Biology Review 2013
advertisement

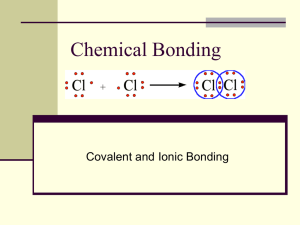
BIOLOGY REVIEW 2013 LIST ALL 8 CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE 1. Living things are made up of cells 2. Reproduce 3. Universal genetic Code 4. Grow and develop 5. Obtain and use energy 6. Respond to their environment 7. Stable internal environment 8. Change over time IONIC VS COVALENT 1. Define Ionic and Covalent Ionic bonds are between metals and non-metals. They have a high melting point, transfer/steal electrons and are stronger than covalent bonds. Covalent bond are between non-metals and they share their electrons. 2. Give an example of an Ionic and Covalent bond Ionic- NaCl, CaCl2, K2S Covalent: CO2, H2O, O3, H2SO4 PROCESSES 1. List the correct sequence in cellular Respiration. Glycolysis, Krebs, then lastly Electron Transport Chain (ETC) 2. Write out the equation for photosynthesis CO2 + H2O + Energy (light) C6H12O6 + O2 3. Write out the equation for Cellular Respiration C6H12O6 + O2 CO2 + H2O + Energy (ATP) NUCLEOTIDES 1. Draw the 3 parts of a nucleotide 2. Draw 4 nucleotides (include correct number of Hydrogen Bonds A-T Have 2 bonds, C-G 3 Hydrogen bonds NAME THESE FORMULAS 1.NaCl 2.CaBr2 3.NaNO3 Sodium Chloride Calcium Bromide Sodium Nitrate 4 MACROMOLECULES Fill in this chart Macromolecule Monomer 1. 2. 3. 4. Macromolecule Monomer 1.Protien Amino Acid 2. Lipid Triglyceride 3.Carbohydrate Glucose 4. Nucleic Acid Nucleotides MITOSIS Draw the 5 phases of Mitosis. GENETICS A woman is heterozygous for Tay-Sachs (a recessive disorder). What are the chances of her giving birth to a child with Tay-Sachs if the father is normal (homozygous dominant?) What are the chances of giving birth to a carrier? Woman: Tt Man: TT No chance of child with disease; 50% chance of carrier Both you and your sister have attached earlobes, yet your parents have unattached ones. Unattached earlobes are dominant over attached. Give the genotypes of you, your sister, and your parents. Genotypes of you and sis uu Genotypes of parents Uu MORE GENETICS A woman with PKU (kk) marries a man who is genotypically normal (KK). Which best describes the chances that their child will: be genotypically normal (KK), be a carrier for PKU (Kk), or have the disease PKU (kk) ? 25% genotypically normal KK, 50% carrier Kk, 25% PKU kk VARIABLES 1. My cat Harry is a picky eater. I’ve noticed that he eats better when the TV is on. To test this, I set out 0.25 kilograms of food and left the TV on for 4 hours. I measured how much food was left. The next day, I set out 0.25 kilograms of food and left the TV off for 4 hours. I measured the amount of food left. After Day 1, there were 0.08 kilograms of food left and after Day 2, there were 0.12 kilograms of food left. List Independent, Dependent and controlled variables I.V= Presence of TV D.V= Food left over (mass=Kg) Controls= Time, same scale, same cat, time of day VARIABLES 2. Suppose you planted three rows of peppers in your garden. Row 1 was planted with ChemLawn fertilizer and Row 2 was planted with Ortho brand fertilizer. Row 3 did not receive any fertilizer. All other conditions in the field (type of see, soil, light, and water) are the same. Row 1 plants produced an average of 3 fruits per plant. Row 2 plants produced an average of 10 fruits per plant. Row 3 produces an average of 1 fruit per plant. List Independent, Dependent and controlled variables I.V= Type of Fertilizer D.V=number of fruits per plant Controls= same soil, light, water MEASURING REVIEW Convert the following: 1. 12 cm= _______km 2. .85mL= _____ dkL 3. 1.4Kg= ______ dG 1. 0.00012 2. 0.000085 3. 14000.00 List the measurements for Length, Mass, and Volume in English and Metric System Metric= mass (grams) length (meter) volume (liter) English= mass(lbs) length (yard/miles) volume (ounces/cups) DRAW AND LABEL AN ANIMAL CELL FILL IN THIS CHART Organelle 1. Cell Wall 2. Cell Membrane 3. Nucleus 4. Cytoplasm 5. Mitochondria 6. ER 7. Ribosomes 8. Golgi Bodies 9. Chloroplasts 10. Vacuoles 11. Lysosomes Plant/Animal Cell Description of appearance Function RANDOM QUESTIONS 1. Describe a catalyst. 2. Name the first person to see a cell 3. Explain the phospolipid bilayer 4. Explain the difference in exergonic/endergonic reactions 1. Speeds up a reaction 2. Robert Hooke 3. Bilayer the inside is hydrophobic (fear of water) outside is hydrophilic (love water) 4. Exergonic releases or gives off energy/ endergonic takes in energy and heat