2, 132‐139. • G.L. Patrick (2009) 4th edition, An Introduction to Medicinal Chemistry, Oxford, ‐ Chapter 25. • AMH Tutorial Scenario Part 2. • About 3 weeks later Mr Milton visits your pharmacy again • Although his symptoms improved slightly with Ranitidine, they continued to be troublesome, especially at night • He has visited his GP who prescribed Esomeprazole (20 mg daily), He also has his regular prescription for Perindopril (4mg daily). • Mr Milton asks – How does Nexium work and why is it going to be better than what he has been taking? – Is it OK to take this with my blood pressure tablets – Can I take it with antacids? Are there any side‐effects? – How long do I need to take it for, the doctor has only given me enough for 1 month? Learning Outcomes • Predict the activity of a drug based on a its structure and physicochemical properties ‐‐‐ PPIs Learning Outcomes • ‐‐‐ • ‐‐‐ • ‐‐‐ • ‐‐‐ Demonstrate an understanding of how the physical and chemical properties of a drug determine its pharmacology, toxicology, bioavailability and behaviour in formulations antacids, PPIs, H2‐antagonists etc Identify typical examples of drugs which are used to restore physiological functions in the gastrointestinal system Mylanta, Ranitidine, Esomeprazole etc Describe the mechanism of therapeutic action of a selected drug at the molecular, cellular, organ system and whole body levels antacids (neutralize acids), PPIs (inhibitor of the H+/K+/ATP‐ase pumps), H2‐antagonists (inhibit histamine at H2 receptors) Describe the common adverse effects of a selected drug and their mechanism of production Part 2 activity 5 (What are the possible side‐effects of PPIs?) Learning Outcomes • ‐‐‐ • ‐‐‐ • ‐‐‐ • ‐‐‐ • ‐‐‐ Demonstrate an understanding of basic metabolism in relation to drugs and efficacy and safety in relation to the treatment of disease and/or maintenance of health Voltaran (NSAIDs) contribute to the formation of gastric ulcers Apply an understanding of the basic and applied sciences to pharmaceutical care in order to optimise health outcomes Part 2 activity 5 (Why is Esomerprazole better than ranitidine at inhibiting gastric acid release?) Respond to direct product and symptom based requests related to gastrointestinal disorders part 1 pre‐work (symptoms? Treatment?) Have an awareness of the alarm symptoms related to gastrointestinal disorders Part 1 pre‐work Demonstrate an understanding of the clinical and therapeutic principles of treatment and management of gastrointestinal disorders Role play (give suggestions)