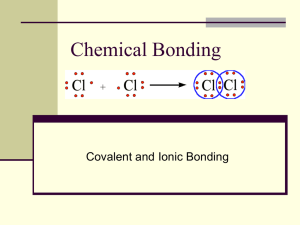
Does the image show ionic or covalent bonding? Support your

Does the image show ionic or covalent bonding? Support your answer.
http://www.powayusd.com/pusdphs/webquests/chemwebquest/chemsite.htm
Objective
• Describe the difference between ionic bonds and covalent bonds.
Lab
• Pre-questions
• Lab setup
• When you finish your lab, clean up your station and return to your seat. Begin working on the post-lab questions.
Post-Lab Discussion
• Why is distilled water used for this lab instead of just tap water? (hint: think about what is in tap water)
– Tap water contains impurities (other substances besides hydrogen and oxygen).
Many of these substances are ions, which will conduct electricity.
– Had we used tap water, our sugar solution could have conducted electricity – providing misleading results.
Post-Lab Discussion
• What properties in general do covalentbonded substances have?
– Low melting/boiling points – evidenced by sugar melting in our flame test.
– Poor conductors of electricity – evidenced by lack of bubbles in battery test.
Post-Lab Discussion
• What properties in general do ionicbonded substances have?
– High melting/boiling points – evidenced by lack of salt melting in our flame test. (salt has a melting point of 800 o C!!)
– Good conductors of electricity – evidenced by production of bubbles in battery test. (bubbles are result of H
2 gas production)
Post-Lab Discussion
• Which compound melted most easily? Is it ionic or covalent?
– Sugar – covalent
Post-Lab Discussion
• Using the periodic table explain how the position of the elements that make up sugar (C
12
H
22
O
6
) and Ethanol (C
2
H
5
OH) can be used to tell if the bonds are ionic or covalent.
– Located on right-hand side (except Hydrogen)
– Non-metals
Post-Lab Discussion
• Using the periodic table explain how the position of the elements that make up salts
NaCl, CaCl
2
, KCl) can be used to tell if the bonds are ionic or covalent.
– Located on opposite sides of periodic table.
– Non-metal bonding with a metal.
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/chemical/bond2.html
Term:
Electronegativity
Definition:
Attraction an atom has for a shared pair of electrons in a chemical bond.
Electronegativity
Characteristics:
•Fluorine is most electronegative element
•Increases diagonally to the right on periodic table
•As you move down a group, electronegativity decreases.
•Elements with the greatest difference in electronegativity form strongest ionic bonds.
In my own words:
Write the definition of electronegativity in your own words
Mine: ability of an atom to attract an electron.
Image of Electronegativity
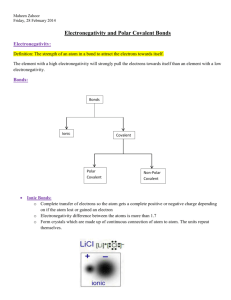
Properties of Ionic Bonds
• Electronegativity difference > 2.
• Typically a bond between metal and a nonmetal.
• Conduct Electricity.
• High melting/boiling points.
Properties of Covalent Bonds
• Electronegativity difference < 2.
• Typically a bond between 2 nonmetals.
• Do Not Conduct Electricity.
• Low melting/boiling points.
• Polar Covalent – unequal sharing of electrons.
• Covalent – equal sharing of electrons.
Oxidation Number
• Definition: indicates how many electrons are lost, gained, or shared when bonding occurs.
– Note: charge is written after the number
• Aligned with valence electrons
• Some atoms have more than one oxidation number
Chemical Formulas
• Tell us how many atoms are in each molecule
• Charge always equals 0
• Criss-Cross method
Writing Formulas
• Positive ion always comes first, then your negative
– Na+ Cl-
• NaCl
Chemical Bonding Worksheet
• You will work with a partner to complete the worksheet.
• You will make a model of your atom using
Fruity Pebbles as valence electrons.
• You MUST then draw your atom with its valence electrons and show which electrons are moving or being shared.